|
St Mary's Church, Aberavon
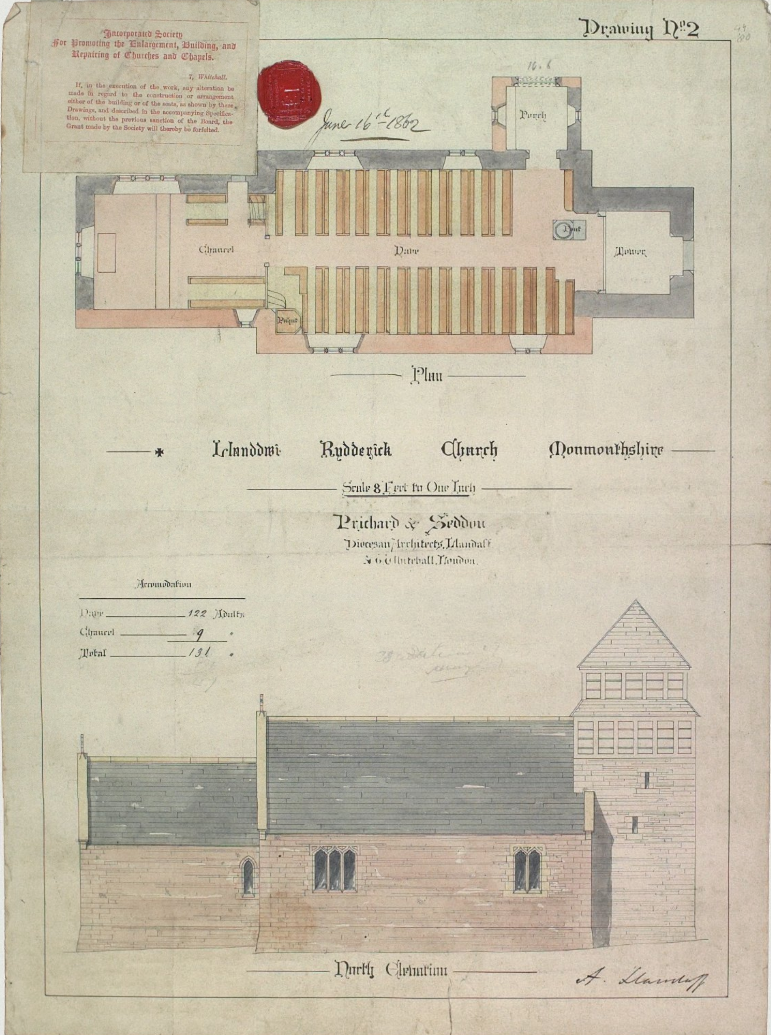
St Mary's Church, Aberavon, is an Anglican church in Port Talbot, UK. It is part of the Rectorial Benefice of Aberavon. It has been a Grade II listed building since 31 January 2000. The first mention of a church on this site was in 1199. The medieval church was rebuilt in the Gothic style in 1858-59 by the architects John Prichard and John Pollard Seddon. The tower was added to around 1870, and the north aisle was added in 1898 by an architect named G. E. Halliday. The alabaster and green marble reredos was designed in 1890 by another well-known partnership of ecclesiastical architects, Frederick R. Kempson and Charles Busteed Fowler, who carried out work in other South Wales churches such as St Catherine's Church, Canton, Cardiff, and St Donat's Church, Welsh St Donats. In 1927, a medieval piscina was placed in the chancel; it did not come from the original church but probably from a chapel elsewhere in the district. The most notable grave in the churchyard is that of Dic P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church In Wales
The Church in Wales ( cy, Yr Eglwys yng Nghymru) is an Anglican church in Wales, composed of six dioceses. The Archbishop of Wales does not have a fixed archiepiscopal see, but serves concurrently as one of the six diocesan bishops. The position is currently held by Andy John, Bishop of Bangor, since 2021. Unlike the Church of England, the Church in Wales is not an established church. Disestablishment took place in 1920 under the Welsh Church Act 1914. As a province of the Anglican Communion, the Church in Wales recognises the Archbishop of Canterbury as a focus of unity but without any formal authority. A cleric of the Church in Wales can be appointed to posts in the Church of England, including the See of Canterbury; a former Archbishop of Canterbury, Rowan Williams, was from Wales and served as Archbishop of Wales before his appointment to Canterbury. Official name The Church in Wales ( cy, Yr Eglwys yng Nghymru) adopted its name by accident. The Welsh Church Act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Talbot
Port Talbot (, ) is a town and community in the county borough of Neath Port Talbot, Wales, situated on the east side of Swansea Bay, approximately from Swansea. The Port Talbot Steelworks covers a large area of land which dominates the south east of the town and is one of the biggest steelworks in the world but has been under threat of closure since the 1980s. The population was 37,276 in 2011. History Modern Port Talbot is a town formed from the merging of multiple villages, including Baglan, Margam, and Aberafan. The name 'Port Talbot' first appears in 1837 as the name of the new docks built on the south-east side of the river Afan by the Talbot family. Over time it came to be applied to the whole of the emerging conurbation. The earliest evidence of humans in the Port Talbot area has been found on the side of Mynydd Margam where Bronze Age farming ditches can be found from 4,000 BC. There were Iron Age hill forts on Mynydd Dinas, Mynydd Margam, Mynydd Emroch and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th Century In Wales
This article is about the particular significance of the century 1101–1200 to Wales and its people. Events 1102 * Henry I of England has a series of charges drawn up against the rebel Robert of Bellême, Earl of Shrewsbury and, when Robert refuses to answer to them, has Robert's former vassal and ally Iorwerth ap Bleddyn, prince of Powys, persuaded to besiege and capture Robert's castles in Shropshire; Iorwerth also delivers his own brother Maredudd ap Bleddyn to the king. The king banishes Robert and his brothers from England and Wales; his brother Arnulf of Montgomery, lord of Pembroke, goes to serve his father-in-law, Muirchertach Ua Briain, High King of Ireland. *Gerald de Windsor is appointed by Henry I of England as Constable of Pembroke Castle. 1103 *Iorwerth ap Bleddyn, prince of Powys, having been insufficiently rewarded for his actions the previous year, again rebels against Henry I and is arraigned before a royal tribunal at Shrewsbury, convicted and imprisoned, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Revival Architecture
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly serious and learned admirers of the neo-Gothic styles sought to revive medieval Gothic architecture, intending to complement or even supersede the neoclassical styles prevalent at the time. Gothic Revival draws upon features of medieval examples, including decorative patterns, finials, lancet windows, and hood moulds. By the middle of the 19th century, Gothic had become the preeminent architectural style in the Western world, only to fall out of fashion in the 1880s and early 1890s. The Gothic Revival movement's roots are intertwined with philosophical movements associated with Catholicism and a re-awakening of high church or Anglo-Catholic belief concerned by the growth of religious nonconformism. Ultimately, the " Anglo-Catholicis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Prichard
John Prichard (6 May 1817 – 13 October 1886) was a Welsh architect in the neo-Gothic style. As diocesan architect of Llandaff, he was involved in the building or restoration of many churches in south Wales. Personal history John Prichard was born in Llangan, near Cowbridge, Wales on 6 May 1817, the twelfth son of the rector Richard Prichard, who served as vicar-choral of Llandaff for 35 years. He was descended from the Prichard family of Collenna. John Prichard trained as an architect under Thomas Larkins Walker, and as a result was deeply influenced by the ideas of Augustus Pugin; much of his work was in a neo-Gothic style. He established a practice in Llandaff, Cardiff, becoming 'Resident Diocesan Architect' in December 1844. Between 1852 and 1863 he was in partnership with John Pollard Seddon. Many of his major commissions were restoration works, most famously for Llandaff Cathedral (1843–69); Prichard and Seddon worked on the cathedral from the 1840s until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Pollard Seddon
John Pollard Seddon FRIBA (19 September 1827 – 1 February 1906) was a British architect, working largely on churches. His father was a cabinetmaker, and his brother Thomas Seddon (1821–1856) a landscape painter. Born in London, he was educated at Bedford School. He was later a pupil of Thomas Leverton Donaldson, though Donaldson was a classical architect and Seddon preferred the Gothic Revivalism of John Ruskin. Between 1852 and 1863, Seddon formed a partnership with John Prichard. Many of their major commissions were church restoration works, most famously for Llandaff Cathedral. In 1871 he submitted a design in a competition for Holloway Sanatorium. C. F. A. Voysey was articled as a pupil of Seddon in 1873. From 1884 to 1904 he was in partnership with John Coates Carter. In 1904 he was Diocesan Architect for London and designed a gigantic Imperial Monumental Halls, with a tall tower, to be added to Westminster Abbey; it was intended to restore the dominance of the ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reredos
A reredos ( , , ) is a large altarpiece, a screen, or decoration placed behind the altar in a church. It often includes religious images. The term ''reredos'' may also be used for similar structures, if elaborate, in secular architecture, for example very grand carved chimneypieces. It also refers to a simple, low stone wall placed behind a hearth. Description A reredos can be made of stone, wood, metal, ivory, or a combination of materials. The images may be painted, carved, gilded, composed of mosaics, and/or embedded with niches for statues. Sometimes a tapestry or another fabric such as silk or velvet is used. Derivation and history of the term ''Reredos'' is derived through Middle English from the 14th-century Anglo-Norman ''areredos'', which in turn is from''arere'' 'behind' +''dos'' 'back', from Latin ''dorsum''. (Despite its appearance, the first part of the word is not formed by doubling the prefix "re-", but by an archaic spelling of "rear".) In the 14th and 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Catherine's Church, Canton
St Catherine's Church, Canton is a listed Anglican church which serves the areas of Canton and Riverside in Cardiff, Wales. Originally a small hamlet in the parish of Llandaff, separate from Cardiff, Canton had seen drastic urbanisation and expansion as Cardiff industrialised during the 19th Century. The church of St John the Evangelist had already been established in the 1850s, but as the area continued to grow, further places of worship were needed, even after St Johns had been enlarged in 1870. The first rector of St John's, the Reverend Vincent Saulez, founded St Catherine's in the early 1880s and later also founded St Paul's in Grangetown. The founding stone of St Catherine's was laid by Catherine Vaughan, the wife of the Dean of Llandaff. She also contributed £1000 towards the building. It has been speculated that the church's name was influenced by this generosity. The plans of diocesan architect John Prichard had intended a cruciform design, but this proved overambiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Donat's Church, Welsh St Donats
St Donat's Church is a Grade I listed church in Welsh St Donats, in the Vale of Glamorgan, south Wales. It became a Grade I listed building on 28 January 1963. Records of 1180 describe the church as a chapel confirmed to the Abbey of Tewkesbury. By 1563 it was known to have served as a parish church for the community. In 1603 it was considered to be a chapel of the church at Llanblethian, but by 1764 it received a stipend from Queen Anne's Bounty and was described as a curacy. 19th century As early as 1859, the church was reported as being in need of repair. In 1890, a local newspaper reported that the church was in such poor condition it was "unfit for use". The news story also noted that it would undergo a major restoration; this was done by Kempson and Fowler and completed the next year with opening ceremonies held 14 October 1891. A local newspaper story detailed the structural problems with the church prior to the start of restoration. The church's open oak roof was unsafe, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piscina
A piscina is a shallow basin placed near the altar of a church, or else in the vestry or sacristy, used for washing the communion vessels. The sacrarium is the drain itself. Anglicans usually refer to the basin, calling it a piscina. For Roman Catholics, a sacrarium is “special sink used for the reverent disposal of sacred substances. This sink has a cover, a basin, and a special pipe and drain that empty directly into the earth, rather than into the sewer system” (USCCB, Built of Living Stones, 236). Precious or sacred items are disposed of, when possible, by returning them to the ground. They are in some cases used to dispose of materials used in the sacraments and water from liturgical ablutions. They are found in Roman Catholic, Anglican, and Lutheran churches, and a similar vessel is used in Eastern Orthodox churches. History The ''piscina'' is a Latin word originally applied to a fish pond, and later used for natural or artificial pools for bathing, and also for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may terminate in an apse. Overview The chancel is generally the area used by the clergy and choir during worship, while the congregation is in the nave. Direct access may be provided by a priest's door, usually on the south side of the church. This is one definition, sometimes called the "strict" one; in practice in churches where the eastern end contains other elements such as an ambulatory and side chapels, these are also often counted as part of the chancel, especially when discussing architecture. In smaller churches, where the altar is backed by the outside east wall and there is no distinct choir, the chancel and sanctuary may be the same area. In churches with a retroquire area behind the altar, this may only be included in the broader definition of chance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
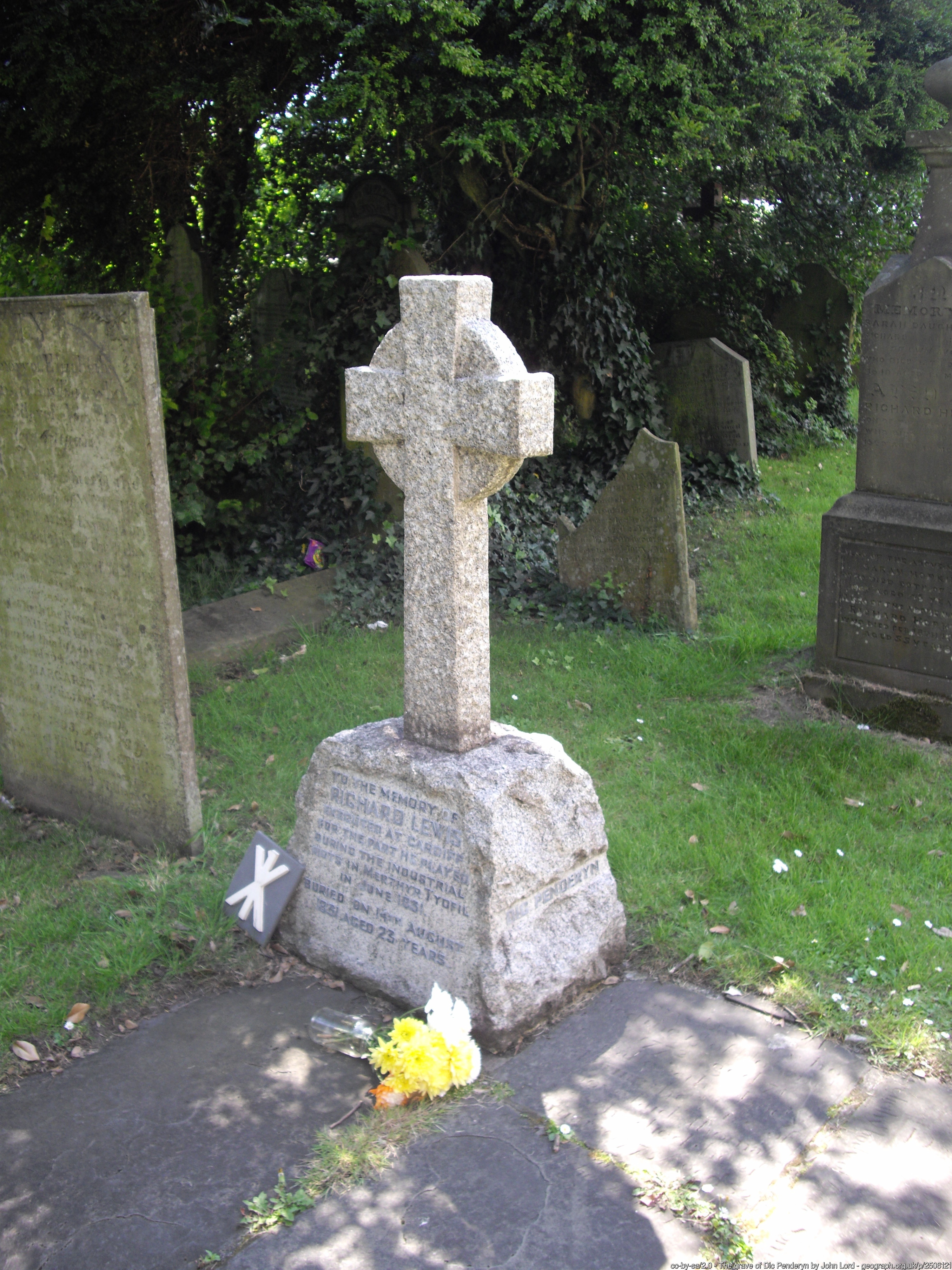
Dic Penderyn
Richard Lewis (1807/8 – 13 August 1831), known as Dic Penderyn, was a Welsh labourer and coal miner who lived in Merthyr Tydfil and was involved with the Merthyr Rising of 3 June 1831. In the course of the riot he was arrested alongside Lewis Lewis, one of the primary figures in the uprising, and charged with stabbing a soldier with a bayonet. The people of Merthyr Tydfil doubted his guilt, and signed a petition for his release. However, he was found guilty and hanged on 13 August 1831. After his death he was treated as a martyr in Merthyr and across Wales. Early life Richard Lewis was born in Aberavon, Glamorgan, Wales in 1807 or 1808, in a cottage named ''Penderyn''. He was the son of Lewis Lewis, a cordwainer and later a miner from Cornelly, and his wife, Margaret. He moved to Merthyr Tydfil with his family in 1819, where he and his father found work in the mines. He was literate with some chapel schooling. His family were Methodists, and his sister Elizabeth married the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |