|
Spinal Cord Injuries Australia
Spinal Cord Injuries Australia (SCIA) is a non-government organisation which provides advocacy and services to people with spinal cord injury (paraplegia, quadriplegia) and similar conditions. History SCIA was established in 1967 as the Australian Quadriplegic Association (AQA) by a group of patients in Prince Henry Hospital in Sydney, Australia. They were unable to leave hospital because there was no accommodation or services to support them in the community. AQA was renamed in 2003. Under SCIA's constitution at least 50% of its board of directors must have a spinal cord injury or similar condition. The founding members were Trevor Annetts, Tom Clarke, Graeme Dunne, David Fox, Peter Harris, George Mamo, Jim McGrath, Robert McKenzie, Alan Moore, John Munday, Cecil Murr, Brian Shirt, Paul Sorgo, Stan Wanless, and Warren Mowbray. David Fox was the first president. They were encouraged to set up an organisation by social worker Gary Garrison, supported by Dr George Burniston. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-government Organisation
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent from government. They are typically nonprofit entities, and many of them are active in humanitarianism or the social sciences; they can also include clubs and associations that provide services to their members and others. Surveys indicate that NGOs have a high degree of public trust, which can make them a useful proxy for the concerns of society and stakeholders. However, NGOs can also be lobby groups for corporations, such as the World Economic Forum. NGOs are distinguished from international and intergovernmental organizations (''IOs'') in that the latter are more directly involved with sovereign states and their governments. The term as it is used today was first introduced in Article 71 of the newly-formed United Nations' Charter in 1945. While there is no fixed or formal definition for what NGOs are, they are general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
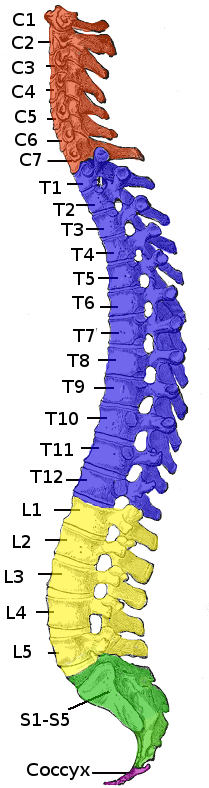
Spinal Cord Injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cord below the level of the injury. Injury can occur at any level of the spinal cord and can be ''complete'', with a total loss of sensation and muscle function at lower sacral segments, or ''incomplete'', meaning some nervous signals are able to travel past the injured area of the cord up to the Sacral S4-5 spinal cord segments. Depending on the location and severity of damage, the symptoms vary, from numbness to paralysis, including bowel or bladder incontinence. Long term outcomes also range widely, from full recovery to permanent tetraplegia (also called quadriplegia) or paraplegia. Complications can include muscle atrophy, loss of voluntary motor control, spasticity, pressure sores, infections, and breathing problems. In the majority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraplegia
Paraplegia, or paraparesis, is an impairment in motor or sensory function of the lower extremities. The word comes from Ionic Greek () "half-stricken". It is usually caused by spinal cord injury or a congenital condition that affects the neural (brain) elements of the spinal canal. The area of the spinal canal that is affected in paraplegia is either the thoracic, lumbar, or sacral regions. If four limbs are affected by paralysis, tetraplegia or quadriplegia is the correct term. If only one limb is affected, the correct term is monoplegia. Spastic paraplegia is a form of paraplegia defined by spasticity of the affected muscles, rather than flaccid paralysis. The American Spinal Injury Association classifies spinal cord injury severity in the following manner. ASIA A is the complete loss of sensory function and motor skills below the injury. ASIA B is having some sensory function below the injury, but no motor function. In ASIA C, there is some motor function below the level of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Henry Hospital
The Prince Henry Hospital site, formerly known as the Prince Henry Hospital, Sydney, is a heritage-listed former teaching hospital and infectious diseases hospital and now University of New South Wales, UNSW teaching hospital and rehabilitation in spinal cord injury, spinal rehabilitation unit located at 1430 Anzac Parade, Sydney, Anzac Parade, Little Bay, New South Wales, Little Bay, City of Randwick, New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by NSW New South Wales Government Architect, NSW Colonial Architect and NSW Government Architect and built from 1881 by NSW Public Works Department. It is also known as Prince Henry Hospital and The Coast Hospital. The property is owned by Landcom, an government agency, agency of the Government of New South Wales. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 May 2003. History Aboriginal historical context The greater Sydney region has been inhabited by Aboriginal people for at least 20,000 years with dated sheltere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountains to the west, Hawkesbury to the north, the Royal National Park to the south and Macarthur to the south-west. Sydney is made up of 658 suburbs, spread across 33 local government areas. Residents of the city are known as "Sydneysiders". The 2021 census recorded the population of Greater Sydney as 5,231,150, meaning the city is home to approximately 66% of the state's population. Estimated resident population, 30 June 2017. Nicknames of the city include the 'Emerald City' and the 'Harbour City'. Aboriginal Australians have inhabited the Greater Sydney region for at least 30,000 years, and Aboriginal engravings and cultural sites are common throughout Greater Sydney. The traditional custodians of the land on which modern Sydney stands are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a Megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with Deserts of Australia, deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approximately Early human migrations#Nearby Oceania, 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Worker
Social work is an academic discipline and practice-based profession concerned with meeting the basic needs of individuals, families, groups, communities, and society as a whole to enhance their individual and collective well-being. Social work practice draws from areas, such as psychology, sociology, health, political science, community development, law, and economics to engage with systems and policies, conduct assessments, develop interventions, and enhance social functioning and responsibility. The ultimate goal of social work is the improvement of people's lives and the achievement of social justice. Social work practice is often divided into three levels. Micro-work involves working directly with individuals and families, such as providing individual counseling/therapy or assisting a family in accessing services. Mezzo-work involves working with groups and communities, such as conducting group therapy or providing services for community agencies. Macro-work involves fost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Burniston
George Garrett Burniston (23 November 1914 – 27 June 1992) was an Australian physician who specialised in rehabilitation medicine. He had a long association with Prince of Wales Hospital in Sydney and the University of New South Wales, having earlier worked as a public servant with the Department of Post-War Reconstruction and Department of Social Services. Early life Burniston was born on 23 November 1914 in Campsie, New South Wales. He was the son of Daisy Belle (née Boxwell) and George Benjamin Burniston; his father was a butcher. He attended Summer Hill Intermediate High School and Sydney Boys' High School. He matriculated to the University of Sydney in 1933, graduating MBBS in 1939. Medical career Burniston began his career as a resident at Hornsby District Hospital. He joined the medical branch of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) in 1940 and was soon seconded to the Royal Air Force's orthopaedic service in England, working under Reginald Watson-Jones and Henry O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coogee, New South Wales
Coogee is a beachside suburb of local government area City of Randwick 8 kilometres south-east of the Sydney central business district, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It is typically associated as being part of the Eastern Suburbs region. The Tasman Sea and Coogee Bay along with Coogee Beach lie towards the eastern side of the suburb. The boundaries of Coogee are formed mainly by Clovelly Road, Carrington Road and Rainbow Street, with arbitrary lines drawn to join these thoroughfares to the coast in the north-east and south-east corners. History Aboriginal The name Coogee is said to be taken from a local Aboriginal word ''koojah'' which means "smelly place". Another version is ''koo-chai'' or ''koo-jah'', both of which mean "the smell of the seaweed drying" in the Bidigal language, or "stinking seaweed", a reference to the smell of decaying kelp washed up on the beach. Early visitors to the area, from the 1820s onwards, were never able to confirm exactl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maroubra, New South Wales
Maroubra is a beachside suburb in the Eastern Suburbs of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It is 10 kilometres south-east of the Sydney central business district in the local government area of the City of Randwick. Maroubra is the largest suburb within Randwick City Council by both area and population;. Maroubra Junction is a locality in the centre of the suburb. History 1800s Maroubra is a local Aboriginal word meaning ''place of thunder''. In 1861, the first house was built in the area by Humphrey McKeon. A number of other settlers arrived on the land in the 1870s to work on the wool scouring works located at the northern end of the bay. ''The Hereward'' The suburb first made headlines on 6 May 1898, when the ''Hereward'', a fully rigged iron ship weighing 1,513 tons was caught by the gale-force winds and shipwrecked at the northern end of Maroubra Beach while heading north toward Newcastle. The shipwreck remained on the beach for a number of years unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Housing
Public housing is a form of housing tenure in which the property is usually owned by a government authority, either central or local. Although the common goal of public housing is to provide affordable housing, the details, terminology, definitions of poverty, and other criteria for allocation vary within different contexts. Public housing developments are classified as housing projects that are owned by a city's Housing authority or Federally subsidized public housing operated through HUD. Social housing is any rental housing that may be owned and managed by the state, by non-profit organizations, or by a combination of the two, usually with the aim of providing affordable housing. Social housing is generally rationed by a government through some form of means-testing or through administrative measures of housing need. One can regard social housing as a potential remedy for housing inequality. Private housing is a form of housing tenure in which the property is owned by an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |