|
St David's Church, Laleston
St David's Church, Laleston is a Grade I listed church in Laleston, Bridgend County Borough, southern Wales. It is listed Grade 1 as a medieval church with its fabric, including timber roofs, mainly intact, and having group value with the churchyard cross and Cliff Cottage. History In 1180, William, Earl of Gloucester is recorded as having granted land in the area to William Lageles, from whom the village is thought to have got its name. The current church was built later, to replace the nearby church of St Cewydd, the site of which is known. The nave and chancel are believed to date to the late 13th and 14th centuries, and the southern porch and tower to the later medieval period. During the 16th century the church and the manor of Laleston belonged to Margam Abbey, and in 1522, the parishioners were given a lease on the tithe barn. At the Dissolution, Sir Rice Mansel purchased the manor. Those who officiated as parish priests or curates over the years included John Evans (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridgend County Borough
Bridgend County Borough ( cy, Bwrdeistref Sirol Pen-y-bont ar Ogwr) is a county borough in the south-east of Wales. The county borough has a total population of 139,200 people, and contains the town of Bridgend, after which it is named. Its members of the Senedd are Sarah Murphy MS, representing the Bridgend Constituency, and Huw Irranca-Davies MS representing the Ogmore Constituency, and its members of UK parliament are Jamie Wallis and Chris Elmore. The county borough lies at the geographical heart of south Wales. Its land area of 110 mi2 (285 km2) stretches 12 miles (20 km) from east to west and occupies the Llynfi, Garw and Ogmore valleys. The largest town is Bridgend (pop: 39,773), followed by Maesteg (pop: 20,700) and seaside resort of Porthcawl (pop: 19,238). It is situated on the Ogmore River and its tributaries, although the Ewenny and Ogwr Fach rivers form the border with the Vale of Glamorgan for much of their length. It was formed on 1 April 1996 under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margam Abbey
Margam Abbey ( cy, Abaty Margam) was a Cistercian monastery, located in the village of Margam, a suburb of modern Port Talbot in Wales. History The abbey was founded in 1147 as a daughter house of Clairvaux by Robert, Earl of Gloucester, and was dedicated to the Blessed Virgin Mary. Early Christian crosses found in the close vicinity and conserved in the nearby Margam Stones Museum suggest the existence of an earlier Celtic monastic community. The founding abbot was William of Clairvaux. The third abbot, Conan, enjoyed the praise of Giraldus Cambrensis, whom he appears to have entertained prior to his official visit with Baldwin of Forde, Archbishop of Canterbury, to preach the Crusade in 1188. Conan (or Cunan) contributed to Patristic literature, as he is credited with the '' capitula'' or chapter-headings prefixing each section of St. Bernard's ''Sermons on the Song of Songs'', one of the works for which that author was titled a Doctor of the Church. The ''Annales ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
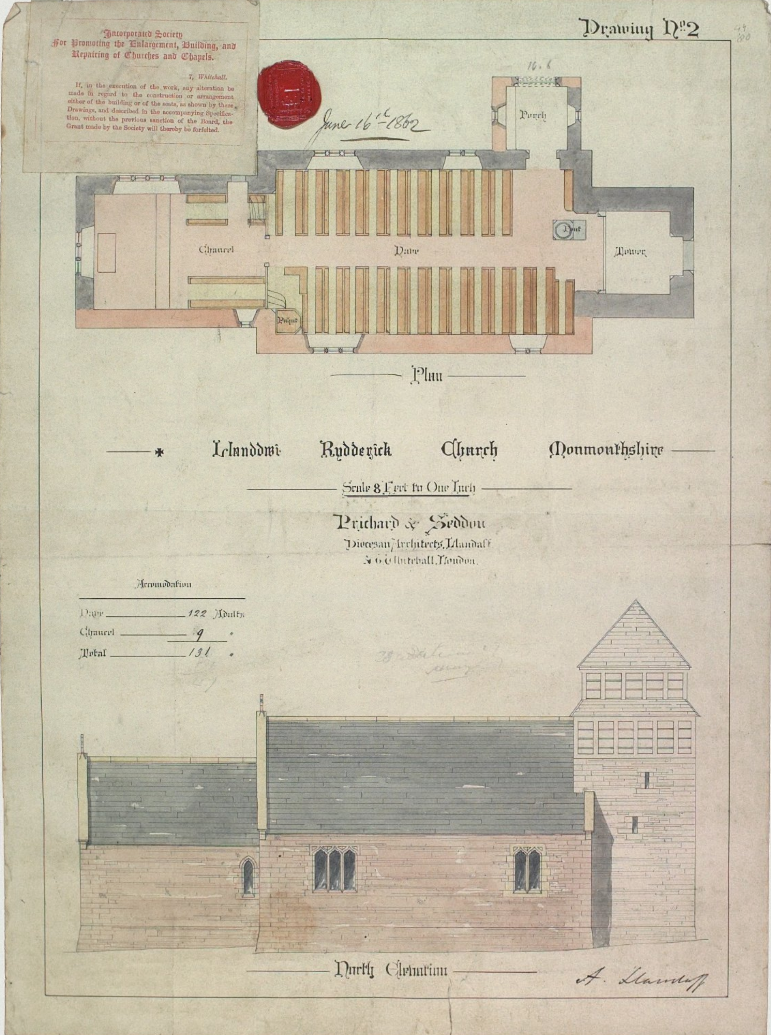
John Prichard
John Prichard (6 May 1817 – 13 October 1886) was a Welsh architect in the neo-Gothic style. As diocesan architect of Llandaff, he was involved in the building or restoration of many churches in south Wales. Personal history John Prichard was born in Llangan, near Cowbridge, Wales on 6 May 1817, the twelfth son of the rector Richard Prichard, who served as vicar-choral of Llandaff for 35 years. He was descended from the Prichard family of Collenna. John Prichard trained as an architect under Thomas Larkins Walker, and as a result was deeply influenced by the ideas of Augustus Pugin; much of his work was in a neo-Gothic style. He established a practice in Llandaff, Cardiff, becoming 'Resident Diocesan Architect' in December 1844. Between 1852 and 1863 he was in partnership with John Pollard Seddon. Many of his major commissions were restoration works, most famously for Llandaff Cathedral (1843–69); Prichard and Seddon worked on the cathedral from the 1840s until 1869, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpendicular Gothic
Perpendicular Gothic (also Perpendicular, Rectilinear, or Third Pointed) architecture was the third and final style of English Gothic architecture developed in the Kingdom of England during the Late Middle Ages, typified by large windows, four-centred arches, straight vertical and horizontal lines in the tracery, and regular arch-topped rectangular panelling. Perpendicular was the prevailing style of Late Gothic architecture in England from the 14th century to the 17th century. Perpendicular was unique to the country: no equivalent arose in Continental Europe or elsewhere in the British Isles. Of all the Gothic architectural styles, Perpendicular was the first to experience a second wave of popularity from the 18th century on in Gothic Revival architecture. The pointed arches used in Perpendicular were often four-centred arches, allowing them to be rather wider and flatter than in other Gothic styles. Perpendicular tracery is characterized by mullions that rise vertically as fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Stephen Glynne, 9th Baronet
Sir Stephen Richard Glynne, 9th Baronet (22 September 1807 – 17 June 1874) was a Welsh landowner and Conservative Party politician. He is principally remembered as an assiduous antiquary and student of British church architecture. He was a brother-in-law of the Liberal Prime Minister William Ewart Gladstone. Background and education Stephen Glynne was born on 22 September 1807, the son of Sir Stephen Glynne, 8th Baronet, and Hon. Mary Griffin, second daughter of the 2nd Baron Braybrooke. His father died on 5 March 1815, aged 35, and so at the age of seven Stephen inherited both the baronetcy and the family estates, including Hawarden Castle in Flintshire. He was educated at Eton, where he displayed a "singular indisposition to mix or associate even with his school fellows", although his intellect and prodigious memory were remarked on. He went on to study at Christ Church, Oxford, but was too indolent to flourish, and graduated with a third class degree in Classic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Evans (Methodist)
John Evans of Llwynffortun (October 1779 – 6 October 1847), was a Welsh Methodist. Evans was born at Cwmgwen, Pencader, Carmarthenshire, in October 1779. His parents gave him a religious education, and he could read his Bible when he was four. He was sent to the best schools within reach, and under one Jones of Maesnoni he is supposed to have learned Latin, Greek, and Hebrew. As a boy he often preached without hearers. His parents were members, and his father a deacon, of the independent church at Pencader. At the age of fourteen he was taken to hear Jones of Llangan, one of the great Methodist preachers of the day. At sixteen, when his father had failed to make an independent of him, he joined the Calvinistic Methodists. At nineteen he went to the Presbyterian College, Carmarthen, but soon left, although his tutor thought highly of him. At twenty-nine he received deacon's orders, after examination, at the hands of Watson, bishop of Llandaff. He held several curacies in succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice Mansel
Sir Rhys Mansel (c. 1487 – 1559), also Sir Rice Mansel, also Sir Rice Manxell, also Sir Rice Maunsell, Vice-Admiral, was High Sheriff of Glamorgan, a Commissioner of Peace and served as Chamberlain of Chester to King Henry VIII of England. He was High Sheriff of Glamorgan for 1542. Sir Rice owned estates at Penrice and Oxwich, and at the Dissolution of the Monasteries he purchased Margam Abbey, which remained the property of his descendants until 1941. He married three times. His children with his third wife, Cecily Dabridgecourt, included: *Sir Edward Mansel (d. 1595), who married Jane Somerset, daughter of the Earl of Worcester, and was the father of Robert Mansell sailor and glass-making entrepreneur. * Mary Mansel, married Sir Thomas Southwell of Woodrising, Norfolk, and was the mother of Sir Robert Southwell Sir Robert Southwell PRS (31 December 1635 – 11 September 1702) was a diplomat. He was Secretary of State for Ireland and President of the Royal S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tithe Barn
A tithe barn was a type of barn used in much of northern Europe in the Middle Ages for storing rents and tithes. Farmers were required to give one-tenth of their produce to the established church. Tithe barns were usually associated with the village church or rectory, and independent farmers took their tithes there. The village priests did not have to pay tithes—the purpose of the tithe being their support. Some operated their own farms anyway. The former church property has sometimes been converted to village greens. Many were monastic barns, originally used by the monastery itself or by a monastic grange. The word 'grange' is (indirectly) derived from Latin ('granary'). Identical barns were found on royal domains and country estates. The medieval aisled barn was developed in the 12th and 13th centuries, following the examples of royal halls, hospitals and market halls. Its predecessors included Roman horrea and Neolithic long houses. According to English Heritage, "exact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cewydd
Saint Cewydd was a pre-congregational saint of Wales in the Early Middle Ages (6th century). He is known as the Welsh 'Rain Saint', like Medard in France, Gildas in Brittany and Swithin in England. It would appear that a pre-Christian rain day might have been associated with a date in July, when, if it rained on that day, it was believed rain would continue for forty days. Very little is known of his life due to the scarcity of records in the early Dark Ages in Wales. He is known mainly from churches associated with him, which are on Anglesey (Wales), Lancaut in Chepstow (Wales/England border), Cusop (Wales/England border), Kewstoke (Somerset, England), Steynton in Rhos (Pembrokeshire, Wales), Aberedw (Radnorshire, Wales], Disserth yn Elfael (Radnorshire, Wales), Llangewydd and Laleston (Bridgend, Wales), Capel Cewy, Mynachlogddu (Pembrokeshire, Wales). Ecclesiastical records in the Book of Llandaff refer to a religious establishment of ''lann ceuid'', probably at Lancaut, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laleston
Laleston is a village and a community in Bridgend County Borough, south Wales, directly west of Bridgend town centre. The village takes its name from the Norman Lageles family who settled in the area. Buildings of note in the village include St David's Church, which still possesses features dating back to the 13th and 14th centuries, the Great House which was built in the early 16th century and Horeb Welsh Presbyterian Church (1831). As a community, Laleston includes the areas of Bryntirion, Cefn Glas, Tythegston and Broadlands. The boundaries of the community are almost entirely set by transportation routes, with the western and north western border defined by the M4 motorway, where it then turns south-easterly at Stormy Down following the A48 back towards Bridgend town centre. It then takes in the Greenfields area, briefly following the banks of the River Ogmore, before heading north to Cefn Glas, but skirting Bridgend town centre and Newcastle. At the 2001 census, the communi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Fitz Robert, 2nd Earl Of Gloucester
William FitzRobert, 2nd Earl of Gloucester (23 November 1116 – 23 November 1183) was the son and heir of Sir Robert de Caen, 1st Earl of Gloucester, and Mabel FitzRobert of Gloucester, daughter of Robert Fitzhamon, and nephew of Empress Matilda. Lineage William FitzRobert was the son of Robert, 1st Earl of Gloucester, an illegitimate son of King Henry I of England, during whose reign William was born. Thus William was a nephew of the Empress Maud and a first cousin once removed of King Stephen, the principal combatants of the English Anarchy period. It also meant that William is the great-grandson of the famed William the Conqueror. Early career In October 1141, William looked after the Baronial estates, when his father fell into the hands of partisans at Winchester. His father was exchanged for King Stephen, and during his father's absence in Normandy in 1144 he served as Governor of Wareham. In 1147, he overthrew Henry de Tracy at Castle Cary. In 1154 he made an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Architecture
Medieval architecture is architecture common in the Middle Ages, and includes religious, civil, and military buildings. Styles include pre-Romanesque, Romanesque, and Gothic. While most of the surviving medieval architecture is to be seen in churches and castles, examples of civic and domestic architecture can be found throughout Europe, in manor houses, town halls, almshouses, bridges, and residential houses. Designs Religious architecture The Latin cross plan, common in medieval ecclesiastical architecture, takes the Roman basilica as its primary model with subsequent developments. It consists of a nave, transepts, and the altar stands at the east end (see '' Cathedral diagram''). Also, cathedrals influenced or commissioned by Justinian employed the Byzantine style of domes and a Greek cross (resembling a plus sign), with the altar located in the sanctuary on the east side of the church. Military architecture Surviving examples of medieval secular architecture mainly s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |