|
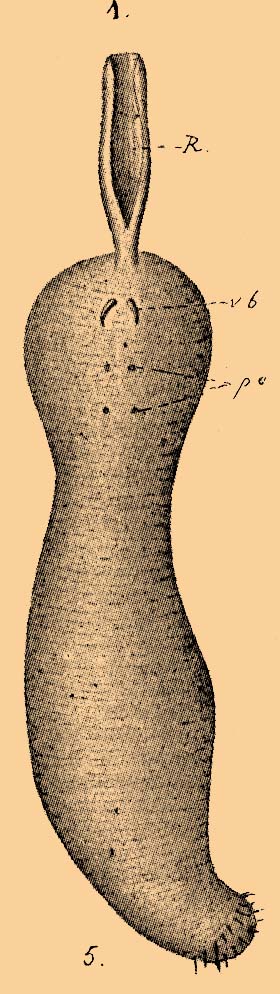
Spoon Worms
The Echiura, or spoon worms, are a small group of marine animals. Once treated as a separate phylum, they are now considered to belong to Annelida. Annelids typically have their bodies divided into segments, but echiurans have secondarily lost their segmentation. The majority of echiurans live in burrows in soft sediment in shallow water, but some live in rock crevices or under boulders, and there are also deep sea forms. More than 230 species have been described. Spoon worms are cylindrical, soft-bodied animals usually possessing a non-retractable proboscis which can be rolled into a scoop-shape to feed. In some species the proboscis is ribbon-like, longer than the trunk and may have a forked tip. Spoon worms vary in size from less than a centimetre in length to more than a metre. Most are deposit feeders, collecting detritus from the sea floor. Fossils of these worms are seldom found and the earliest known fossil specimen is from the Upper Carboniferous ( Pennsylvanian). Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
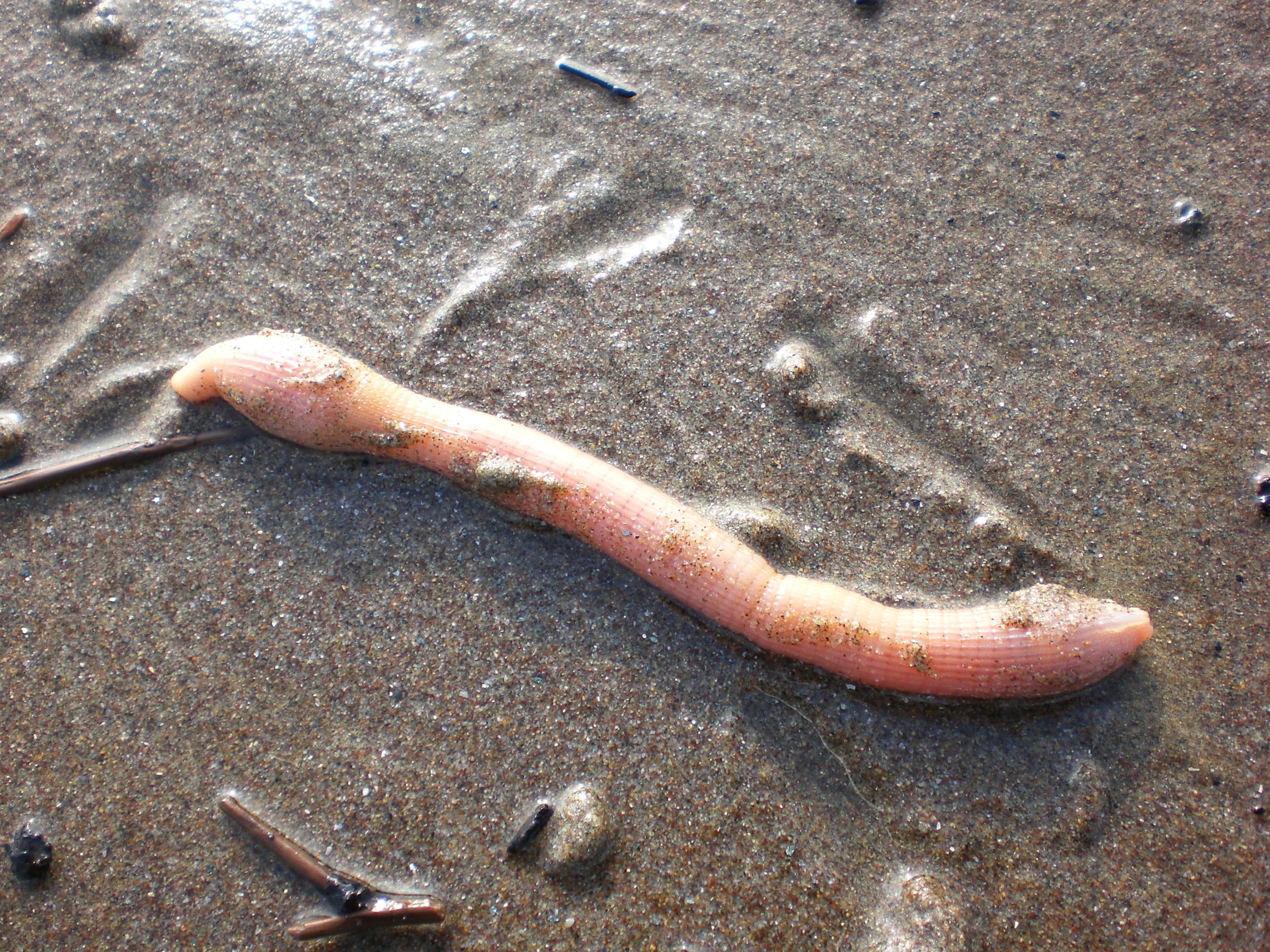
Urechis Caupo
''Urechis caupo'' is a species of spoon worm in the family Urechidae, commonly known as the innkeeper echiuran, the fat innkeeper worm (because the tunnels often contain other animals), the innkeeper worm, or the penis fish. It is found in shallow water on the west coast of North America, between southern Oregon and Baja California, where it forms a U-shaped burrow in the sediment and feeds on plankton using a mucus net. Description ''Urechis caupo'' is a plump, unsegmented, cylindrical pink worm growing to a length of up to , with being a more typical length. There are a pair of setae (bristles) on the ventral surface at the anterior end, and a distinctive ring of about ten setae around the anus at the posterior end. The proboscis is short. Distribution and habitat Shallow water in the northeastern Pacific Ocean is the habitat of ''U. caupo''; its range extends from southern Oregon to northern Baja California. It lives in a burrow in muddy sand in the lower intertidal and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
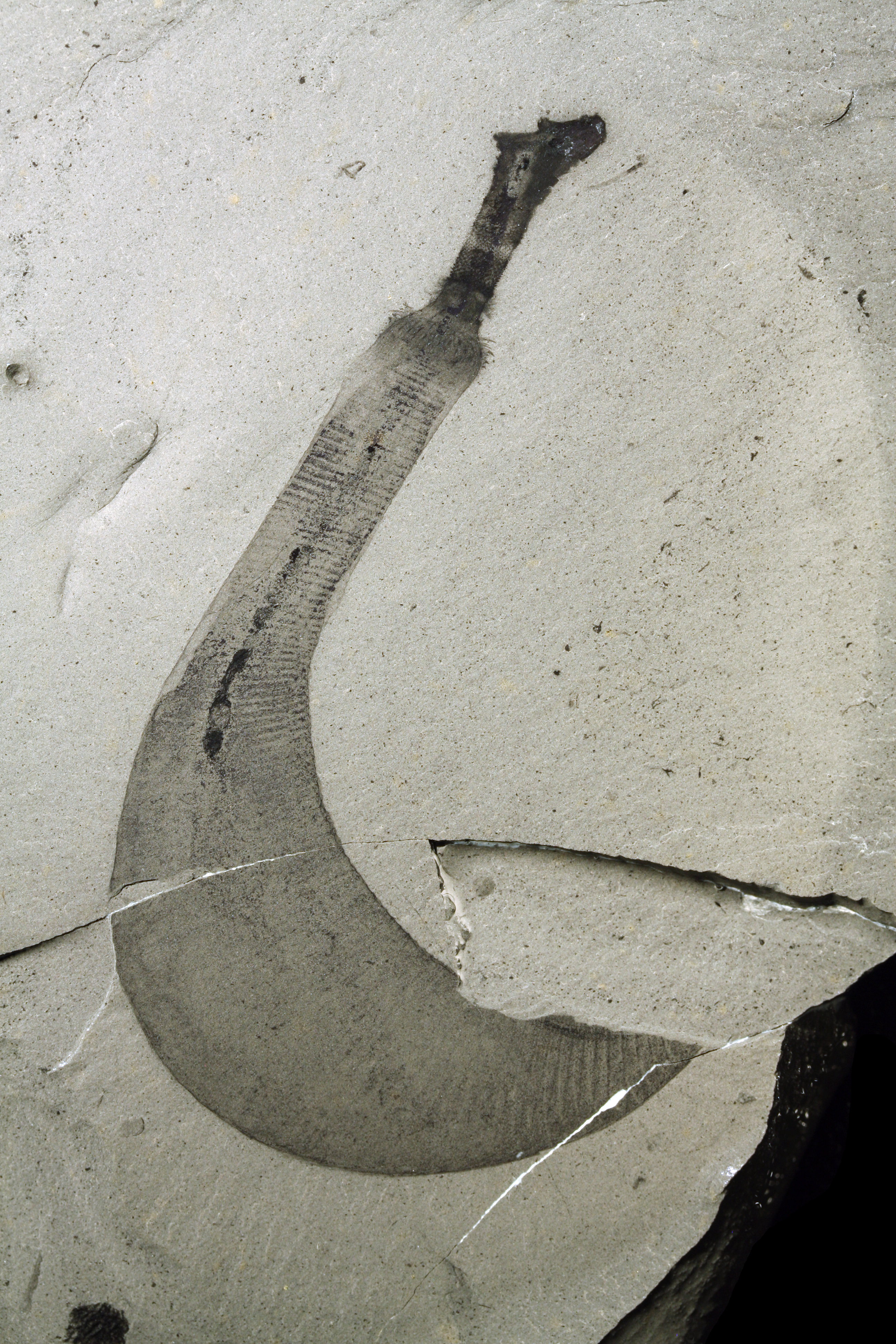
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin '' carbō'' ("coal") and '' ferō'' ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern 'system' names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian. Terrestrial animal life was well established by the Carboniferous Period. Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates), which had originated from lobe-finned fish during the preceding Devonian, became pentadactylous in and diversified during the Carboniferous, including early amphibian line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burrow Fossil
