|
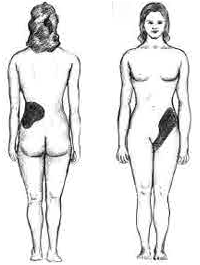
Staghorn Kidney Stone Progression , a type of kidney stone, also referred to as ''Staghorn calculus''
{{disambiguation, plant ...
Staghorn may refer to: *The Horn (anatomy) of a stag *Staghorn calculus, a type of kidney stone *Staghorn coral, a branching coral *''Rhus typhina'', a shrub commonly called ''Staghorn sumac'' *''Lycopodium clavatum'', a moss commonly called ''Staghorn moss'' *''Platycerium'', a fern commonly called ''Staghorn fern'' *Pacific staghorn sculpin, a type of fish *Staghorn (He-Man), an action figure from the Mattel *Struvite Struvite (magnesium ammonium phosphate) is a phosphate mineral with formula: NH4MgPO4·6H2O. Struvite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system as white to yellowish or brownish-white pyramidal crystals or in platy mica-like forms. It is a soft m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
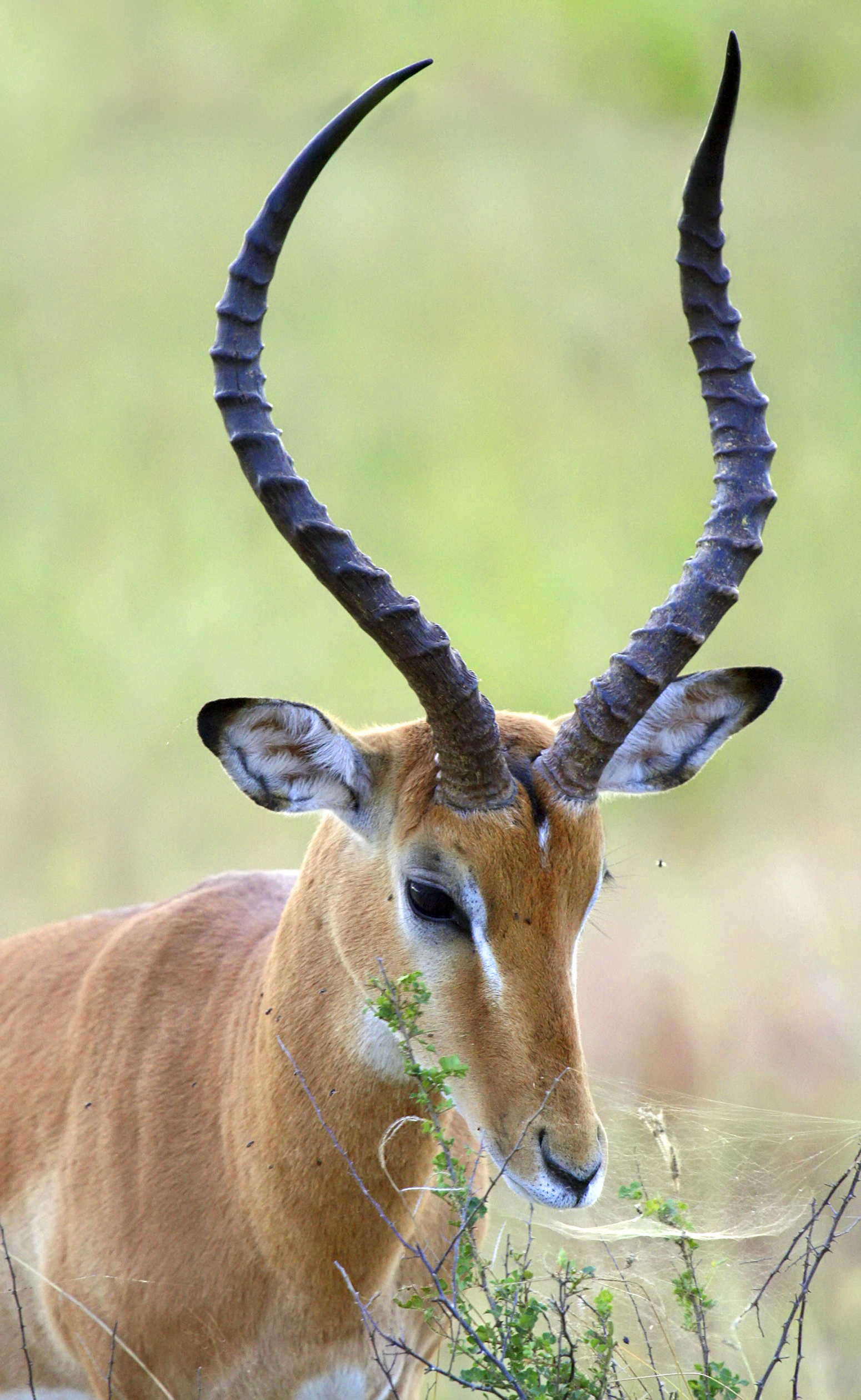
Horn (anatomy)
A horn is a permanent pointed projection on the head of various animals that consists of a covering of keratin and other proteins surrounding a core of live bone. Horns are distinct from antlers, which are not permanent. In mammals, true horns are found mainly among the ruminant artiodactyls, in the families Antilocapridae (pronghorn) and Bovidae (cattle, goats, antelope etc.). Cattle horns arise from subcutaneous connective tissue (under the scalp) and later fuse to the underlying frontal bone. One pair of horns is usual; however, two or more pairs occur in a few wild species and in some domesticated breeds of sheep. Polycerate (multi-horned) sheep breeds include the Hebridean, Icelandic, Jacob, Manx Loaghtan, and the Navajo-Churro. Horns usually have a curved or spiral shape, often with ridges or fluting. In many species, only males have horns. Horns start to grow soon after birth and continue to grow throughout the life of the animal (except in pronghorns, which shed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stag
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the reindeer (caribou), white-tailed deer, the roe deer, and the moose. Male deer of all species (except the water deer), as well as female reindeer, grow and shed new antlers each year. In this they differ from permanently horned antelope, which are part of a different family (Bovidae) within the same order of even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla). The musk deer (Moschidae) of Asia and chevrotains (Tragulidae) of tropical African and Asian forests are separate families that are also in the ruminant clade Ruminantia; they are not especially closely related to Cervidae. Deer appear in art from Paleolithic cave paintings onwards, and they have played a role in mythology, religion, and literature throughout history, as well as in heraldry, such as red dee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staghorn Calculus
Kidney stone disease, also known as nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material (kidney stone) develops in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine stream. A small stone may pass without causing symptoms. If a stone grows to more than , it can cause blockage of the ureter, resulting in sharp and severe pain in the lower back or abdomen. A stone may also result in blood in the urine, vomiting, or painful urination. About half of people who have had a kidney stone will have another within ten years. Most stones form by a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Risk factors include high urine calcium levels, obesity, certain foods, some medications, calcium supplements, hyperparathyroidism, gout and not drinking enough fluids. Stones form in the kidney when minerals in urine are at high concentration. The diagnosis is usually based on symptoms, urine testing, and medical i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staghorn Coral
The staghorn coral (''Acropora cervicornis'') is a branching, stony coral with cylindrical branches ranging from a few centimetres to over two metres in length and height. It occurs in back reef and fore reef environments from depth. The upper limit is defined by wave forces, and the lower limit is controlled by suspended sediments and light availability. Fore reef zones at intermediate depths were formerly dominated by extensive single-species stands of staghorn coral until the mid-1980s. This coral exhibits the fastest growth of all known western Atlantic fringe corals, with branches increasing in length by per year. This has been one of the three most important Caribbean corals in terms of its contribution to reef growth and fishery habitat. Distribution Staghorn coral is found throughout the Florida Keys, the Bahamas, and the Caribbean islands. This coral occurs in the western Gulf of Mexico, but is absent from U.S. waters in the Gulf of Mexico, as well as Bermuda and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhus Typhina
''Rhus typhina'', the staghorn sumac, is a species of flowering plant in the family Anacardiaceae, native to eastern North America. It is primarily found in southeastern Canada, the northeastern and midwestern United States, and the Appalachian Mountains, but it is widely cultivated as an ornamental throughout the temperate world. Etymology The specific epithet ''typhina'' is explained in Carl Linnaeus and Ericus Torner's description of the plant with the phrase "Ramis hirtis uti typhi cervini", meaning "the branches are rough like antlers in velvet". In both French and German, the common name of the species (''sumac vinaigrier; Essigbaum'') means "vinegar tree". Description ''Rhus typhina'' is a dioecious, deciduous shrub or small tree growing up to tall by broad. It has alternate, pinnately compound leaves long, each with 9–31 serrate leaflets long. Leaf petioles and stems are densely covered in rust-colored hairs. The velvety texture and the forking pattern of the branc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycopodium Clavatum
''Lycopodium clavatum'' (common club moss, stag's-horn clubmoss, running clubmoss, or ground pineBailey, L.H.; Bailey, E.Z.; the staff of the Liberty Hyde Bailey Hortorium. 1976. ''Hortus third: A concise dictionary of plants cultivated in the United States and Canada''. Macmillan, New York.) is the most widespread species in the genus ''Lycopodium'' in the clubmoss family. Description ''Lycopodium clavatum'' is a spore-bearing vascular plant, growing mainly prostrate along the ground with stems up to long; the stems are much branched, and densely clothed with small, spirally arranged microphyll leaves. The leaves are 3–5 mm long and 0.7–1 mm broad, tapered to a fine hair-like white point. The branches bearing strobili or spore cones turn erect, reaching above ground, and their leaves are modified as sporophylls that enclose the spore capsules or sporangia. The spore cones are yellow-green, long, and broad. The horizontal stems produce roots at frequent interval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platycerium
''Platycerium'' is a genus of about 18 fern species in the polypod family, Polypodiaceae. Ferns in this genus are widely known as staghorn or elkhorn ferns due to their uniquely shaped fronds. This genus is epiphytic and is native to tropical and temperate areas of South America, Africa, Southeast Asia, Australia, and New Guinea. Description ''Platycerium'' sporophytes (adult plants) have tufted roots, growing from a short rhizome, and bear two types of fronds - basal and fertile fronds. Basal fronds are sterile, shield- or kidney-shaped, and laminate against the tree, to protect the fern's roots from damage and desiccation. In some ''Platycerium'' species, the top margin of these fronds will grow into an open crown of lobes; catching rainwater, falling forest litter, bird/animal droppings, and even the occasional fallen baby bird or deceased animal, these plants build up their own “compost” system of nutrition over many years. Fertile fronds bear spores on their undersurfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Staghorn Sculpin
The Pacific staghorn sculpin (''Leptocottus armatus'') is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Cottidae, the typical sculpins. This species is found in the eastern Pacific Ocean. It is the only species in the monospecific genus ''Lepidocottus''. Taxonomy The Pacific staghorn sculpin was first formally described in 1854 by the French biologist Charles Frédéric Girard with its type locality given as San Francisco in California. Girard placed it in a new monospecific genus, ''Leptocottus''. The 5th edition of ''Fishes of the World'' classifies the genus ''Leptocottus'' within the subfamily Cottinae of the family Cottidae, Etymology The Pacific staghorn sculpin's genus name, ''Leptocottus'', is a combination of ''leptos'', meaning "slender", and '' Cottus''. The specific name ''armatus'' means "armed", a reference to the large and sharp spines on the preoperculum. Description Pacific staghorn sculpins are slender fish, with a wide, large, highly flattened ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staghorn (He-Man)
The ''He-Man and the Masters of the Universe'' franchise debuted in 1982 with the creation of American company Mattel and the toyline of the same name. This is a list of characters that appear in the toyline, television series ''He-Man and the Masters of the Universe'', ''The New Adventures of He-Man'', ''He-Man and the Masters of the Universe'' (2002), '' Masters of the Universe: Revelation'' and ''He-Man and the Masters of the Universe'' (2021) and the films ''The Secret of the Sword'', '' He-Man & She-Ra: A Christmas Special'', and '' Masters of the Universe''. Overview Heroic Warriors Vintage toyline characters (1982–88) All of these characters were released in the vintage Mattel toyline. Battle Cat / Cringer Battle Cat is He-Man's faithful feline companion, an armored tiger who carries him into battle. When He-Man is in the form of Prince Adam, Battle Cat is Cringer, the royal pet. Both Cringer and Battle Cat are green with orange stripes, but Battle Cat is much larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)