|
St Cecilia's Hall
St Cecilia's Hall is a small concert hall and museum in the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, in the United Kingdom. It is on the corner of Niddry Street and the Cowgate, about south of the Royal Mile. The hall dates from 1763 and was the first purpose-built concert hall in Scotland. It is a Category A listed building. The hall belongs to the University of Edinburgh, and houses part of the university's collection of musical instruments, including the Russell Collection and the collections of Rodger Mirrey and Anne Macaulay. It is used for a classical chamber music concerts and, during summer, as a venue of the Edinburgh International Festival. History St Cecilia's Hall was originally commissioned by the Edinburgh Musical Society (EMS) and designed by the Scottish architect Robert Mylne, who also designed Blackfriars Bridge in London. The EMS was founded in 1728, and for its first 35 years its members met in the upper hall of St Mary’s Chapel, a small church that formerly stood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowgate
The Cowgate (Scots language, Scots: The Cougait) is a street in Edinburgh, Scotland, located about southeast of Edinburgh Castle, within the city's World Heritage Site. The street is part of the lower level of Edinburgh's Old Town, Edinburgh, Old Town, which lies below the elevated streets of South Bridge, Edinburgh, South Bridge and George IV Bridge. It meets the Grassmarket at its west end and Holyrood, Edinburgh, Holyrood Road to the east. History Early history The Cowgate developed around 1330 and represented Edinburgh’s first municipal extension. The original settlement on the Cowgate was concentrated on the south side because of a burn on the north, though that was filled in around 1490 and built upon. Archaeological excavations in the 2006 and 2007 found a boundary ditch, dating to the 14th century, near St Patrick's Church, Edinburgh, St Patrick's Church which might have been the full extent of the Cowgate at that time. The street's name is recorded from 1428, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wynd
In Scotland and Northern England, a wynd () is a narrow lane between houses. The word derives from Old Norse ''venda'' ("to turn"), implying a turning off a main street, without implying that it is curved. In fact, most wynds are straight. In many places wynds link streets at different heights and thus are mostly thought of as being ways up or down hills. Locations There are many wynds in North Yorkshire and County Durham, such as "Bull Wynd" in Darlington and Castle Wynd in Richmond, North Yorkshire. The Old Town of Edinburgh had many wynds, such as St. Mary's Wynd, Blackfriars Wynd and Niddry Wynd, until Victorian street improvements in the 19th century led them to be widened and thus, renamed "streets". Wynds feature prominently in the city centre of Aberdeen, a testament to the medieval street pattern in the city's past. Before the levelling of St. Catherine's Hill and the construction of Union Street, Back Wynd served as the main thoroughfare to and from The Green, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipse
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focus (geometry), focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in which the two focal points are the same. The elongation of an ellipse is measured by its eccentricity (mathematics), eccentricity e, a number ranging from e = 0 (the Limiting case (mathematics), limiting case of a circle) to e = 1 (the limiting case of infinite elongation, no longer an ellipse but a parabola). An ellipse has a simple algebraic solution for its area, but only approximations for its perimeter (also known as circumference), for which integration is required to obtain an exact solution. Analytic geometry, Analytically, the equation of a standard ellipse centered at the origin with width 2a and height 2b is: : \frac+\frac = 1 . Assuming a \ge b, the foci are (\pm c, 0) for c = \sqrt. The standard parametric e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashlar
Ashlar () is finely dressed (cut, worked) stone, either an individual stone that has been worked until squared, or a structure built from such stones. Ashlar is the finest stone masonry unit, generally rectangular cuboid, mentioned by Vitruvius as opus isodomum, or less frequently trapezoidal. Precisely cut "on all faces adjacent to those of other stones", ashlar is capable of very thin joints between blocks, and the visible face of the stone may be quarry-faced or feature a variety of treatments: tooled, smoothly polished or rendered with another material for decorative effect. One such decorative treatment consists of small grooves achieved by the application of a metal comb. Generally used only on softer stone ashlar, this decoration is known as "mason's drag". Ashlar is in contrast to rubble masonry, which employs irregularly shaped stones, sometimes minimally worked or selected for similar size, or both. Ashlar is related but distinct from other stone masonry that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and (much less) ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman architecture, followed, from about the start of the 19th century, by a second wave of Greek Revival architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Bell (educationalist)
Andrew Bell (27 March 1753 – 27 January 1832) was a Scottish Episcopalian priest and educationalist who pioneered the Madras System of Education (also known as "mutual instruction" or the "monitorial system") in schools and was the founder of Madras College, a secondary school in St Andrews. Life and work Andrew Bell was born at St. Andrews, in Scotland on 27 March 1753 and attended St. Andrews University where he did well in mathematics and natural philosophy, graduating in 1774.Blackie 901 In 1774 he sailed to Virginia as a private tutor and remained there until 1781 when he left to avoid involvement in the war of independence. He returned to Scotland, surviving a shipwreck on the way, and officiated at the Episcopal Chapel in Leith. He was ordained Deacon in 1784 and Priest in the Church of England in 1785. In February 1787 he went out to India and went ashore at Madras, where he stayed for 10 years. He became chaplain to a number of British regiments and gave a course ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freemason
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities and clients. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of two main recognition groups: * Regular Freemasonry insists that a volume of scripture be open in a working lodge, that every member profess belief in a Supreme Being, that no women be admitted, and that the discussion of religion and politics be banned. * Continental Freemasonry consists of the jurisdictions that have removed some, or all, of these restrictions. The basic, local organisational unit of Freemasonry is the Lodge. These private Lodges are usually supervised at the regional level (usually coterminous with a state, province, or national border) by a Grand Lodge or Grand Orient. There is no international, worldwide Grand Lodge that supervises all of Freemasonry; each Grand Lod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baptist Church In Scotland
The Baptist Union of Scotland is a Baptist Christian denomination in Scotland. It is affiliated with the Baptist World Alliance. The headquarters is in Glasgow. History From the 1650s to 1869 Baptists first arrived in Scotland with the armies of English republican Oliver Cromwell in the 1650s, who established small churches in Leith, Perth, Cupar, Ayr and Aberdeen, but they did not survive for long, partly because of their association with Cromwell (who was generally not welcomed in Scotland), but more especially as a result of strident and often violent opposition instigated and inspired by the Church of Scotland and the Parliament of Scotland which it controlled. Baptists later emerged in the 18th century—in 1750 at Keiss, where the leader was William Sinclair and the church was established on the English Baptist pattern. The group who in Edinburgh came to Baptist convictions in 1765 under the leadership of Robert Carmichael and Archibald McLean became known as Scotch Baptist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
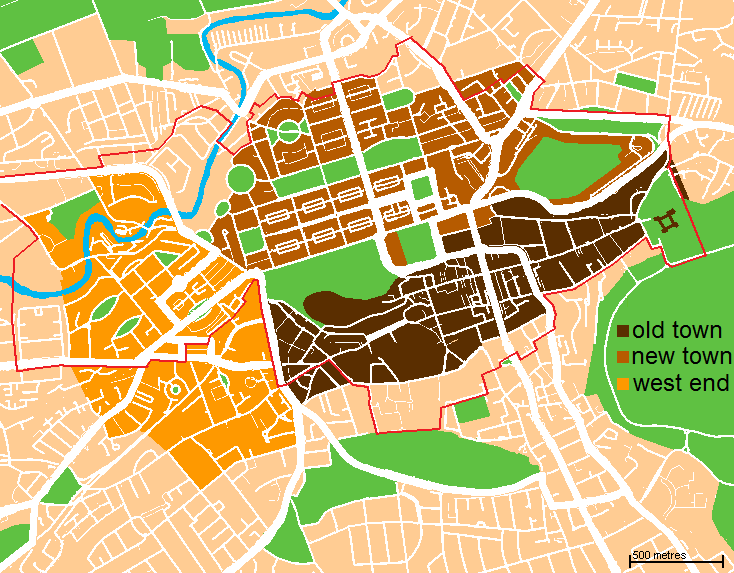
New Town, Edinburgh
The New Town is a central area of Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It was built in stages between 1767 and around 1850, and retains much of its original neo-classical and Georgian period architecture. Its best known street is Princes Street, facing Edinburgh Castle and the Old Town across the geological depression of the former Nor Loch. Together with the West End, the New Town was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site alongside the Old Town in 1995. The area is also famed for the New Town Gardens, a heritage designation since March 2001. Proposal and planning The idea of a New Town was first suggested in the late 17th century when the Duke of Albany and York (later King James VII and II), when resident Royal Commissioner at Holyrood Palace, encouraged the idea of having an extended regality to the north of the city and a North Bridge. He gave the city a grant:That, when they should have occasion to enlarge their city by purchasing ground without the town, or to build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assembly Rooms (Edinburgh)
The Assembly Rooms are meeting halls in central Edinburgh, Scotland. Originally solely a meeting place for social gatherings, it is now also used as an arts venue and for public events, including the Edinburgh Festival Fringe and the Hogmanay celebrations. There are four rooms, with moveable chairs or tables, that are used year-round and are available for private functions: Music Hall, Ballroom, Supper Room and Edinburgh Suite. The total meeting space, as remodeled in 2012, covers . The building is protected as a category A listed building as "an outstanding example of the late 18th century public building, continuing its original use". History The Assembly Rooms opened on 11 January 1787 for the Caledonian Hunt Ball. The building was funded by public subscription, costing over £6,000. The prominent site at the centre of George Street, in the centre of the recently established New Town, was donated by the town council. The Assembly Rooms was designed by John Henderson, who wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenement
A tenement is a type of building shared by multiple dwellings, typically with flats or apartments on each floor and with shared entrance stairway access. They are common on the British Isles, particularly in Scotland. In the medieval Old Town, in Edinburgh, tenements were developed with each apartment treated as a separate house, built on top of each other (such as Gladstone's Land). Over hundreds of years, custom grew to become law concerning maintenance and repairs, as first formally discussed in Stair's 1681 writings on Scots property law. In Scotland, these are now governed by the Tenements Act, which replaced the old Law of the Tenement and created a new system of common ownership and procedures concerning repairs and maintenance of tenements. Tenements with one or two room flats provided popular rented accommodation for workers, but in some inner-city areas, overcrowding and maintenance problems led to shanty towns, which have been cleared and redeveloped. In more affluen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Closes On The Royal Mile
The Old Town of Edinburgh, Scotland, consisted originally of the main street, now known as the Royal Mile, and the small alleyways and courtyards that led off it to the north and south. These were usually named after a memorable occupant of one of the apartments reached by the common entrance, or a trade plied by one or more residents. Generically such an alleyway is termed a close , a Scots term for alleyway, although it may be individually named close, entry, court, or wynd. A close is private property, hence gated and closed to the public, whereas a wynd is an open thoroughfare, usually wide enough for a horse and cart . Most slope steeply down from the Royal Mile creating the impression of a herring-bone pattern formed by the main street and side streets when viewed on a map. Many have steps and long flights of stairs. Because of the need for security within its town walls against English attacks in past wars, Edinburgh experienced a pronounced density in housing. Closes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)