|
Sri Wikrama Wira
According to the ''Malay Annals'', Paduka Sri Wikrama Wira or Sri Pikrama Wira ('Vikramavira') was the eldest son of Sang Nila Utama and the second Raja of Singapura. He was known as ''Raja Kecil Besar'' before his accession and married to an Indian princess named Nila Panjadi. His reign was from 1347 to 1362. His reign marks the first attempt by the Siamese to subjugate the island kingdom. As recorded by Wang Dayuan in 1349, a Siamese fleet consisted of 70 junks descended upon the island kingdom. The heavily fortified city managed to withstand the siege of the Siamese until the fleet fleeing with the arrival of Chinese ships; this incident was recorded by a Chinese merchant named Wang Dayuan in his own account, the '' Daoyi Zhilue''. At the same time, the increasingly powerful Javanese kingdom of Majapahit, began eyeing the growing influence of the tiny island kingdom. Under the leadership of its ambitious warlord, Gajah Mada, Majapahit started to embark on overseas expansions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
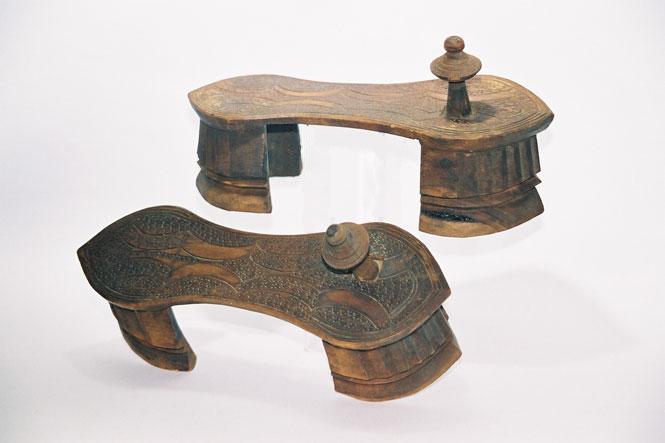
Paduka
''Paduka'' is an ancient form of footwear in India, consisting of a sole with a post and knob which is positioned between the big and second toe. It has been historically worn in South Asia and Southeast Asia. ''Paduka'' exist in a variety of forms and materials. They might be made in the shape of actual feet, or of fish, for example, and have been made of wood, ivory and silver. They may be elaborately decorated, such as when used as part of a bride's trousseau, but could also be given as religious offerings or themselves be the object of veneration. Although simple wooden ''padukas'' could be worn by common people, ''padukas'' of fine teak, ebony and sandalwood, inlaid with ivory or wire, were a mark of the wearer's high status. In the modern world, ''padukas'' are worn as footwear by mendicants and saints of Hinduism, Buddhism,and Jainism. Its significance in Hinduism is linked to the epic ''Ramayana''. ''Paduka'' can also refer to the footprints of deities and saints that ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gajah Mada
Gajah Mada (c. 1290 – c. 1364), also known as JirnnodharaMunandar, 2010: 77 was, according to Old Javanese manuscripts, poems, and inscriptions, a powerful military leader and '' Mahapatih'' (the approximate equivalent of a modern Prime Minister) of the Javanese empire of Majapahit during the 14th century. He is credited with bringing the empire to its peak of glory. He delivered an oath called ''Sumpah Palapa'', in which he vowed to live an ascetic lifestyle (by not consuming food containing spices) until he had conquered all of the Southeast Asian archipelago of Nusantara for Majapahit. During his reign, the Hindu epics, including the Ramayana and the Mahabharata, became ingrained in the Javanese culture and worldview through the performing arts of wayang kulit (“leather puppets”).Mark Juergensmeyer and Wade Clark Roof, 2012Encyclopedia of Global Religion Volume 1, Page 557. He is considered an important national hero in modern Indonesia, as well as a symbol of pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Malaysia
Malaysia is located on a strategic sea lane that exposes it to global trade and various cultures. The name "Malaysia" is a modern concept, created in the second half of the 20th century. However, contemporary Malaysia regards the entire history of Malaya and Borneo, spanning thousands of years back to prehistoric times, as its own history. An early western account of the area is seen in Ptolemy's book ''Geographia'', which mentions a " Golden Khersonese," now identified as the Malay Peninsula. Hinduism and Buddhism from India and China dominated early regional history, reaching their peak during the reign of the Palembang, Sumatra, Indonesia - based Srivijaya civilisation, whose influence extended through Sumatra, West Java, East Borneo and the Malay Peninsula from the 7th to the 13th centuries. Although Muslims passed through the Malay Peninsula as early as the 10th century, it was not until the 14th century that Islam first firmly established itself. The adoption of Islam in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaysian Hindus
Hinduism is the fourth largest religion in Malaysia. About 1.78 million Malaysian residents (6.3% of the total population) are Hindus, according to 2010 Census of Malaysia. This is up from 1,380,400 (6.2% of the total population) in 2000. Most Malaysian Hindus are settled in western parts of Peninsular Malaysia. There are 3 states in Malaysia that qualify to be a Hindu enclave, where the Hindu percentage is greater than 10% of the population. The Malaysian state with highest percentage of Hindus, according to 2010 Census, is Negeri Sembilan (13.4%), followed by Selangor (11.6%), Perak (10.9%) and Federal Territory of Kuala Lumpur (8.5%). The first three mentioned technically count as being Hindu enclaves. The state with the least percentage of Hindu population is Sabah (0.1%). Indians, along with other ethnic groups such as Chinese, began arriving in Malaysia in the ancient and medieval era. In 2010, Malaysian Census reported there were 1.91 million citizens of Indian ethnic or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Monarchs
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. The term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Old Persian which derived these names from the Sanskrit name ''Sindhu'' (सिन्धु ), referring to the river Indus. The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent around or beyond the Sindhu (Indus) River. By the 16th century CE, the term began to refer to residents of the subcontinent who were not Turkic or Muslims. Hindoo is an archaic spelling variant, whose use today is considered derogatory. The historical development of Hindu self-identity within the local In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th-century Monarchs In Asia
As a means of recording the passage of time, the 14th century was a century lasting from 1 January 1301 ( MCCCI), to 31 December 1400 ( MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Europe and the Mongol Empire. West Africa experienced economic growth and prosperity. In Europe, the Black Death claimed 25 million lives wiping out one third of the European population while the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of France fought in the protracted Hundred Years' War after the death of Charles IV, King of France led to a claim to the French throne by Edward III, King of England. This period is considered the height of chivalry and marks the beginning of strong separate identities for both England and France as well as the foundation of the Italian Renaissance and Ottoman Empire. In Asia, Tamerlane (Timur), established the Timurid Empire, history's third largest empire to have been ever establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajas Of Singapore
Rajas (Sanskrit: रजस्) is one of the three Guṇas (tendencies, qualities, attributes), a philosophical and psychological concept developed by the Samkhya school of Hindu philosophy.James G. Lochtefeld, Rajas, in The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism: A-M, Vol. 2, Rosen Publishing, , pages 546-547 The other two qualities are ''Sattva'' (goodness, balance) and '' Tamas'' (lethargy, violence, disorder). ''Rajas'' is innate tendency or quality that drives motion, energy and activity.Ian Whicher (1998), ''The Integrity of the Yoga Darśana'', State University of New York Press, pages 86-87, 124-125, 163-167, 238-243 ''Rajas'' is sometimes translated as passion, where it is used in the sense of activity, without any particular value and it can contextually be either good or bad. Rajas helps actualize the other two gunas. Description In Samkhya philosophy, a is one of three "tendencies, qualities": sattva, rajas and tamas. This category of qualities have been widely adopted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raja Of Singapura
The Kingdom of Singapura (Malay: ''Kerajaan Singapura'') was an Indianised Malay Hindu-Buddhist kingdom thought to have been established during the early history of Singapore upon its main island Pulau Ujong, then also known as Temasek, from 1299 until its fall in 1398. Conventional view marks as the founding year of the kingdom by Sang Nila Utama (also known as "Sri Tri Buana"), whose father is Sang Sapurba, a semi-divine figure who according to legend is the ancestor of several Malay monarchs in the Malay World. The historicity of this kingdom based on the account given in the ''Malay Annals'' is uncertain, and many historians only consider its last ruler Parameswara (king), Parameswara (or Sri Iskandar Shah) a historically attested figure. Archaeological evidence from Fort Canning Hill and the nearby banks of the Singapore River has nevertheless demonstrated the existence of a thriving settlement and a trade port in the 14th century. The settlement developed in the 13th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sang Sapurba
Sri Maharaja Sang Sapurba Paduka Sri Trimurti Tri Buana, (1245–1316) also known as Sri Nila Pahlawan, is a figure in the Malay Annals, highly revered as the legendary great ancestor of some of the major dynasties of the Malay world: Singapura, Malacca, Pahang, Johor, Perak, Kelantan, Terengganu and Siak Sri Indrapura. Legend has it that after his accession to Seguntang Hill with his two younger brothers, Sang Sapurba enters into a sacred covenant with Demang Lebar Daun the native ruler of Palembang, which laid the basis of the proper relationship between the Malay rulers and the subjects. The legendary sword believed to be carried by the king, the '' Cura Si Manjakini'', is now formed part of the regalia of Perak Sultanate, whose rulers are said directly descended from the king. The details of Sang Sapurba stories are mainly composed of folklore and legends, and thus his historical existence is debated and disputed by modern historians. Even so, as De Jong argued in her article ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hayam Wuruk
Hayam Wuruk (Sanskrit: हयम् वुरुक्, Kawi: ꦲꦪꦩ꧀ꦮꦸꦫꦸꦏ꧀) (1334–1389), also called Rajasanagara, Pa-ta-na-pa-na-wu, or Bhatara Prabhu after 1350, was a Javanese Hindu emperor from the Rajasa Dynasty and the 4th emperor of the Majapahit Empire. Together with his prime minister Gajah Mada, he reigned the empire at the time of its greatest power. During his reign, the Hindu epics, the Ramayana and the Mahabharata, became ingrained in the culture and worldview of the Javanese through the '' wayang kulit'' (leather puppets).Mark Juergensmeyer and Wade Clark Roof, 2012Encyclopedia of Global Religion Volume 1, Page 557. He was preceded by Tribhuwana Wijayatunggadewi, and succeeded by his son-in-law Wikramawardhana. Most of the accounts of his life were taken from the ''Nagarakretagama'', a eulogy to Hayam Wuruk, and the ''Pararaton'' ("Book of Kings"), a Javanese historical chronicle. Early life According to the ''Nagarakretagama'', Canto 1, St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nusantara (archipelago)
''Nusantara'' is the Indonesian name of Maritime Southeast Asia (or parts of it). It is an Old Javanese term that literally means "outer islands". In Indonesia, it is generally taken to mean the Indonesian Archipelago. Outside of Indonesia, the term has been adopted to refer the Malay Archipelago. The word Nusantara is taken from an oath by Gajah Mada in 1336, as written in the Old Javanese ''Pararaton'' and ''Nagarakretagama''. Gajah Mada was a powerful military leader and prime minister of Majapahit credited with bringing the empire to its peak of glory. Gajah Mada delivered an oath called ''Palapa oath'', in which he vowed not to eat any food containing spices until he had conquered all of Nusantara under the glory of Majapahit. The concept of Nusantara as a unified region was not invented by Gajah Mada in 1336. The term Nusantara was first used by Kertanegara of Singhasari in Mula Malurung inscription dated 1255. Furthermore, in 1275, the term ''Cakravala Mandala Dvipanta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majapahit
Majapahit ( jv, ꦩꦗꦥꦲꦶꦠ꧀; ), also known as Wilwatikta ( jv, ꦮꦶꦭ꧀ꦮꦠꦶꦏ꧀ꦠ; ), was a Javanese people, Javanese Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was based on the island of Java (in modern-day Indonesia). It existed from 1293 to circa 1527 and reached its peak of glory during the era of Hayam Wuruk, whose reign from 1350 to 1389 was marked by conquests that extended throughout Southeast Asia. His achievement is also credited to his prime minister, Gajah Mada. According to the () written in 1365, Majapahit was an empire of 98 tributaries, stretching from Sumatra to New Guinea; consisting of present-day Indonesia, Singapore, Malaysia, Brunei, southern Thailand, Timor Leste, southwestern Philippines (in particular the Sulu Archipelago) although the scope of Majapahit sphere of influence is still the subject of debate among historians. The nature of Majapahit relations and influences upon its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)