|
Squamish Volcanic Field
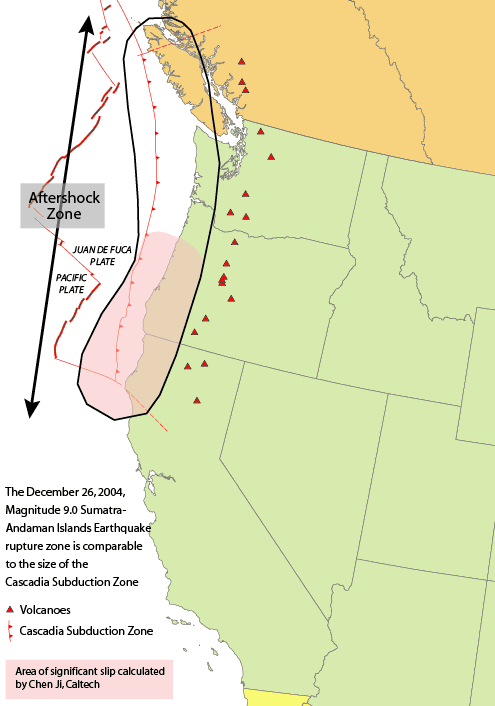
The Squamish volcanic field is a small north–south trending volcanic field on the South Coast of British Columbia, Canada. It extends for only about from the eastern side of Howe Sound northeast of Britannia Beach to the heavily forested slope on the western side of the Squamish River mouth. It forms the southernmost end of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, which comprises part of the Canadian Cascade Arc. Its volcanoes are relatively minor to the more voluminous stratovolcanoes found throughout the Garibaldi Belt and are composed of dacite and lesser basaltic andesite. The field gets its name from the nearby community of Squamish at the north end of Howe Sound on the Sea to Sky Highway. Volcanism in the Squamish field has constructed at least two volcanic zones known as the Watts Point volcanic centre and Monmouth Creek complex. The most recent eruptive activity at these volcanoes is likely Pleistocene in age and are both likely products of glaciovolcanism during the last glacial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garibaldi Volcanic Belt
The Garibaldi Volcanic Belt is a northwest–southeast trending volcanic chain in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains that extends from Watts Point in the south to the Ha-Iltzuk Icefield in the north. This chain of volcanoes is located in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It forms the northernmost segment of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, which includes Mount St. Helens and Mount Baker. Most volcanoes of the Garibaldi chain are dormant stratovolcanoes and subglacial volcanoes that have been eroded by glacial ice. Less common volcanic landforms include cinder cones, volcanic plugs, lava domes and calderas. These diverse formations were created by different styles of volcanic activity, including Peléan and Plinian eruptions. Eruptions along the length of the chain have created at least three major volcanic zones. The first began in the Powder Mountain Icefield 4.0 million years ago. Mount Cayley began its formation during this period. Multiple eruptions from 2.2& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamish, British Columbia
Squamish (; Squamish language, Sḵwx̱wú7mesh sníchim: Sḵwx̱wú7mesh, ; 2016 census population 19,512) is a community and a district municipality in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of British Columbia, located at the north end of Howe Sound on the British Columbia Highway 99, Sea to Sky Highway. The population of the Squamish census agglomeration, which includes Indian reserve, First Nation reserves of the Squamish Nation although they are not governed by the municipality, is 19,893. Indigenous Squamish people have lived in the area for thousands of years. The town of Squamish had its beginning during the construction of the BC Rail, Pacific Great Eastern Railway in the 1910s. It was the first southern terminus of that railway (now a part of Canadian National Railway, CN). The town remains important in the operations of the line and also the port. Forestry has traditionally been the main industry in the area, and the town's largest employer was the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Fields Of Canada
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Cayley Volcanic Field
The Mount Cayley volcanic field (MCVF) is a remote volcanic zone on the South Coast of British Columbia, Canada, stretching from the Pemberton Icefield to the Squamish River. It forms a segment of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, the Canadian portion of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, which extends from Northern California to southwestern British Columbia. Most of the MCVF volcanoes were formed during periods of volcanism under sheets of glacial ice throughout the last glacial period. These subglacial eruptions formed steep, flat-topped volcanoes and subglacial lava domes, most of which have been entirely exposed by deglaciation. However, at least two volcanoes predate the last glacial period and both are highly eroded. The field gets its name from Mount Cayley, a volcanic peak located at the southern end of the Powder Mountain Icefield. This icefield covers much of the central portion of the volcanic field and is one of the several glacial fields in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge River Cones
The Bridge River Cones, sometimes referred to as the Lillooet Cones and Salal Creek Cones, is the name given to a volcanic field located on the north flank of the Bridge River, upper Bridge River, about west of the town of Gold Bridge, British Columbia, Gold Bridge. The cones are in the lee of the Lillooet Icecap and sit astride a group of passes between the Bridge River, which flows W-E to their south, and the Lord River, which flows north to the Taseko Lakes in the Chilcotin District. Geology The Bridge River Cones consist of small trachybasaltic and basaltic eruptive centers. Sham Hill (), a high steep-sided volcanic plug, is the oldest volcano in the field with a potassium-argon dating, potassium-argon date of one million years. The plug is approximately wide and its bare glaciated surface, strewn with glacial erratics, consists of large subhorizontal columns formed within the central conduit of an eroded stratovolcano. The Salal Glacier volcanic complex (), with a potass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciovolcanism
Glaciovolcanism is volcanism and related phenomena associated with glacial ice. The ice commonly constrains the erupted material and melts to create meltwater. Considerable melting of glacial ice can create massive lahars and glacial outburst floods known as jökulhlaups. General Three forms of glaciovolcanism are known. Subglacial eruptions occur when a volcano erupts under ice. Such activity can produce landforms such as tuyas and subglacial mounds. Ice-marginal volcanism takes place when material from a subaerial eruption makes lateral contact with ice. Ice-marginal lava flows are a product of this phenomenon. Supraglacial eruptions deposit ejecta onto the surface of an ice sheet. World regions identified for possible glaciovolcanic activity include Alaska, and western parts of Canada, southern Chile, Argentina, Iceland, and a couple of regions along Antarctica's coast, such as the Antarctic Peninsula and the Ross Ice Shelf. Volcanologist Bill McGuire noted in 2014, Examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monmouth Creek Complex
The Monmouth Creek complex is a volcanic complex in southwestern British Columbia, Canada, located southwest of the community of Squamish on the west side of the Squamish River mouth. It lies in the southern Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains and is part of the Squamish volcanic field in the southern Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, which represents the northernmost extension of the Cascade Volcanic Arc. Its prominent and enigmatic edifice is composed of basaltic andesite to dacite of unknown age and may represent a group of dikes and lava domes that formed subglacially. At least four dikes protrude its summit. These form the ribs of to high lava spine Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...s, the tallest being The Castle, which contains horizontal and radiating columnar j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watts Point Volcanic Centre
The Watts Point volcanic centre is a small outcrop of Pleistocene age volcanic rock at Watts Point in British Columbia, Canada, about south of Squamish and north of Vancouver, and just north of Britannia Beach. It is the southernmost volcanic zone in the Squamish volcanic field and of the Garibaldi segment of the Cascade Volcanic Arc. The latest research indicates that it is most likely a subglacial mound. It comprises a continuous mass of sparsely porphyritic highly jointed dacitic lava overlying the mid-Cretaceous Coast Plutonic Complex and overlain locally by clay and of glacial till. The volcanic outcrop at Watts Point extends from below the present sea level up the side of a steep slope over . The outcrop is less than long, with an area of about and an eruptive volume of roughly . The location is heavily forested, and the BC Rail mainline passes through the lower portion of the outcrop about above sea level. Two railroad track ballast quarries, one near the middle an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia Highway 99
Highway 99 is a provincial highway in British Columbia that serves Greater Vancouver and the Squamish–Lillooet corridor over a length of . It is a major north–south artery within Vancouver and connects the city to several suburbs as well as the U.S. border, where it continues south as Interstate 5. The central section of the route, also known as the Sea to Sky Highway, serves the communities of Squamish, Whistler, and Pemberton. Highway 99 continues through Lillooet and ends at a junction with Highway 97 near Cache Creek. The highway's number, assigned in 1940, was derived from former U.S. Route 99, the predecessor to Interstate 5 and a major route for the U.S. West Coast. Highway 99 originally comprised the King George Highway in Surrey, portions of Kingsway from New Westminster to Vancouver, and local streets. It was extended across the Lions Gate Bridge and to Horseshoe Bay in the 1950s along a new highway that would later be incorporated into Highway 1 (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basaltic Andesite
Basaltic andesite is a volcanic rock that is intermediate in composition between basalt and andesite. It is composed predominantly of augite and plagioclase. Basaltic andesite can be found in volcanoes around the world, including in Central America and the Andes of South America. Description Basaltic andesite is a fine-grained (aphanitic) igneous rock that is moderately low in silica and low in alkali metal oxides. It is not separately defined in the QAPF classification, which is based on the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, plagioclase feldspar, and feldspathoids, but would fall in the basalt-andesite field. This corresponds to rock in which feldspathoid makes up less than 10% and quartz less than 20% of the total QAPF fraction, and in which at least 65% of the feldspar is plagioclase. Basaltic andesite would be further distinguished from basalt and andesite by a silica content between 52% and 57%. Although classification by mineral content is preferred by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |