|
Spin Density Wave
Spin-density wave (SDW) and charge-density wave (CDW) are names for two similar low-energy ordered states of solids. Both these states occur at low temperature in anisotropic, low-dimensional materials or in metals that have high densities of states at the Fermi level N(E_F). Other low-temperature ground states that occur in such materials are superconductivity, ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism. The transition to the ordered states is driven by the condensation energy which is approximately N(E_F) \Delta^2 where \Delta is the magnitude of the energy gap opened by the transition. Fundamentally SDWs and CDWs involve the development of a superstructure in the form of a periodic modulation in the density of the electronic spins and charges with a characteristic spatial frequency q that does not transform according to the symmetry group that describes the ionic positions. The new periodicity associated with CDWs can easily be observed using scanning tunneling microscopy or elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-density Wave
A charge density wave (CDW) is an ordered quantum fluid of electrons in a linear chain compound or layered crystal. The electrons within a CDW form a standing wave pattern and sometimes collectively carry an electric current. The electrons in such a CDW, like those in a superconductor, can flow through a linear chain compound en masse, in a highly correlated fashion. Unlike a superconductor, however, the electric CDW current often flows in a jerky fashion, much like water dripping from a faucet, due to its electrostatic properties. In a CDW, the combined effects of pinning (due to impurities) and electrostatic interactions (due to the net electric charges of any CDW kinks) likely play critical roles in the CDW current's jerky behavior, as discussed in sections 4 & 5 below. Most CDW's in metallic crystals form due to the wave-like nature of electrons – a manifestation of quantum mechanical wave–particle duality – causing the electronic charge density to become spatially mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi Surface
In condensed matter physics, the Fermi surface is the surface in reciprocal space which separates occupied electron states from unoccupied electron states at zero temperature. The shape of the Fermi surface is derived from the periodicity and symmetry of the crystalline lattice and from the occupation of electronic band structure, electronic energy bands. The existence of a Fermi surface is a direct consequence of the Pauli exclusion principle, which allows a maximum of one electron per quantum state. The study of the Fermi surfaces of materials is called fermiology. Theory Consider a Spin (physics), spin-less ideal Fermi gas of N particles. According to Fermi–Dirac statistics, the mean occupation number of a state with energy \epsilon_i is given by : \langle n_i\rangle =\frac, where * \left\langle n_i\right\rangle is the mean occupation number of the ith state * \epsilon_i is the kinetic energy of the ith state * \mu is the chemical potential (at zero temperature, this is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohm's Law
Ohm's law states that the electric current through a Electrical conductor, conductor between two Node (circuits), points is directly Proportionality (mathematics), proportional to the voltage across the two points. Introducing the constant of proportionality, the Electrical resistance, resistance, one arrives at the three mathematical equations used to describe this relationship: V = IR \quad \text\quad I = \frac \quad \text\quad R = \frac where is the current through the conductor, ''V'' is the voltage measured across the conductor and ''R'' is the electrical resistance, resistance of the conductor. More specifically, Ohm's law states that the ''R'' in this relation is constant, independent of the current. If the resistance is not constant, the previous equation cannot be called ''Ohm's law'', but it can still be used as a definition of Electrical resistance and conductance#Static and differential resistance, static/DC resistance. Ohm's law is an empirical law, empirical rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Domain
A magnetic domain is a region within a magnetic material in which the magnetization is in a uniform direction. This means that the individual magnetic moments of the atoms are aligned with one another and they point in the same direction. When cooled below a temperature called the Curie temperature, the magnetization of a piece of ferromagnetic material spontaneously divides into many small regions called magnetic domains. The magnetization within each domain points in a uniform direction, but the magnetization of different domains may point in different directions. Magnetic domain structure is responsible for the magnetic behavior of ferromagnetic materials like iron, nickel, cobalt and their alloys, and ferrimagnetic materials like Ferrite (magnet), ferrite. This includes the formation of permanent magnets and the attraction of ferromagnetic materials to a magnetic field. The regions separating magnetic domains are called Domain wall (magnetism), domain walls, where the mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dislocations
In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to slide over each other at low stress levels and is known as ''glide'' or Slip (materials science), slip. The crystalline order is restored on either side of a ''glide dislocation'' but the atoms on one side have moved by one position. The crystalline order is not fully restored with a ''partial dislocation''. A dislocation defines the boundary between ''slipped'' and ''unslipped'' regions of material and as a result, must either form a complete loop, intersect other dislocations or defects, or extend to the edges of the crystal. A dislocation can be characterised by the distance and direction of movement it causes to atoms which is defined by the Burgers vector. Plasticity (physics), Plastic deformation of a material occurs by the creation and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of the state of a system on its history. For example, a magnet may have more than one possible magnetic moment in a given magnetic field, depending on how the field changed in the past. Plots of a single component of the moment often form a loop or hysteresis curve, where there are different values of one variable depending on the direction of change of another variable. This history dependence is the basis of memory in a hard disk drive and the remanence that retains a record of the Earth's magnetic field magnitude in the past. Hysteresis occurs in ferromagnetic and ferroelectricity, ferroelectric materials, as well as in the deformation (mechanics), deformation of rubber bands and shape-memory alloys and many other natural phenomena. In natural systems, it is often associated with irreversible process, irreversible thermodynamic change such as phase transitions and with internal friction; and dissipation is a common side effect. Hysteresis can be fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Reconstruction
Surface reconstruction refers to the process by which atoms at the surface of a crystal assume a different structure than that of the bulk. Surface reconstructions are important in that they help in the understanding of surface chemistry for various materials, especially in the case where another material is Adsorption, adsorbed onto the surface. Basic principles In an ideal infinite crystal, the equilibrium position of each individual atom is determined by the forces exerted by all the other atoms in the crystal, resulting in a periodic structure. If a surface is introduced to the surroundings by terminating the crystal along a given plane, then these forces are altered, changing the equilibrium positions of the remaining atoms. This is most noticeable for the atoms at or near the surface plane, as they now only experience inter-atomic forces from one direction. This imbalance results in the atoms near the surface assuming positions with different spacing and/or symmetry from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
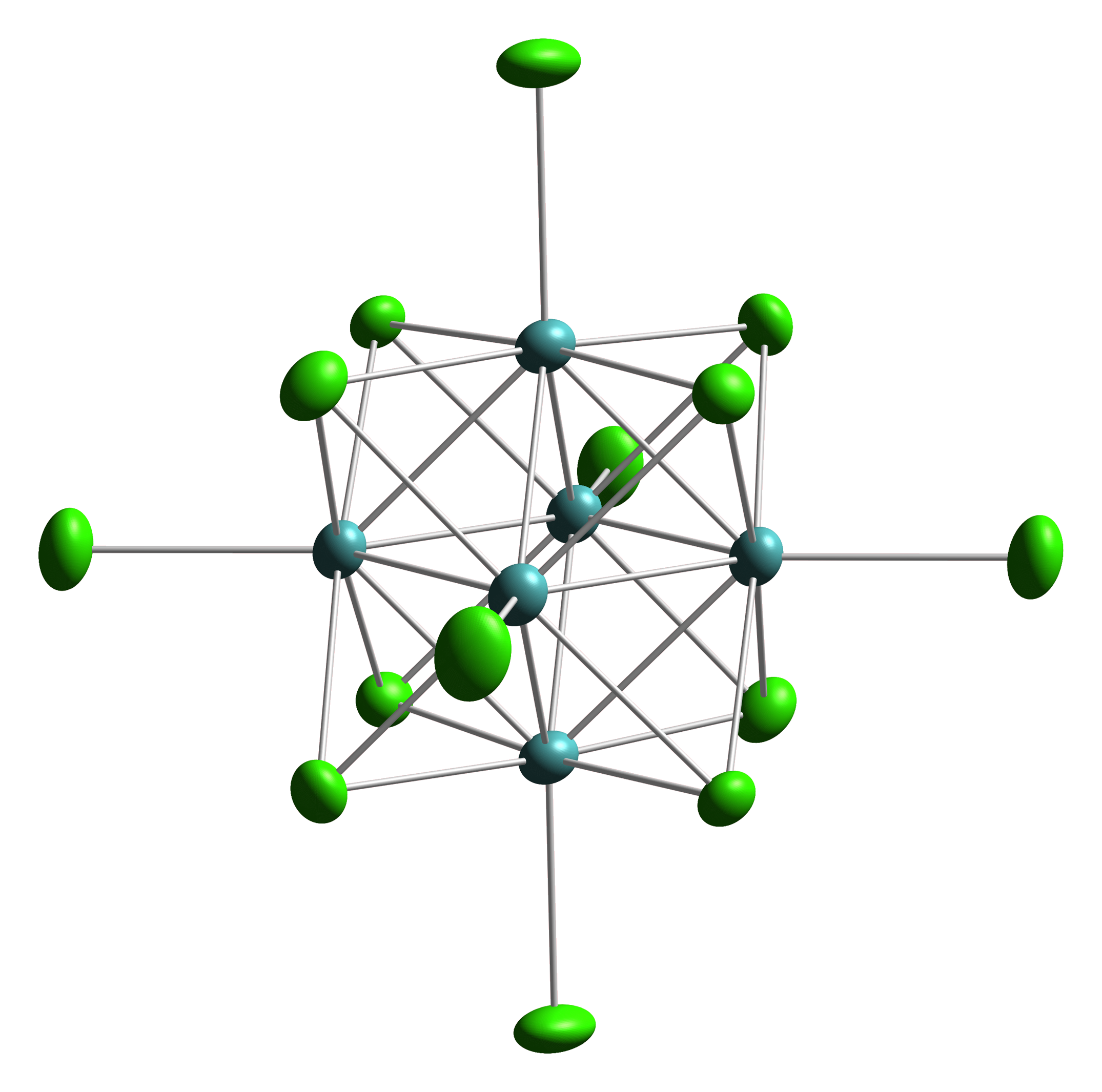
Chevrel Phase
Octahedral clusters are inorganic or organometallic cluster compounds composed of six metals in an octahedral array.Eric J. Welch and Jeffrey R. Long ''Atomlike Building Units of Adjustable Character: Solid-State and Solution Routes to Manipulating Hexanuclear Transition Metal Chalcohalide Clusters'' in Progress in Inorganic Chemistry, Volume 54 Kenneth D. Karlin 2005''Link/ref> Many types of compounds are known, but all are synthetic. Octahedral chalcogenide and halide clusters These compounds are bound together by metal-metal bonding as well as two kinds of ligands. Ligands that span the faces or edges of the M6 core are labeled Li, for ''inner'' (innen in the original German description), and those ligands attached only to one metal are labeled outer, or La for ''ausser''. Typically, the outer ligands can be exchanged whereas the bridging ligands are more inert toward substitution. Face-capped halide clusters The premier example is of the class is Mo6Cl142−. This dianion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University
The University of Oxford is a collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the second-oldest continuously operating university globally. It expanded rapidly from 1167, when Henry II prohibited English students from attending the University of Paris. When disputes erupted between students and the Oxford townspeople, some Oxford academics fled northeast to Cambridge, where they established the University of Cambridge in 1209. The two English ancient universities share many common features and are jointly referred to as ''Oxbridge''. The University of Oxford comprises 43 constituent colleges, consisting of 36 semi-autonomous colleges, four permanent private halls and three societies (colleges that are departments of the university, without their own royal charter). and a range of academic departments that are organised into four divisions. Each college ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Peierls
Sir Rudolf Ernst Peierls, (; ; 5 June 1907 – 19 September 1995) was a German-born British physicist who played a major role in Tube Alloys, Britain's nuclear weapon programme, as well as the subsequent Manhattan Project, the combined Allied nuclear bomb programme. His 1996 obituary in ''Physics Today'' described him as "a major player in the drama of the eruption of nuclear physics into world affairs". Peierls studied physics at the University of Berlin, at the University of Munich under Arnold Sommerfeld, the University of Leipzig under Werner Heisenberg, and ETH Zurich under Wolfgang Pauli. After receiving his DPhil from Leipzig in 1929, he became an assistant to Pauli in Zurich. In 1932, he was awarded a Rockefeller Fellowship, which he used to study in Rome under Enrico Fermi, and then at the Cavendish Laboratory at the University of Cambridge under Ralph H. Fowler. Because of his Jewish background, he elected to not return home after Adolf Hitler's rise to power in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purdue
Purdue University is a public land-grant research university in West Lafayette, Indiana, United States, and the flagship campus of the Purdue University system. The university was founded in 1869 after Lafayette businessman John Purdue donated land and money to establish a college of science, technology, and agriculture; the first classes were held on September 16, 1874. Purdue University is a member of the Association of American Universities and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". Purdue enrolls the largest student body of any individual university campus in Indiana, as well as the ninth-largest foreign student population of any university in the United States. The university is home to the oldest computer science program in the United States. Purdue is the founding member of the Big Ten Conference and sponsors 18 intercollegiate sports teams. It has been affiliated with 13 Nobel laureates, 1 Turing Award laureate, 1 Bharat Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Overhauser
Albert W. Overhauser (August 17, 1925 – December 10, 2011) was an American physicist and a member of the National Academy of Sciences. He is best known for his theory of the Overhauser effect in nuclear magnetic resonance. The Overhauser effect was the first example of dynamic nuclear polarization whereby spin polarization is transferred from unpaired electrons in paramagnetic metals to nuclei resulting in a dramatic increase in their NMR intensity. The Nuclear Overhauser Effect, which follows the same mechanism, is also widely used in nuclear magnetic resonance and formed the basis for early protein structure determinations, for which Kurt Wüthrich was ultimately awarded the Nobel prize in Chemistry. Life Born in San Diego, California, Overhauser attended high school in San Francisco at Lick-Wilmerding High School and began his undergraduate work at the University of California, Berkeley in 1942. He interrupted his studies during World War II for a two-year stint in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |