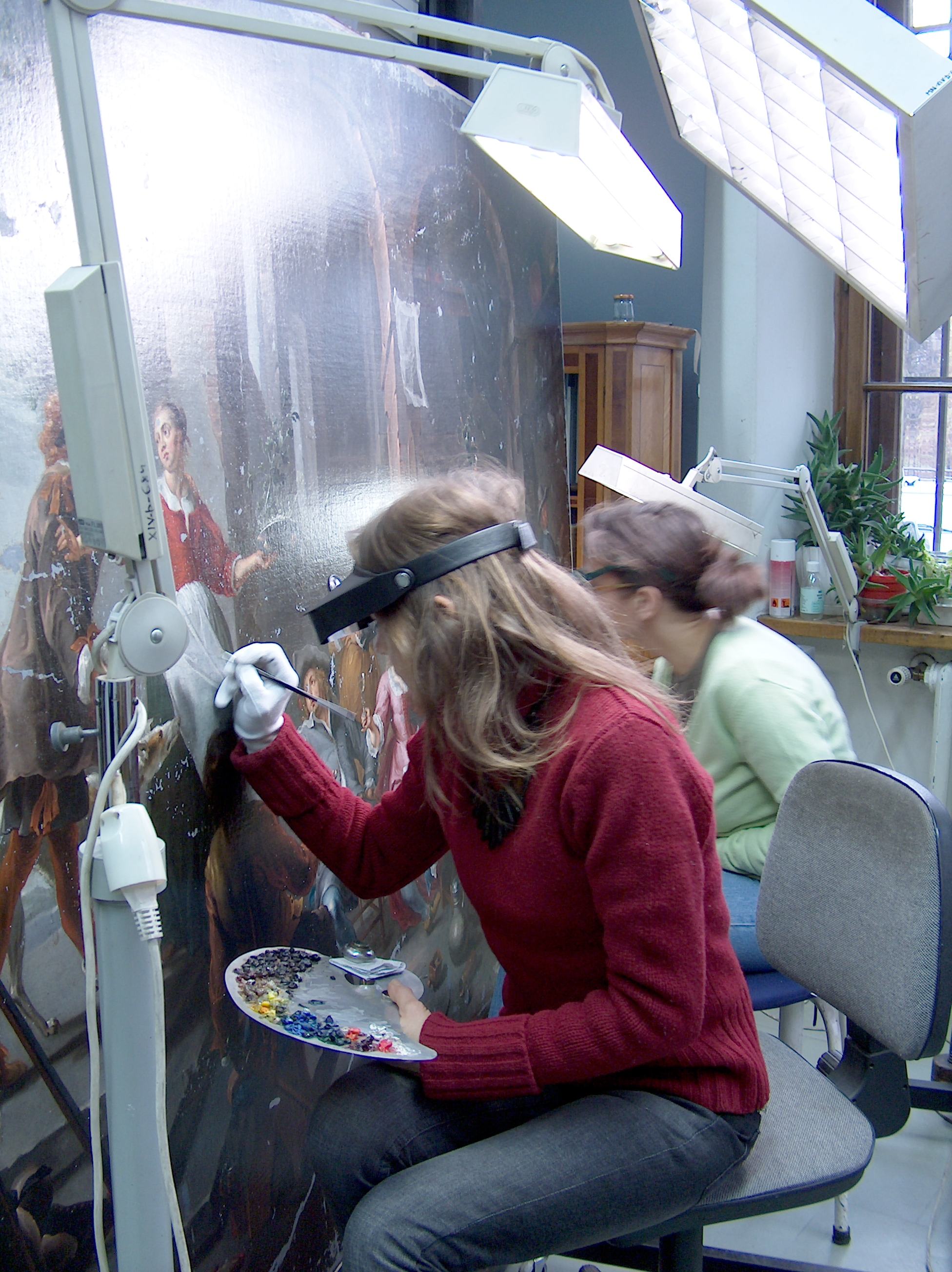|
St. Nicholas' Church, Tallinn
St. Nicholas Church ( et, Niguliste kirik, german: Nikolaikirche) is a medieval church building in Tallinn (Reval), Estonia. It was dedicated to Saint Nicholas, the patron of the fishermen and sailors. Originally built in the 13th century, it was partially destroyed in the Soviet bombing of Tallinn in World War II. The building itself has since been restored, however, as a church without own congregation, it has not been used for regular religious activities since World War II. At present it houses the Niguliste Museum, a branch of the Art Museum of Estonia, focusing mainly on ecclesiastical art from the Middle Ages onward. It is also used as a concert hall. History The church was founded and built around 1230–1275 by Westphalian merchants, who came from Gotland in the 13th century. While the city was still unfortified, the church had heavy bars for closing the entrances, loopholes and hiding places for refugees. When the fortifications around Tallinn were finished in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju ''maakond'' (county). Tallinn is the main financial, industrial, and cultural centre of Estonia. It is located northwest of the country's second largest city Tartu, however only south of Helsinki, Finland, also west of Saint Petersburg, Russia, north of Riga, Latvia, and east of Stockholm, Sweden. From the 13th century until the first half of the 20th century, Tallinn was known in most of the world by variants of its other historical name Reval. Tallinn received Lübeck city rights in 1248,, however the earliest evidence of human population in the area dates back nearly 5,000 years. The medieval indigenous population of what is now Tallinn and northern Estonia was one of the last " pagan" civilisations in Europe to adopt Christianit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Architecture
Gothic architecture (or pointed architecture) is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture. It originated in the Île-de-France and Picardy regions of northern France. The style at the time was sometimes known as ''opus Francigenum'' (lit. French work); the term ''Gothic'' was first applied contemptuously during the later Renaissance, by those ambitious to revive the architecture of classical antiquity. The defining design element of Gothic architecture is the pointed or ogival arch. The use of the pointed arch in turn led to the development of the pointed rib vault and flying buttresses, combined with elaborate tracery and stained glass windows. At the Abbey of Saint-Denis, near Paris, the choir was reconstructed between 1140 and 1144, draw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tallinn Niguliste Museum Reredos 01
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju ''maakond'' (county). Tallinn is the main financial, industrial, and cultural centre of Estonia. It is located northwest of the country's second largest city Tartu, however only south of Helsinki, Finland, also west of Saint Petersburg, Russia, north of Riga, Latvia, and east of Stockholm, Sweden. From the 13th century until the first half of the 20th century, Tallinn was known in most of the world by variants of its other historical name Reval. Tallinn received Lübeck city rights in 1248,, however the earliest evidence of human population in the area dates back nearly 5,000 years. The medieval indigenous population of what is now Tallinn and northern Estonia was one of the last "pagan" civilisations in Europe to adopt Christianity fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Renaissance
The Northern Renaissance was the Renaissance that occurred in Europe north of the Alps. From the last years of the 15th century, its Renaissance spread around Europe. Called the Northern Renaissance because it occurred north of the Italian Renaissance, this period became the German, French, English, Low Countries, Polish Renaissances and in turn other national and localized movements, each with different attributes. In France, King Francis I imported Italian art, commissioned Italian artists (including Leonardo da Vinci), and built grand palaces at great expense, starting the French Renaissance. Trade and commerce in cities like Bruges in the 15th century and Antwerp in the 16th increased cultural exchange between Italy and the Low Countries, however in art, and especially architecture, late Gothic influences remained present until the arrival of Baroque even as painters increasingly drew on Italian models. Universities and the printed book helped spread the spirit of the age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Art
Gothic art was a style of medieval art that developed in Northern France out of Romanesque art in the 12th century AD, led by the concurrent development of Gothic architecture. It spread to all of Western Europe, and much of Northern, Southern and Central Europe, never quite effacing more classical styles in Italy. In the late 14th century, the sophisticated court style of International Gothic developed, which continued to evolve until the late 15th century. In many areas, especially Germany, Late Gothic art continued well into the 16th century, before being subsumed into Renaissance art. Primary media in the Gothic period included sculpture, panel painting, stained glass, fresco and illuminated manuscripts. The easily recognizable shifts in architecture from Romanesque to Gothic, and Gothic to Renaissance styles, are typically used to define the periods in art in all media, although in many ways figurative art developed at a different pace. The earliest Gothic art was monumental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernt Notke Danse Macabre
Bernt is a Scandinavian variant of the German masculine given name Berend, which is the Low German form of Bernard (Bernhard). The name Bernhard means "strong bear" (from Old German ''bero'', "bear", and ''harti'', "strong"). Its use in Sweden was first documented in 1395.Eva Brylla, ''Förnamn i Sverige'' (2004), cited aftenordicnames.de Notable people with the name include: * Bernt Albert (born 1944), Norwegian politician for the Conservative Party * Bernt Balchen, D.F.C. (1899–1973), Norwegian, and later Norwegian-American, polar and aviation pioneer * Bernt Bjørnsgaard (born 1973), Norwegian orienteering competitor and World champion * Bernt Bull (born 1946), Norwegian politician for the Labour Party * Bernt Carlsson (1938–1988), Assistant-Secretary-General of the United Nations and United Nations Commissioner for Namibia * Bernt Johan Collet (born 1941), son of Chamberlain and Master of the Royal Hunt, Harald Collet and landscape architect Else Collett * Bernt Evens (bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernt Notke
Bernt Notke (; – before May 1509) was a late Gothic artist, working in the Baltic region. He has been described as one of the foremost artists of his time in northern Europe. Life Very little is known about the life of Bernt Notke. The Notke family came from Tallinn (Estonia) and his father was probably the trader and ship-owner Michel Notke, who had his main business there. His mother was probably Michel's second wife Gertraut, who was from Visby. Bernt Notke was born in the small town of Lassan in Pomerania. He was married (at least once), but the name of his wife remains unknown; she died before he did and is not mentioned in his last will and testament. The couple is known to have had two daughters, one named Anneke and another whose name has not been preserved and who seems to have had an intellectual disability. He seems to have spent part of his youth in Flanders and there begun to learn his trade as an artist. He probably worked in the workshop of tapestry weaver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the state of Schleswig-Holstein, after its capital of Kiel, and is the 35th-largest city in Germany. The city lies in Holstein, northeast of Hamburg, on the mouth of the River Trave, which flows into the Bay of Lübeck in the borough of Travemünde, and on the Trave's tributary Wakenitz. The city is part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region, and is the southwesternmost city on the Baltic, as well as the closest point of access to the Baltic from Hamburg. The port of Lübeck is the second-largest German Baltic port after the port of Rostock. The city lies in the Northern Low Saxon dialect area of Low German. Lübeck is famous for having been the cradle and the ''de facto'' capital of the Hanseatic League. Its city centre is Germany's most extens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
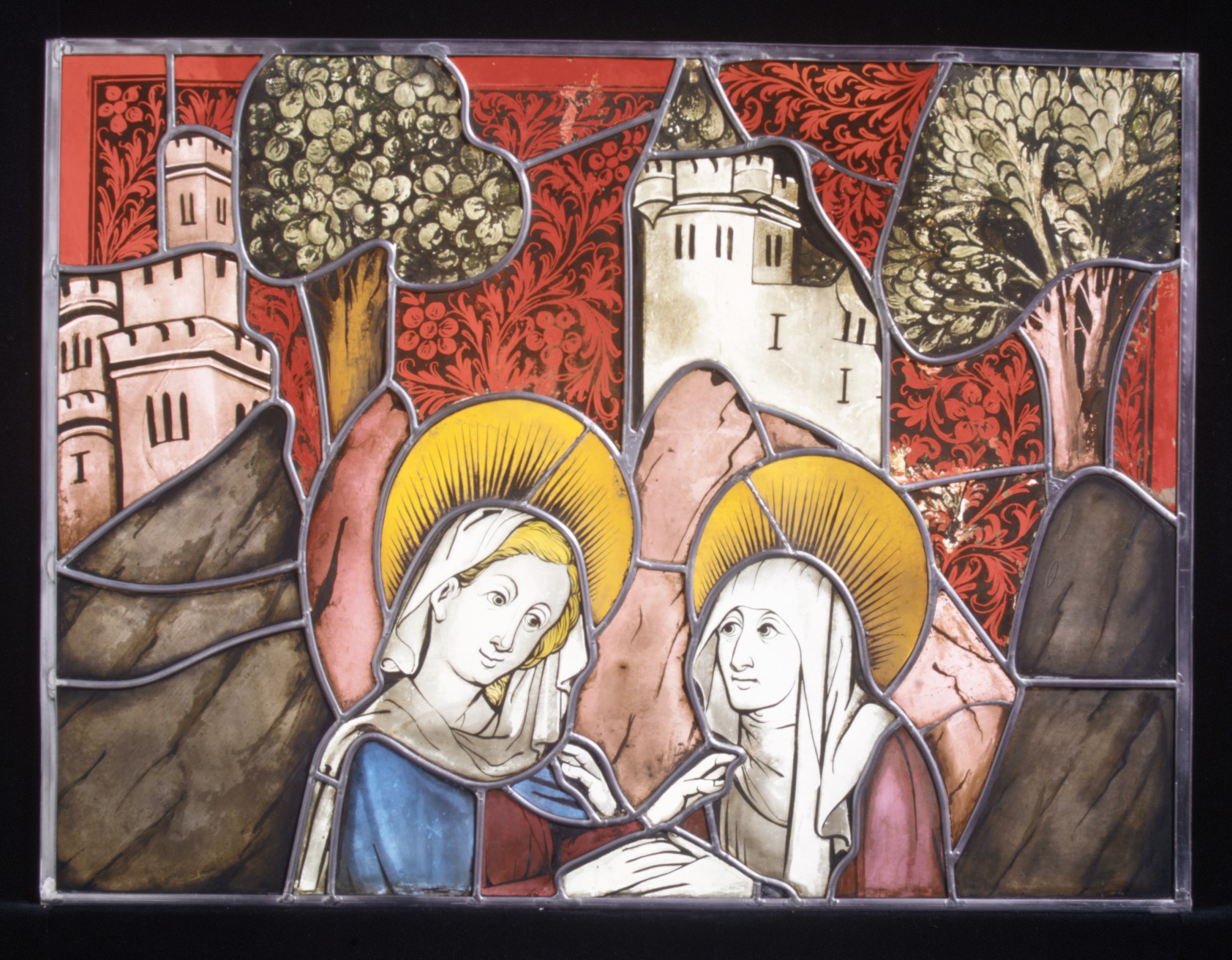
Danse Macabre (Notke)
''Danse Macabre'' is a painting by Bernt Notke. A fragment of the late fifteenth-century painting, originally some 30 meters (98.4 ft) wide, is displayed in the St. Nicholas Church, Tallinn. It is regarded as the best-known and as one of the most valuable medieval artworks in Estonia. It is the only surviving medieval Dance Macabre in the world painted on canvas. The Dance of Death theme is frequent in the art and literature of the late Middle Ages, where it functions as a memento mori, the admonition that all must die. In the face of Death all are equal. The skeletal figure of Death dances with mortals, hierarchically arranged to begin with popes and emperors and ending with peasants, fools, or infants.Anu Mänd, Bernt Notke. Uuenduste ja traditsioonide vahel, näituse kataloog, Eesti Kunstimuuseum, 2010 The figures are accompanied by a winging band in the Low German language, a dialogue in verse between Death and the other characters. Created at the end of the 15th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villem Raam
Villem is an Estonian language, Estonian masculine given name. It is a cognate of the English language William (given name), William and the German Wilhelm (name), Wilhelm and may refer to: *Villem Gross (1922–2001), Estonian writer and journalist *Villem Grünthal-Ridala (1885–1942), Estonian poet, translator, linguist and folklorist *Villem Kapp (1913–1964), Estonian composer *Villem Maaker (1891–1966), Estonian politician *Villem Maasik (1883–1919), Estonian lawyer, trade unionist, and politician *Villem Orav (1883-1952), Estonian historian, teacher, and scholar of pedagogy *Villem Raam (1910-1996), Estonian art historian, art critic and conservator-restorer *Villem Reimann (1906–1992), Estonian composer and pedagogue *Villem Tammai (1892–1973), Estonian politician *Villem Tomiste (born 1975), Estonian architect {{Given name Estonian masculine given names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservator-restorer
A conservator-restorer is a professional responsible for the preservation of artistic and cultural artifacts, also known as cultural heritage. Conservators possess the expertise to preserve cultural heritage in a way that retains the integrity of the object, building or site, including its historical significance, context and aesthetic or visual aspects.Defining the Conservator: Essential Competencies. (2003). Retrieved from http://www.conservation-us.org/docs/default-source/governance/defining-the-conservator-essential-competencies.pdf. This kind of preservation is done by analyzing and assessing the condition of cultural property, understanding processes and evidence of deterioration, planning collections care or site management strategies that prevent damage, carrying out conservation treatments, and conducting research.Careers in Conservation. (2014). Retrieved from http://www.conservation-us.org/publications-resources/careers-in-conservation/become-a-conservator#.VPPIxMaLTwN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Of Padua
Anthony of Padua ( it, Antonio di Padova) or Anthony of Lisbon ( pt, António/Antônio de Lisboa; born Fernando Martins de Bulhões; 15 August 1195 – 13 June 1231) was a Portuguese people, Portuguese Catholic Church, Catholic priesthood (Catholic Church), priest and friar of the Franciscan Order. He was born and raised by a wealthy family in Lisbon, Portugal, and died in Padua, Italy. Noted by his contemporaries for his powerful preaching, expert knowledge of scripture, and undying love and devotion to the poor and the sick, he was one of the most quickly canonization, canonized saints in church history, being canonized less than a year after his death. He was proclaimed a Doctor of the Church by Pope Pius XII on 16 January 1946. Life Early years Fernando Martins de Bulhões was born in Lisbon, Portugal. While 15th-century writers state that his parents were Vicente Martins and Teresa Pais Taveira, and that his father was the brother of Pedro Martins de Bulhões, the an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)