Burrow fossils are the remains of burrows - holes or tunnels excavated into the ground or seafloor - by animals to create a space suitable for habitation, temporary refuge, or as a byproduct of locomotion preserved in the rock record. Because burrow fossils represent the preserved byproducts of behavior rather than physical remains, they are considered a kind of trace fossil. One common kind of burrow fossil is known as Skolithos, and the similar Trypanites, Ophiomorpha and Diplocraterion. Vertebrate burrows Fish burrows Fossil Lungfish burrows are preserved in the Rocky Point Member of the Chinle Formation in Canyonlands National Park. Invertebrate burrows Examples are Treptichnus pedum ''Treptichnus'' (formerly named ''Phycodes'', ''Manykodes'' by J. Dzik, and also known as ''Trichophycus''See e.gfossiilid.info: paleodiversity in Baltoscandia: Trichophycus pedum/ref>) is the preserved burrow of an animal. As such, it is regar ... and Arenicolites franconicus. Footnote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mazon Creek Fossil Beds
The Mazon Creek fossil beds are a conservation ' found near Morris, in Grundy County, Illinois. The fossils are preserved in ironstone concretions, formed approximately in the mid- Pennsylvanian epoch of the Carboniferous period. These concretions frequently preserve both hard and soft tissues of animal and plant materials, as well as many soft-bodied organisms that do not normally fossilize. The quality, quantity and diversity of fossils in the area, known since the mid-nineteenth century, make the Mazon Creek ' important to paleontologists, in attempting to reconstruct the paleoecology of the sites. The locality was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1997.. Geology The Mazon Creek fossils are found in the Upper Carboniferous Francis Creek Shale; the type locality is the Mazon River (or Mazon Creek), a tributary of the Illinois River near Morris, Grundy County, Illinois. The 25 to 30 meters of shale were formed approximately , during the Pennsylvanian period. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitellidae
Capitellidae is a polychaete worm family in the subclass Scolecida. Genera * ''Abyssocapitella'' * ''Amastigos'' * ''Anotomastus'' * ''Baldia (worm), Baldia'' * ''Barantolla'' * ''Branchiocapitella'' * ''Capitella'' * ''Capitellethus'' * ''Capitobranchus'' * ''Dasybranchetus'' * ''Dasybranchus'' * ''Decamastus'' * ''Ditrocha'' * ''Dodecaseta'' * ''Eunotomastus'' * ''Heteromastides'' * ''Heteromastus'' * ''Leiocapitella'' * ''Leiocapitellides'' * ''Leiochrides'' * ''Leiochrus'' * ''Lumbricomastus'' * ''Mastobranchus'' * ''Mediomastus'' * ''Neoheteromastus'' * ''Neomediomastus'' * ''Neonotomastus'' * ''Neopseudocapitella'' * ''Nonatus'' * ''Notodasus'' * ''Notomastus'' * ''Octocapitella'' * ''Paracapitella'' * ''Paraleiocapitella'' * ''Parheteromastides'' * ''Parheteromastus'' * ''Peresiella'' * ''Protomastobranchus'' * ''Pseudocapitella'' * ''Pseudoleiocapitella'' * ''Pseudomastus'' * ''Pseudonotomastus'' * ''Pulliella'' * ''Rashgua'' * ''Scyphoproctus'' * ''Undecimastus'' Refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annelid
The annelids (Annelida , from Latin ', "little ring"), also known as the segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments. The Annelids are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate, invertebrate organisms. They also have parapodia for locomotion. Most textbooks still use the traditional division into polychaetes (almost all marine), oligochaetes (which include earthworms) and leech-like species. Cladistic research since 1997 has radically changed this scheme, viewing leeches as a sub-group of oligochaetes and oligochaetes as a sub-group of polychaetes. In addition, the Pogonophora, Echiura and Sipuncula, previously regarded as separate phyla, are now regarded as sub-groups of polycha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holothuria
''Holothuria'' is the type genus of the marine animal family Holothuriidae, part of the class Holothuroidea, commonly known as sea cucumbers. Members of the genus are found in coastal waters in tropical and temperate regions. They are soft bodied, limbless invertebrates that dwell on the ocean floor and are usually detritivore. They resemble a cucumber in form. The genus contains some species that are harvested and sold as food. Species The following species are recognised in the genus ''Holothuria'': * Subgenus ''Acanthotrapeza'' ** '' Holothuria coluber'' ** '' Holothuria kubaryi'' ** ''Holothuria pyxis'' ** ''Holothuria tripilata'' * Subgenus ''Cystipus'' ** ''Holothuria casoae'' ** ''Holothuria cubana'' ** ''Holothuria dura'' ** ''Holothuria hartmeyeri'' ** ''Holothuria inhabilis'' ** ''Holothuria jousseaumei'' ** ''Holothuria mammosa'' ** ''Holothuria occidentalis'' ** '' Holothuria pseudofossor'' ** '' Holothuria rigida'' ** ''Holothuria sucosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gephyrea
Gephyrea is a now-dismantled taxon for a group of non-annulated worms, considered intermediate between annelids and holothurians, containing the three modern phyla Echiura, Sipuncula, and Priapulida. References Obsolete animal taxa Protostome classes {{protostome-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priapulida
Priapulida (priapulid worms, from Gr. πριάπος, ''priāpos'' 'Priapus' + Lat. ''-ul-'', diminutive), sometimes referred to as penis worms, is a phylum of unsegmented marine worms. The name of the phylum relates to the Greek god of fertility, because their general shape and their extensible spiny introvert (eversible) proboscis may resemble the shape of a human penis. They live in the mud and in comparatively shallow waters up to deep. Some species show a remarkable tolerance for hydrogen sulfide and anoxia. They can be quite abundant in some areas. In an Alaskan bay as many as 85 adult individuals of ''Priapulus caudatus'' per square meter has been recorded, while the density of its larvae can be as high as 58,000 per square meter. Together with Echiura and Sipuncula, they were once placed in the taxon Gephyrea, but consistent morphological and molecular evidence supports their belonging to Ecdysozoa, which also includes arthropods and nematodes. Fossil findings show that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sipuncula
The Sipuncula or Sipunculida (common names sipunculid worms or peanut worms) is a class containing about 162 species of unsegmented marine annelid worms. The name ''Sipuncula'' is from the genus name ''Sipunculus'', and comes from the Latin ''siphunculus'' meaning a "small tube". Sipuncula was once considered a phylum, but was demoted to a class of Annelida, based on recent molecular work. Sipunculans vary in size but most species are under in length. The body is divided into an unsegmented, bulbous trunk and a narrower, anterior section, called the "introvert", which can be retracted into the trunk. The mouth is at the tip of the introvert and is surrounded in most groups by a ring of short tentacles. With no hard parts, the body is flexible and mobile. Although found in a range of habitats throughout the world's oceans, the majority of species live in shallow water habitats, burrowing under the surface of sandy and muddy substrates. Others live under stones, in rock crevic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumbricus
The genus ''Lumbricus'' contains some of the most commonly seen earthworms in Europe among its nearly 700 valid species. Characteristics of some commonly encountered species are: * ''Lumbricus rubellus'' is usually reddish brown or reddish violet, iridescent dorsally, and pale yellow ventrally. They are usually about 25–105 mm in length, and have around 95-120 segments. * '' Lumbricus castaneus'' varies from chesnut to violet brown; brown or yellow ventrally, and has an orange clitellum. They are usually about 30–70 mm long, and have around 82–100 segments. * ''Lumbricus terrestris'' has several common names, including common earthworm, nightcrawler, and dew worm. It is strongly pigmented, brown-red dorsally, and yellowish ventrally. Setae are widely paired at both ends of the body. It is about 90–300 mm long, and has around 110–160 segments. * '' Lumbricus festivus'' is not found in large numbers. It is red-brown, lighter ventrally, iridescent dorsally. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |