|
Spine Of The Scapula
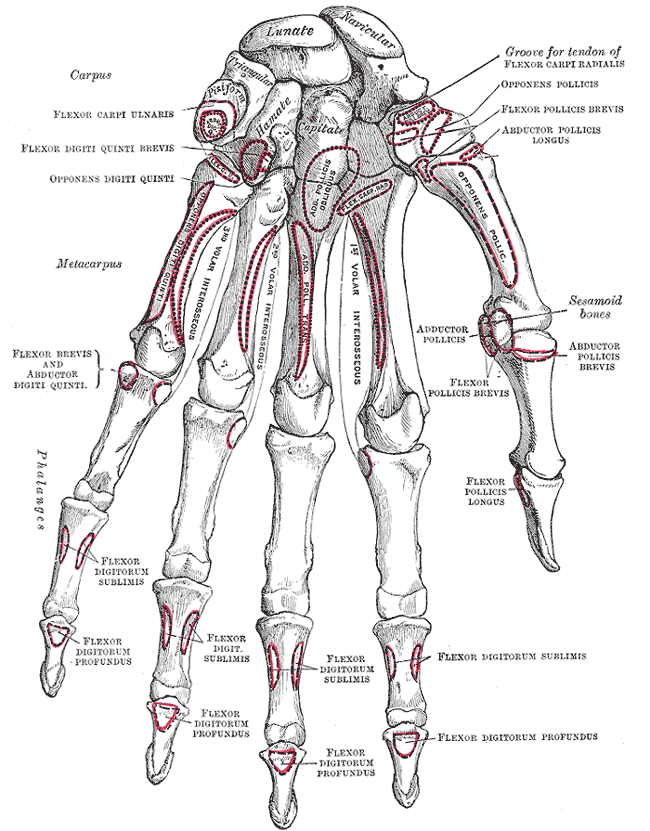
The spine of the scapula or scapular spine is a prominent plate of bone, which crosses obliquely the medial four-fifths of the scapula at its upper part, and separates the supra- from the infraspinatous fossa. Structure It begins at the vertical ertebral or medial borderborder by a smooth, triangular area over which the tendon of insertion of the lower part of the Trapezius glides, and, gradually becoming more elevated, ends in the acromion, which overhangs the shoulder-joint. The spine is triangular, and flattened from above downward, its apex being directed toward the vertebral border. Root The ''root of the spine'' of the scapula is the most medial part of the scapular spine. It is termed "triangular area of the spine of scapula", based on its triangular shape giving it distinguishable visible shape on x-ray images. The root of the spine is on a level with the tip of the spinous process of the third thoracic vertebra.Gray's Anatomy (1918)p.1306/ref> File:Root of spine - l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble. In compound terms, the prefix omo- is used for the shoulder blade in medical terminology. This prefix is derived from ὦμος (ōmos), the Ancient Greek word for shoulder, and is cognate with the Latin , which in Latin signifies either the shoulder or the upper arm bone. The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage. Structure The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: intrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray's Anatomy
''Gray's Anatomy'' is a reference book of human anatomy written by Henry Gray, illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter, and first published in London in 1858. It has gone through multiple revised editions and the current edition, the 42nd (October 2020), remains a standard reference, often considered "the doctors' bible". Earlier editions were called ''Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical'', ''Anatomy of the Human Body'' and ''Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied'', but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, ''Gray's Anatomy''. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject. Publication history Origins The English anatomist Henry Gray was born in 1827. He studied the development of the endocrine glands and spleen and in 1853 was appointed Lecturer on Anatomy at St George's Hospital Medical School in London. In 1855, he approached his colleague Henry Vandyke Carter with his idea to produce an inexpensive and ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Scapular Notch
The great scapular notch (or ''spinoglenoid notch'') is a notch which serves to connect the supraspinous fossa and infraspinous fossa. It lies immediately medial to the attachment of the acromion to the lateral angle of the scapular spine. The Suprascapular artery and suprascapular nerve pass around the great scapular notch anteroposteriorly. Supraspinatus and infraspinatus are both supplied by the suprascapular nerve, which originates from the superior trunk of the brachial plexus (roots C5-C6). Additional images File:Great scapular notch - animation01.gif, Left scapula. Great scapular notch shown in red. File:Great scapular notch - animation04.gif, Animation. Great scapular notch shown in red. See also * Suprascapular notch The suprascapular notch (or ''scapular notch'') is a notch in the superior border of the scapula, just medial to the base of the coracoid process. It forms the entrance site into the suprascapular canal. Structure This notch is converted into ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltoid Muscle
The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle appears to be made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the # anterior or clavicular part (pars clavicularis) # posterior or scapular part (pars scapularis) # intermediate or acromial part (pars acromialis) However, electromyography suggests that it consists of at least seven groups that can be independently coordinated by the nervous system. It was previously called the deltoideus (plural ''deltoidei'') and the name is still used by some anatomists. It is called so because it is in the shape of the Greek capital letter delta (Δ). Deltoid is also further shortened in slang as "delt". A study of 30 shoulders revealed an average mass of in humans, ranging from to . Structure Previous studies showed that the insertions of the tendons of the delto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
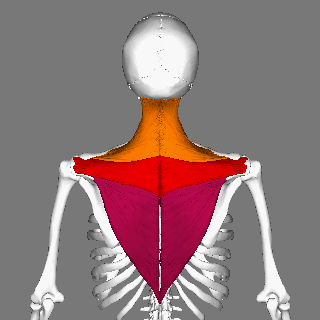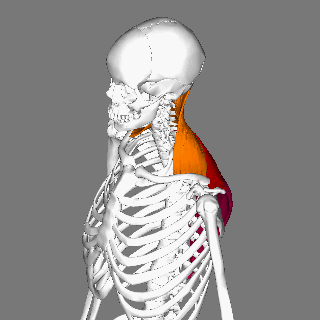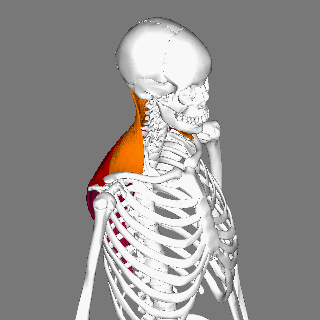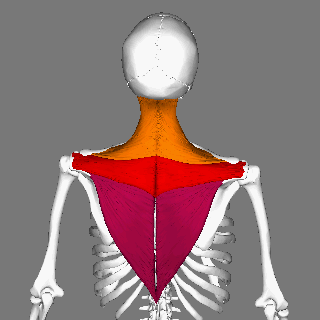
Trapezius Muscle
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the arm. The trapezius has three functional parts: an upper (descending) part which supports the weight of the arm; a middle region (transverse), which retracts the scapula; and a lower (ascending) part which medially rotates and depresses the scapula. Name and history The trapezius muscle resembles a trapezium, also known as a trapezoid, or diamond-shaped quadrilateral. The word "spinotrapezius" refers to the human trapezius, although it is not commonly used in modern texts. In other mammals, it refers to a portion of the analogous muscle. Similarly, the term "tri-axle back plate" was historically used to describe the trapezius muscle. Structure The ''superior'' or ''upper'' (or descending) fibers of the trapezius originate from the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutrient Canal
All bones possess larger or smaller foramina (openings) for the entrance of blood-vessels; these are known as the nutrient foramina, and are particularly large in the shafts of the larger long bones, where they lead into a nutrient canal, which extends into the medullary cavity. The nutrient canal(foramen)is directed away from the growing end of bone. The growing ends of bones in upper limb are upper end of humerus and lower ends of radius and ulna. In lower limb, the lower end of femur and upper end of tibia are the growing ends. The nutrient arteries along with veins pass through this canal. A nutrient canal is found in long bones, in the mandible, and in dental alveoli Dental alveoli (singular ''alveolus'') are sockets in the jaws in which the roots of teeth are held in the alveolar process with the periodontal ligament. The lay term for dental alveoli is tooth sockets. A joint that connects the roots of the t .... In long bones the nutrient canal is found in the shaft. Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infraspinatus Muscle
In human anatomy, the infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa.'' Gray's Anatomy'', see infobox. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspinatus is to externally rotate the humerus and stabilize the shoulder joint. Structure It attaches medially to the infraspinous fossa of the scapula and laterally to the middle facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The muscle arises by fleshy fibers from the medial two-thirds of the infraspinatous fossa, and by tendinous fibers from the ridges on its surface; it also arises from the infraspinatous fascia which covers it, and separates it from the teres major and teres minor. The fibers converge to a tendon, which glides over the lateral border of the spine of the scapula and passing across the posterior part of the capsule of the shoulder-joint, is inserted into the middle impression on the greater tubercle of the humerus. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraspinatus Muscle
The supraspinatus (plural ''supraspinati'') is a relatively small muscle of the upper back that runs from the supraspinous fossa superior portion of the scapula (shoulder blade) to the greater tubercle of the humerus. It is one of the four rotator cuff muscles and also abducts the arm at the shoulder. The spine of the scapula separates the supraspinatus muscle from the infraspinatus muscle, which originates below the spine. Structure The supraspinatus muscle arises from the supraspinous fossa, a shallow depression in the body of the scapula above its spine. The supraspinatus muscle tendon passes laterally beneath the cover of the acromion. Research in 1996 showed that the postero-lateral origin was more lateral than classically described. The supraspinatus tendon is inserted into the superior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The distal attachments of the three rotator cuff muscles that insert into the greater tubercle of the humerus can be abbreviated as SIT when vie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraspinatous Fossa
The supraspinous fossa (supraspinatus fossa, supraspinatous fossa) of the posterior aspect of the scapula (the shoulder blade) is smaller than the infraspinous fossa, concave, smooth, and broader at its vertebral than at its humeral end. Its medial two-thirds give origin to the Supraspinatus. Structure The fossa can be exposed by the removal of skin and the superficial fascia of the back and the trapezius muscle. The supraspinous fossa is bounded by the spine of scapula on the inferior side, acromion process on the lateral side and the superior angle of scapula on the superior side. Supraspinatus muscle originates from the supraspinous fossa. Distal attachment of the levator scapulae muscle is also on the medial aspect of the fossa. Function The suprascapular artery and nerve are found within the fossa. The posterior branch of the suprascapular artery supplies the supraspinatous muscle. Dorsal scapular artery also gives off a collateral branch and anastomoses with the supr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Thoracic Vertebra
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae; they increase in size going towards the lumbar vertebrae, with the lower ones being much larger than the upper. They are distinguished by the presence of facets on the sides of the bodies for articulation with the heads of the ribs, as well as facets on the transverse processes of all, except the eleventh and twelfth, for articulation with the tubercles of the ribs. By convention, the human thoracic vertebrae are numbered T1–T12, with the first one (T1) located closest to the skull and the others going down the spine toward the lumbar region. General characteristics These are the general characteristics of the second through eighth thoracic vertebrae. The first and ninth through twelfth vertebrae contain certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable animal locomotion, mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple Function (biology), functions. Bone tissue (osseous tissue), which is also called bone in the mass noun, uncountable sense of that word, is hard tissue, a type of specialized connective tissue. It has a honeycomb-like matrix (biology), matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity. Bone tissue is made up of different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts and osteocytes are involved in the formation and mineralization (biology), mineralization of bone; osteoclasts are involved in the bone resorption, resor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinous Process
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |