|
Spiral
In mathematics, a spiral is a curve which emanates from a point, moving farther away as it revolves around the point. Helices Two major definitions of "spiral" in the American Heritage Dictionary are:Spiral ''American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language'', Houghton Mifflin Company, Fourth Edition, 2009. # a curve on a plane that winds around a fixed center point at a continuously increasing or decreasing distance from the point. # a three-dimensional curve that turns around an axis at a constant or continuously varying distance while moving parallel to the axis; a . The first definition describes a |
Spiral Galaxy
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''Alt URL pp. 124–151) and, as such, form part of the . Most spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating containing s, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as the |
Logarithmic Spiral
A logarithmic spiral, equiangular spiral, or growth spiral is a self-similar spiral curve that often appears in nature. The first to describe a logarithmic spiral was Albrecht Dürer (1525) who called it an "eternal line" ("ewige Linie"). More than a century later, the curve was discussed by Descartes (1638), and later extensively investigated by Jacob Bernoulli, who called it ''Spira mirabilis'', "the marvelous spiral". The logarithmic spiral can be distinguished from the Archimedean spiral by the fact that the distances between the turnings of a logarithmic spiral increase in geometric progression, while in an Archimedean spiral these distances are constant. Definition In polar coordinates (r, \varphi) the logarithmic spiral can be written as r = ae^,\quad \varphi \in \R, or \varphi = \frac \ln \frac, with e being the base of natural logarithms, and a > 0, k\ne 0 being real constants. In Cartesian coordinates The logarithmic spiral with the polar equation r = a e^ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archimedean Spiral
The Archimedean spiral (also known as the arithmetic spiral) is a spiral named after the 3rd-century BC Greek mathematician Archimedes. It is the locus corresponding to the locations over time of a point moving away from a fixed point with a constant speed along a line that rotates with constant angular velocity. Equivalently, in polar coordinates it can be described by the equation r = a + b\cdot\theta with real numbers and . Changing the parameter moves the centerpoint of the spiral outward from the origin (positive toward and negative toward ) essentially through a rotation of the spiral, while controls the distance between loops. From the above equation, it can thus be stated: position of particle from point of start is proportional to angle as time elapses. Archimedes described such a spiral in his book '' On Spirals''. Conon of Samos was a friend of his and Pappus states that this spiral was discovered by Conon. Derivation of general equation of spiral A p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornu Spiral
An Euler spiral is a curve whose curvature changes linearly with its curve length (the curvature of a circular curve is equal to the reciprocal of the radius). Euler spirals are also commonly referred to as spiros, clothoids, or Cornu spirals. Euler spirals have applications to diffraction computations. They are also widely used in railway and highway engineering to design transition curves between straight and curved sections of railway or roads. A similar application is also found in photonic integrated circuits. The principle of linear variation of the curvature of the transition curve between a tangent and a circular curve defines the geometry of the Euler spiral: *Its curvature begins with zero at the straight section (the tangent) and increases linearly with its curve length. *Where the Euler spiral meets the circular curve, its curvature becomes equal to that of the latter. Applications Track transition curve To travel along a circular path, an object needs to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Spiral
In geometry, a golden spiral is a logarithmic spiral whose growth factor is , the golden ratio. That is, a golden spiral gets wider (or further from its origin) by a factor of for every quarter turn it makes. Approximations of the golden spiral There are several comparable spirals that approximate, but do not exactly equal, a golden spiral. For example, a golden spiral can be approximated by first starting with a rectangle for which the ratio between its length and width is the golden ratio. This rectangle can then be partitioned into a square and a similar rectangle and this rectangle can then be split in the same way. After continuing this process for an arbitrary number of steps, the result will be an almost complete partitioning of the rectangle into squares. The corners of these squares can be connected by quarter-circles. The result, though not a true logarithmic spiral, closely approximates a golden spiral. Another approximation is a Fibonacci spiral, which is const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermat's Spiral
A Fermat's spiral or parabolic spiral is a plane curve with the property that the area between any two consecutive full turns around the spiral is invariant. As a result, the distance between turns grows in inverse proportion to their distance from the spiral center, contrasting with the Archimedean spiral (for which this distance is invariant) and the logarithmic spiral (for which the distance between turns is proportional to the distance from the center). Fermat spirals are named after Pierre de Fermat.Anastasios M. Lekkas, Andreas R. Dahl, Morten Breivik, Thor I. Fossen"Continuous-Curvature Path Generation Using Fermat's Spiral" In: ''Modeling, Identification and Control''. Vol. 34, No. 4, 2013, pp. 183–198, . Their applications include curvature continuous blending of curves, modeling plant growth and the shapes of certain spiral galaxies, and the design of variable capacitors, solar power reflector arrays, and cyclotrons. Coordinate representation Polar The representatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Spiral
A hyperbolic spiral is a plane curve, which can be described in polar coordinates by the equation :r=\frac of a hyperbola. Because it can be generated by a circle inversion of an Archimedean spiral, it is called Reciprocal spiral, too.. Pierre Varignon first studied the curve in 1704. Later Johann Bernoulli and Roger Cotes worked on the curve as well. The hyperbolic spiral has a pitch angle that increases with distance from its center, unlike the logarithmic spiral (in which the angle is constant) or Archimedean spiral (in which it decreases with distance). For this reason, it has been used to model the shapes of spiral galaxies, which in some cases similarly have an increasing pitch angle. However, this model does not provide a good fit to the shapes of all spiral galaxies. In cartesian coordinates the hyperbolic spiral with the polar equation :r=\frac a \varphi ,\quad \varphi \ne 0 can be represented in Cartesian coordinates by :x = a \frac \varphi, \qquad y = a \frac \var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiral Of Theodorus
In geometry, the spiral of Theodorus (also called ''square root spiral'', ''Einstein spiral'', ''Pythagorean spiral'', or ''Pythagoras's snail'') is a spiral composed of right triangles, placed edge-to-edge. It was named after Theodorus of Cyrene. Construction The spiral is started with an isosceles right triangle, with each leg having unit length. Another right triangle is formed, an automedian right triangle with one leg being the hypotenuse of the prior triangle (with length the square root of 2) and the other leg having length of 1; the length of the hypotenuse of this second triangle is the square root of 3. The process then repeats; the nth triangle in the sequence is a right triangle with the side lengths \sqrt and 1, and with hypotenuse \sqrt. For example, the 16th triangle has sides measuring 4=\sqrt, 1 and hypotenuse of \sqrt. History and uses Although all of Theodorus' work has been lost, Plato put Theodorus into his dialogue '' Theaetetus'', which tells of his work. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Coordinates
In mathematics, the polar coordinate system is a two-dimensional coordinate system in which each point on a plane is determined by a distance from a reference point and an angle from a reference direction. The reference point (analogous to the origin of a Cartesian coordinate system) is called the ''pole'', and the ray from the pole in the reference direction is the ''polar axis''. The distance from the pole is called the ''radial coordinate'', ''radial distance'' or simply ''radius'', and the angle is called the ''angular coordinate'', ''polar angle'', or ''azimuth''. Angles in polar notation are generally expressed in either degrees or radians (2 rad being equal to 360°). Grégoire de Saint-Vincent and Bonaventura Cavalieri independently introduced the concepts in the mid-17th century, though the actual term "polar coordinates" has been attributed to Gregorio Fontana in the 18th century. The initial motivation for the introduction of the polar system was the study of circula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helix
A helix () is a shape like a corkscrew or spiral staircase. It is a type of smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is formed as two intertwined helices, and many proteins have helical substructures, known as alpha helices. The word ''helix'' comes from the Greek word ''ἕλιξ'', "twisted, curved". A "filled-in" helix – for example, a "spiral" (helical) ramp – is a surface called ''helicoid''. Properties and types The ''pitch'' of a helix is the height of one complete helix turn, measured parallel to the axis of the helix. A double helix consists of two (typically congruent) helices with the same axis, differing by a translation along the axis. A circular helix (i.e. one with constant radius) has constant band curvature and constant torsion. A ''conic helix'', also known as a ''conic spiral'', may be defined as a spiral on a conic surface, with the distance to the apex an expo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
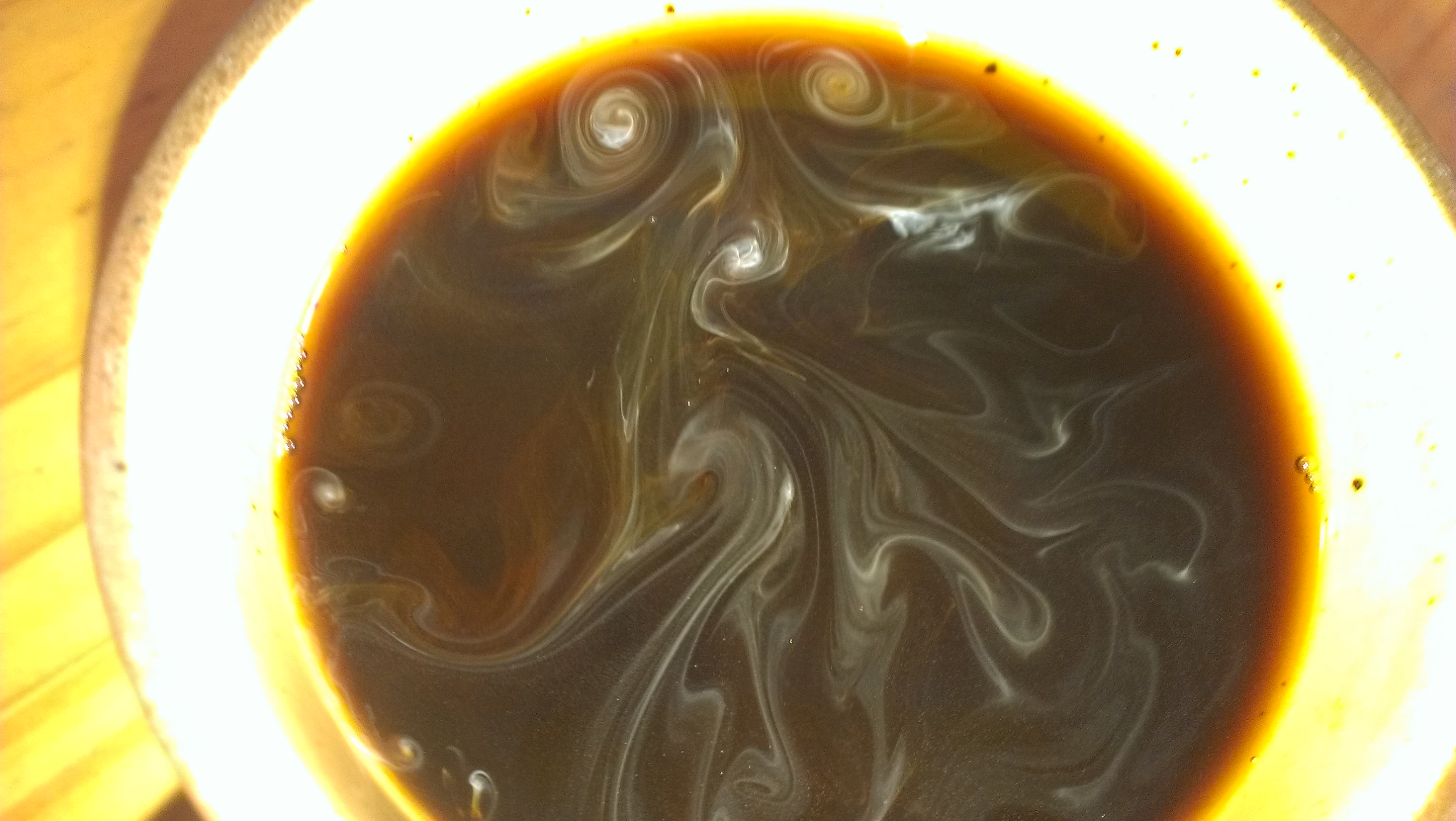
Vortex
In fluid dynamics, a vortex ( : vortices or vortexes) is a region in a fluid in which the flow revolves around an axis line, which may be straight or curved. Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools in the wake of a boat, and the winds surrounding a tropical cyclone, tornado or dust devil. Vortices are a major component of turbulent flow. The distribution of velocity, vorticity (the curl of the flow velocity), as well as the concept of circulation are used to characterise vortices. In most vortices, the fluid flow velocity is greatest next to its axis and decreases in inverse proportion to the distance from the axis. In the absence of external forces, viscous friction within the fluid tends to organise the flow into a collection of irrotational vortices, possibly superimposed to larger-scale flows, including larger-scale vortices. Once formed, vortices can move, stretch, twist, and interact in complex ways. A moving vortex carries s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gear
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic principle behind the operation of gears is analogous to the basic principle of levers. A gear may also be known informally as a cog. Geared devices can change the speed, torque, and direction of a power source. Gears of different sizes produce a change in torque, creating a mechanical advantage, through their ''gear ratio'', and thus may be considered a simple machine. The rotational speeds, and the torques, of two meshing gears differ in proportion to their diameters. The teeth on the two meshing gears all have the same shape. Two or more meshing gears, working in a sequence, are called a gear train or a '' transmission''. The gears in a transmission are analogous to the wheels in a crossed, belt pulley system. An advantage of gears is tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |