|
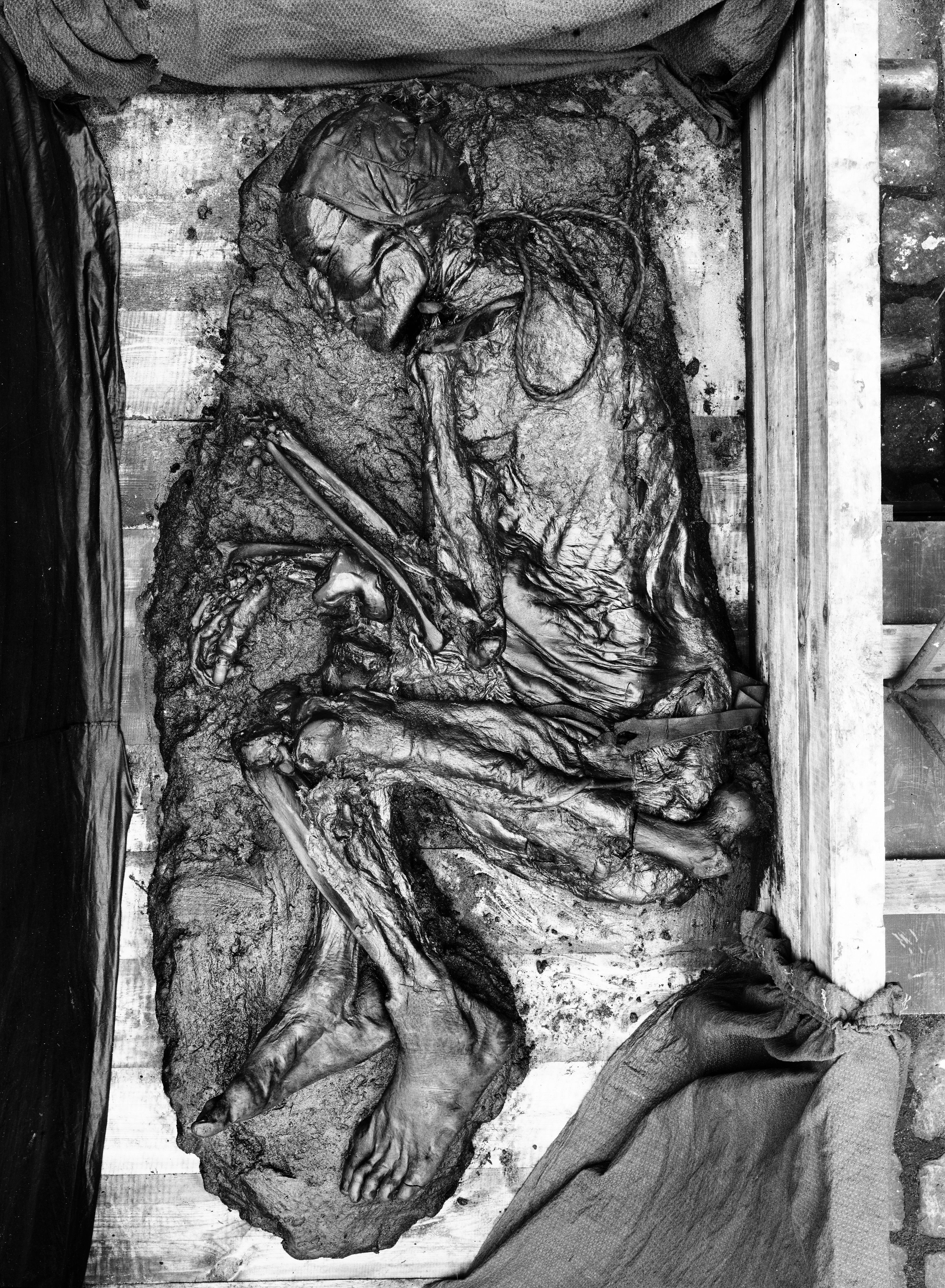
St Bees Man
St Bees Man was the name given to the extremely well preserved body of a medieval man discovered in the grounds of St Bees Priory, Cumbria, in 1981. His identity was subsequently established with a high degree of probability as that of Anthony de Lucy, 3rd Baron Lucy, who died in 1368, probably killed on crusade at New Kaunas, in what is now Lithuania. Discovery The late 12th-century monastic chancel, showing the ruined east end of the chancel aisle on the left. St Bees Man was discovered during an archaeological dig by the University of Leicester on the site of St Bees Priory. The 1981 dig examined two areas of the ruined chancel aisle at the west end of the priory. The aisle was built in about 1300 in the Decorated style, and is thought to have fallen into ruin before the Dissolution of the priory in 1539 due to structural failure caused by poor foundations. The body was found buried in a wooden coffin, wrapped in lead sheet. Despite the lead sheet being damaged at the foot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern history, modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Middle Ages, Early, High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
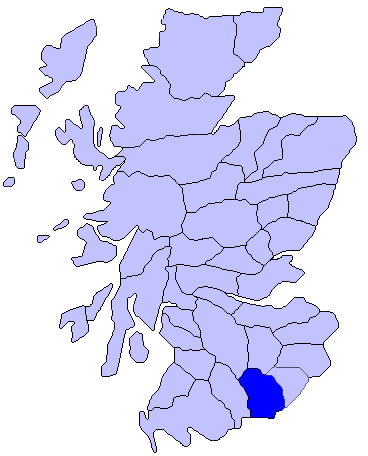
Annandale, Dumfries And Galloway
Annandale (Gaelic: ''Srath Anann'') is a strath in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, named after the dale of the River Annan. It runs north–south through the Southern Uplands from Annanhead (north of Moffat) to Annan on the Solway Firth, and in its higher reaches it separates the Moffat hills on the east from the Lowther hills to the west. A long-distance walking route called Annandale Way running through Annandale (from the source of the River Annan to the sea) was opened in September 2009. History Annandale was also an historic district of Scotland, bordering Liddesdale to the east, Nithsdale to the west, Clydesdale and Tweeddale to the north and the Solway Firth to the south. The district which was in the Sheriffdom of Dumfries and later became part of the County of Dumfries, one of the counties of Scotland. The main reorganisation took place during the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889, which established a uniform system of county councils and town councils in Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1981 Archaeological Discoveries
Events January * January 1 ** Greece enters the European Economic Community, predecessor of the European Union. ** Palau becomes a self-governing territory. * January 10 – Salvadoran Civil War: The FMLN launches its first major offensive, gaining control of most of Morazán and Chalatenango departments. * January 15 – Pope John Paul II receives a delegation led by Polish Solidarity leader Lech Wałęsa at the Vatican. * January 20 – Iran releases the 52 Americans held for 444 days, minutes after Ronald Reagan is sworn in as the 40th President of the United States, ending the Iran hostage crisis. * January 21 – The first DeLorean automobile, a stainless steel sports car with gull-wing doors, rolls off the production line in Dunmurry, Northern Ireland. * January 24 – An earthquake of magnitude in Sichuan, China, kills 150 people. Japan suffers a less serious earthquake on the same day. * January 25 – In South Africa the largest part of the town La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1368 Deaths
Year 1368 ( MCCCLXVIII) was a leap year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–December * January 23 – The Hongwu Emperor (Zhu Yuanzhang) establishes the Ming Dynasty in China, after the disintegration of the Mongol Yuan Dynasty. He immediately orders every county magistrate to set up four granaries, and halts government taxation on books. * March 29 – Emperor Chōkei accedes to the throne of Japan. Date unknown * The Revolt of Saint Titus against rule of the Republic of Venice in the Kingdom of Candia (island of Crete) ends in failure. * Durrës, the second-largest city in modern-day Albania (at this time known as Dyrrhachium), is captured from the Angevins by Karl Thopia, a powerful feudal prince and warlord. * Lațcu, son of Bogdan I, deposes his nephew Petru I, and becomes voivode of Moldavia. * Timur ascends the throne of Samarkand (in modern-day Uzbekistan). * Maha Thammaracha II become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology Of England
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Cumbria
The history of Cumbria as a county of England begins with the Local Government Act 1972. Its territory and constituent parts however have a long history under various other administrative and historic units of governance. Cumbria is an upland, coastal and rural area, with a history of invasions, migration and settlement, as well as battles and skirmishes between the English and the Scots. Overview Cumbria was created as a county in 1974 from territory of the historic counties of Cumberland, Westmorland, Lancashire North of the Sands and a small part of Yorkshire, but the human history of the area is ancient. It is a county of contrasts, with its mountainous central region and lakes, fertile coastal plains in the north and gently undulating hills in the south. Cumbria now relies on farming as well as tourism as economic bases, but industry has historically also played a vital role in the area's fortunes. For much of its history Cumbria was disputed between England and nearby ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bocksten Man
The Bocksten Man ( sv, Bockstensmannen) is the remains of a medieval man's body found in a bog in Varberg Municipality, Sweden. It is one of the best-preserved finds in Europe from that era and is exhibited at the Varberg County Museum. The man had been killed and impaled to the bottom of a lake which later became a bog. The bog where the body was found lies in Rolfstorp about east of Varberg on the west coast of Sweden, close to the most important medieval road in the area: the Via Regia. In 2006, he was reconstructed to show what he may have looked like when he was alive, and it was displayed in the Halland Museum of Cultural History, alongside the original skeleton. The discovery In the 1880s a farm called "Bocksten" was established near a bog. The bog was then regularly drained, and a harrow used to gather peat. The farm owner Albert Johansson had previously found a leather shoe in the wetland and gave it to the Varberg County Museum. A shoe sole was found in the bog in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ötzi The Iceman
Ötzi, also called the Iceman, is the natural mummy of a man who lived some time between 3350 and 3105 BC, discovered in September 1991 in the Ötztal Alps (hence the nickname "Ötzi") on the border between Austria and Italy. Ötzi is believed to have been murdered, due to the discovery of an arrowhead embedded in his left shoulder and various other wounds. The nature of his life and the circumstances of his death are the subject of much investigation and speculation. He is Europe's oldest known natural human mummy, offering an unprecedented view of Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Europeans. His body and belongings are displayed in the South Tyrol Museum of Archaeology in Bolzano, South Tyrol, Italy. Discovery Ötzi was found on 19 September 1991 by two German tourists, at an elevation of on the east ridge of the Fineilspitze in the Ötztal Alps on the Austrian–Italian border, near Similaun mountain and the Tisenjoch pass. When the tourists, Helmut and Erika Simon, first saw the bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lindow Man
Lindow Man, also known as Lindow II and (in jest) as Pete Marsh, is the preserved bog body of a man discovered in a peat bog at Lindow Moss near Wilmslow in Cheshire, North West England. The remains were found on 1 August 1984 by commercial peat cutters. Lindow Man is not the only bog body to have been found in the moss; Lindow Woman was discovered the year before, and other body parts have also been recovered. The find was described as "one of the most significant archaeological discoveries of the 1980s" and caused a media sensation. It helped invigorate study of British bog bodies, which had previously been neglected. Dating the body has proven problematic, but it is thought that he was deposited into Lindow Moss, face down, some time between 2 BC and 119 AD, in either the Iron Age or Romano-British period. At the time of death, Lindow Man was a healthy male in his mid-20s, and may have been of high social status as his body shows little evidence of having d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tollund Man
The Tollund Man (died 405–380 BC) is a naturally mummified corpse of a man who lived during the 5th century BC, during the period characterised in Scandinavia as the Pre-Roman Iron Age. He was found in 1950, preserved as a bog body, near Silkeborg on the Jutland peninsula in Denmark. The man's physical features were so well preserved that he was mistaken for a recent murder victim. Twelve years before his discovery, another bog body, Elling Woman, was found in the same bog. The cause of death has been determined as by hanging. Scholars believe the man was a human sacrifice, rather than an executed criminal, because of the arranged position of his body, and his eyes and mouth being closed.Hart, Edward, dir. "Ghosts of Murdered Kings". NOVA. Prod. Edward Hart and Dan McCabe, PBS, 29 January 2014 Discovery On 8 May 1950, peat cutters Viggo and Emil Hojgaard discovered a corpse in the peat layer of the Bjældskovdal peat bog, west of Silkeborg, Denmark, which was so well pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belfry (architecture)
The belfry is a structure enclosing bells for ringing as part of a building, usually as part of a bell tower or steeple. It can also refer to the entire tower or building, particularly in continental Europe for such a tower attached to a city hall or other civic building. A belfry encloses the bell chamber, the room in which the bells are housed; its walls are pierced by openings which allow the sound to escape. The openings may be left uncovered but are commonly filled with louvers to prevent rain and snow from entering and damaging the bells. There may be a separate room below the bell chamber to house the ringers. Etymology The word ''belfry'' comes from the Old North French or , meaning 'movable wooden siege tower'. The Old French word itself is derived from Middle High German , 'protecting shelter' (cf. the cognate ''bergfried''), combining the Proto-Germanic , 'to protect', or , 'mountain, high place', with , 'peace; personal security', to create , lit. 'high place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Percy, 1st Earl Of Northumberland
Henry Percy, 1st Earl of Northumberland, 4th Baron Percy, titular King of Mann, KG, Lord Marshal (10 November 134120 February 1408) was the son of Henry de Percy, 3rd Baron Percy, and a descendant of Henry III of England. His mother was Mary of Lancaster, daughter of Henry, 3rd Earl of Lancaster, son of Edmund, Earl of Leicester and Lancaster, who was the son of Henry III. Life Henry Percy was originally a follower of Edward III of England, for whom he held high offices in the administration of northern England. At a young age, he was made Warden of the Marches towards Scotland in 1362, with the authority to negotiate with the Scottish government. In February 1367, he was entrusted with the supervision of all castles and fortified places in the Scottish marches. He went on to support King Richard II, was formally created an Earl on Richard's coronation in 1377, and was briefly given the title of Marshal of England. Between 1383 and 1384, he was appointed Admiral of the No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)



.jpg)
