|
Spitamenes
Spitamenes (Old Persian ''Spitamana''; Greek ''Σπιταμένης''; 370 BC – 328 BC) was a Sogdian warlordHolt, Frank L. (1989), ''Alexander the Great and Bactria: the Formation of a Greek Frontier in Central Asia'', Leiden, New York, Copenhagen, Cologne: E. J. Brill, pp 64–65 (see footnote #63 for a discussion on Spitamenes and Apama), . and the leader of the uprising in Sogdiana and Bactria against Alexander the Great, King of Macedon, in 329 BC. He has been credited by modern historians as one of the most tenacious adversaries of Alexander. Biography Spitamenes was an ally of Bessus. In 329, Bessus stirred a revolt in the eastern satrapies, and the same year his allies began to be uncertain about supporting him. Alexander went with his army to Drapsaca, outflanked Bessus and sent him fleeing. Bessus was then removed from power by Spitamenes, and Ptolemy was sent to catch him. While Alexander was founding the new city of Alexandria Eschate on the Jaxartes river, news ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sogdia
Sogdia (Sogdian language, Sogdian: ) or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemenid Empire, and listed on the Behistun Inscription of Darius the Great. Sogdiana was first conquered by Cyrus the Great, the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, and then was annexed by the Macedonian ruler Alexander the Great in 328 BC. It would continue to change hands under the Seleucid Empire, the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, the Kushan Empire, the Sasanian Empire, the Hephthalite Empire, the Western Turkic Khaganate and the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana. The Sogdian city-states, although never politically united, were centered on the city of Samarkand. Sogdian language, Sogdian, an Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian language, is no longer spoken, but a descendant of one of its dialects, Yaghnobi language, Ya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apama
Apama ( grc, Ἀπάμα, Apáma), sometimes known as Apama I or Apame I, was a Sogdian noblewoman and the wife of the first ruler of the Seleucid Empire, Seleucus I Nicator. They married at Susa in 324 BC. According to Arrian, Apama was the daughter of the Sogdian baron Spitamenes. Apame was the only of the Susa wives to become queen as, unlike the other generals, Seleucus kept her after Alexander's death. Apama had three children with her husband: Antiochus I Soter who inherited the Seleucid throne, Achaeus, and a daughter also called Apama. Circa 300-297 BC, Seleucus married Stratonice, daughter of Demetrius I of Macedon, Seleucus had a daughter by Stratonice, who was called Phila. According to Malalas's chronicle, he married her after the death of Apama but, according to other sources, she was still alive, as the people of Miletus honored her with a statue that year. According to Appian (57–8), her husband named three cities Apamea Apamea or Apameia ( grc, Απά� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II of Macedon, Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20, and spent most of his ruling years conducting a lengthy military campaign throughout Western Asia and ancient Egypt, Egypt. By the age of thirty, he had created one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history, stretching from Greece to northwestern Historical India, India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he Alexander's Balkan campaign, campaigned in the Balkans and reasserted control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bessus
Bessus or Bessos ( peo, *Bayaçā; grc-gre, Βήσσος), also known by his throne name Artaxerxes V ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης; died summer 329 BC), was a Persian satrap of the eastern Achaemenid satrapy of Bactria, as well as the self-proclaimed King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 330 to 329 BC. A member of the ruling Achaemenid dynasty, Bessus came to power shortly after killing the legitimate Achaemenid ruler Darius III (), and subsequently attempted to hold the eastern part of the empire against the Macedonian king Alexander the Great (). His realm quickly started to fall apart, including Bactria, which was the main center. Fleeing into Sogdia, he was arrested by his own officers, who handed him over to Alexander, who had him executed at Ecbatana. Bessus appears in the 11th-century Persian epic ''Shahnameh'' under the name of Janusipar/Janushyar. Name "Bessus" (Βήσσος) is the Greek transliteration of the Old P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus I Soter
Antiochus I Soter ( grc-gre, Ἀντίοχος Σωτήρ, ''Antíochos Sōtér''; "Antiochus the Saviour"; c. 324/32 June 261 BC) was a Greek king of the Seleucid Empire. Antiochus succeeded his father Seleucus I Nicator in 281 BC and reigned during a period of instability which he mostly overcame until his death on 2 June 261 BC. He is the last known ruler to be attributed the ancient Mesopotamian title King of the Universe. Biography Antiochus's father was Seleucus I Nicator and his mother was Apama, daughter of Spitamenes, being one of the princesses whom Alexander the Great had given as wives to his generals in 324 BC. The Seleucids fictitiously claimed that Apama was the daughter of Darius III, in order to legitimise themselves as the inheritors of both the Achaemenids and Alexander, and therefore the rightful lords of western and central Asia. In 294 BC, prior to the death of his father Seleucus I, Antiochus married his stepmother, Stratonice, daughter of Demetrius Polio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Afghan Campaign
''The Afghan Campaign'' is a historical novel by the American writer Steven Pressfield. It was first published in 2006 by Doubleday. It is the story of Alexander the Great's invasion of the Afghan kingdoms (the Afghanistan of today) in 330 BC through the eyes of Matthias (Μαντίθεος in Greek), a young soldier from Macedonia, who narrates the adventures of the Macedonian army against the Eastern warriors. Matthias fights for Alexander the Great's infantry confronting ferocious people who, determined to defend their homeland, follow tough war methods. Many pages of the book are dedicated to Alexander's army's fight against the Persian Spitamenes (Σπιταμένης in Greek), the ''Wolf of the Desert'', whose army follows the barbarian war method contrary to their rivals who make war in array. Pressfield presents the brutalities and ferocities of both parties while he does not omit to refer to the vanity and voraciousness of Alexander the Great who in the last page ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharnuches Of Lycia
Pharnuches ( el, Φαρνούχης or Φαρνούχoς) was a Lycian appointed by Alexander the Great to command the force sent into Sogdiana against Spitamenes in 329 BC. The result of the expedition was disastrous, with the destruction of the whole army. Pharnuches had been entrusted with its superintendence, because he was acquainted with the language of the inhabitants of the region, and had shown much dexterity in his intercourse with them. According to Aristobulus he was conscious of his deficiency in military skill, and wished to cede the command to the three Macedonian officers who were acting under him ( Caranus, Menedemus and Andromachus), but they refused to accept it. Notes References * Smith, William (editor); ''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology''"Pharnuchus (3)" Boston Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial cente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire originally founded by Alexander the Great. After receiving the Mesopotamian region of Babylonia in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Persian Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that had covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, and what are now modern Iraq, Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide varie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; ; grc-gre, Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ , ) was a Macedonian Greek general who was an officer and successor ( ''diadochus'') of Alexander the Great. Seleucus was the founder of the eponymous Seleucid Empire. In the power struggles that followed Alexander's death, Seleucus rose from being a secondary player to becoming total ruler of Asia Minor, Syria, Mesopotamia, and the Iranian Plateau, eventually assuming the title of '' basileus'' (king). The state he established on these territories, the Seleucid Empire, was one of the major powers of the Hellenistic world, until being overcome by the Roman Republic and Parthian Empire in the late second and early first centuries BC. After the death of Alexander in June 323 BC, Seleucus initially supported Perdiccas, the regent of Alexander's empire, and was appointed Commander of the Companions and chiliarch at the Partition of Babylon in 323 BC. However, after the outbreak of the Wars of the Diadochi in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenus (general)
Coenus (Greek: Koῖνος; died 326 BC), a son of Polemocrates and son-in-law of Parmenion, was one of the ablest and most faithful of Alexander the Great's generals during his eastern expedition. General of Alexander In the autumn of 334 BC, while Alexander was in Caria, he sent those of his soldiers who had been recently married in Macedonia to spend the ensuing winter with their wives. Coenus was one of the commanders who led them back to Europe. In the spring of the following year (333 BC), Coenus returned with the Macedonians and joined Alexander at Gordium. After the conquest of Drangiana, in the latter part of 330 BC, Coenus joined others in accusing his wife's brother, Philotas, of treason for conspiring against Alexander. This led to the execution of Philotas, and the assassination of Coenus' father-in-law, Parmenion. Coenus commanded a taxeis (unit of 1500 Phalangites) of Alexander's army, and distinguished himself on various occasions. In all of Alexander's major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires. The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with considerable autonomy. The word came to suggest tyranny or ostentatious splendour, and in modern usage refers to any subordinate or local ruler, usually with unfavourable connotations of corruption. A satrapy is the territory governed by a satrap. Etymology The word is derived via Latin from Greek ''satrápes'' (), itself borrowed from an Old Iranian ''*khshathra-pa''. In Old Persian, which was the native language of the Achaemenids, it is recorded as ''khshathapavan'' (, literally "protector of the province"). The Median form is reconstructed as ''*khshathrapavan-''. It is cognate with Sanskrit ''kshetrapal'' (). The Biblical Hebrew form is ''aḥashdarpan'' , as found in . In the Parthian (language of the Arsacid Empire) and Middle Persia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
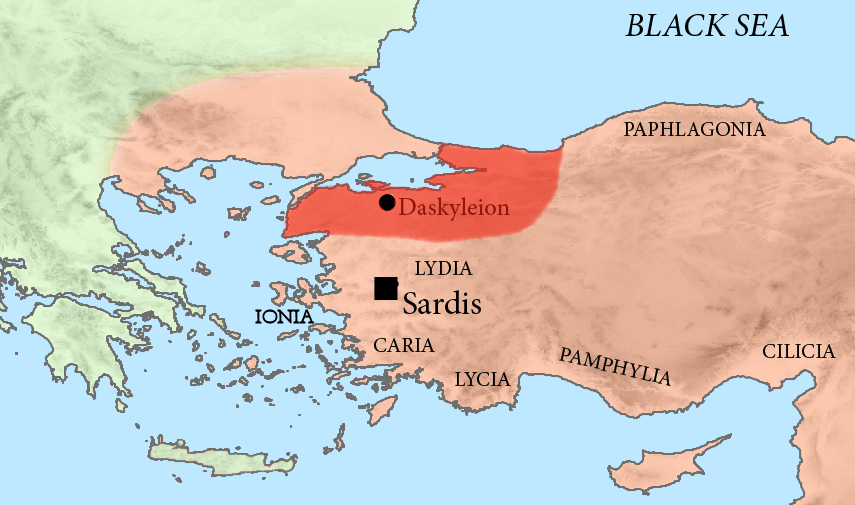
Artabazos II
Artabazos II (in Greek Ἀρτάβαζος) ( fl. 389 – 328 BC) was a Persian general and satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia. He was the son of the Persian satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia Pharnabazus II, and younger kinsman (most probably nephew) of Ariobarzanes of Phrygia who revolted against Artaxerxes II around 356 BC. His first wife was an unnamed Greek woman from Rhodes, sister of the two mercenaries Mentor of Rhodes and Memnon of Rhodes. Towards the end of his life, he became satrap of Bactria for Alexander the Great. Revolt of Datames In 362 BC, Artabazos was sent by Artaxerxes II to capture Datames, the satrap of Cappadocia, who had joined in the Satraps' revolt in which Artabazus' brother, Ariobarzanes, was a participant. However, Artabazos was defeated by Datames. Artaxerxes II ultimately prevailed, and Ariobarzanes was crucified and Datames assassinated. Rebellion against Artaxerxes III Following the capture and death of his brother, Artabazos was made satr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)