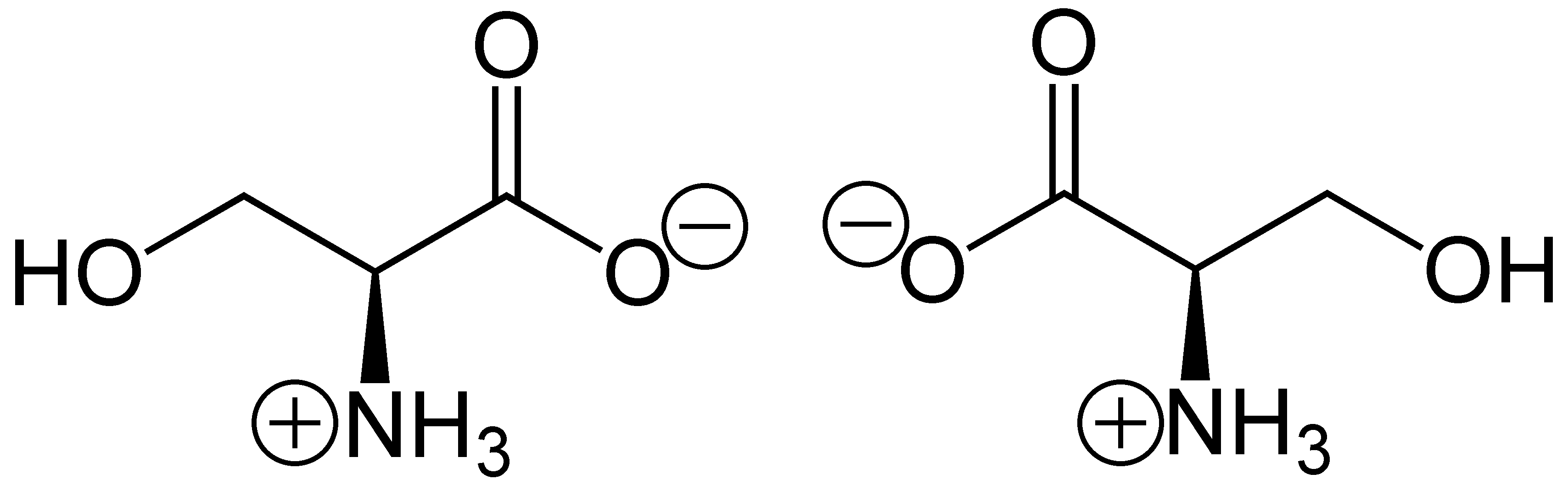|
Sphingosine Structure
Sphingosine (2-amino-4-trans-octadecene-1,3-diol) is an 18-carbon amino alcohol with an unsaturated hydrocarbon chain, which forms a primary part of sphingolipids, a class of cell membrane lipids that include sphingomyelin, an important phospholipid. Functions Sphingosine can be phosphorylated in vivo via two kinases, sphingosine kinase type 1 and sphingosine kinase type 2. This leads to the formation of sphingosine-1-phosphate, a potent signaling lipid. Sphingolipid metabolites, such as ceramides, sphingosine and sphingosine-1-phosphate, are lipid signaling molecules involved in diverse cellular processes. Biosynthesis Sphingosine is synthesized from palmitoyl CoA and serine in a condensation required to yield dihydrosphingosine. Dehydrosphingosine is then reduced by NADPH to dihydrosphingosine (sphinganine), acylated to dihydroceramide finally oxidized by FAD to ceramide. Sphingosine is then solely formed via degradation of sphingolipid in the lysosome. See also * D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Alcohol
In organic chemistry, alkanolamines are organic compounds that contain both hydroxyl () and amino (, , and ) functional groups on an alkane backbone. The term alkanolamine is a broad class term that is sometimes used as a subclassification. Methanolamine.svg, methanolamine, an intermediate in the reaction of ammonia with formaldehyde Ethanolamine.png, Ethanolamine 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol.svg, 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol is a precursor to oxazolines valinol.svg, valinol is derived from the amino acid valine Sphingosine structure.svg, Sphingosine is a component of some cell membrane. 1-Aminoalcohols 1-Aminoalcohols are better known as hemiaminals. Methanolamine is the simplest member. 2-Aminoalcohols Key members: ethanolamine, dimethylethanolamine, ''N''-methylethanolamine, Aminomethyl propanol Two popular drugs, often called alkanolamine beta blockers, are members of this structural class: propranolol, pindolol. Isoetarine is yet another medicinally useful derivative o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmitoyl CoA
Palmitoyl-CoA is an acyl-CoA thioester. It is an "activated" form of palmitic acid and can be transported into the mitochondrial matrix by the carnitine shuttle system (which transports fatty acyl-CoA molecules into the mitochondria), and once inside can participate in beta-oxidation. Alternatively, palmitoyl-CoA is used as a substrate in the biosynthesis of sphingosine (this biosynthetic pathway does not require transfer into the mitochondria). Biosynthesis Palmitoyl CoA formed from palmitic acid, in the reaction below. Palmitate + CoA-SH + ATP -> Palmitoyl-CoA + AMP + Pyrophosphate This reaction is often referred to as the "activation" of a fatty acid. The activation is catalyzed by palmitoyl-coenzyme A synthetase and the reaction proceeds through a two step mechanism, in which palmitoyl-AMP is an intermediate. The reaction is driven to completion by the exergonic hydrolysis of pyrophosphate. The activation of fatty acids occurs in the cytosol and beta-oxidation occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diols
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups ( groups). An aliphatic diol is also called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified. The most common industrial diol is ethylene glycol. Examples of diols in which the hydroxyl functional groups are more widely separated include 1,4-butanediol and propylene-1,3-diol, or beta propylene glycol, . Synthesis of classes of diols Geminal diols A geminal diol has two hydroxyl groups bonded to the same atom. These species arise by hydration of the carbonyl compounds. The hydration is usually unfavorable, but a notable exception is formaldehyde which, in water, exists in equilibrium with methanediol H2C(OH)2. Another example is (F3C)2C(OH)2, the hydrated form of hexafluoroacetone. Many gem-diols undergo further condensation to give dimeric and oligomeric derivatives. This reaction applies to glyoxal and related aldehydes. Vicinal diols In a vicinal diol, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomolecules
A biomolecule or biological molecule is a loosely used term for molecules present in organisms that are essential to one or more typically biological processes, such as cell division, morphogenesis, or development. Biomolecules include large macromolecules (or polyelectrolytes) such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids, as well as small molecules such as primary metabolites, secondary metabolites and natural products. A more general name for this class of material is biological materials. Biomolecules are an important element of living organisms, those biomolecules are often endogenous, produced within the organism but organisms usually need exogenous biomolecules, for example certain nutrients, to survive. Biology and its subfields of biochemistry and molecular biology study biomolecules and their reactions. Most biomolecules are organic compounds, and just four elements—oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen—make up 96% of the human body's mass. But ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochem J
The ''Biochemical Journal'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal which covers all aspects of biochemistry, as well as cell and molecular biology. It is published by Portland Press and was established in 1906. History The journal was established in 1906 by Benjamin Moore, holder of the first UK chair of biochemistry at the University of Liverpool, with financial support from Edward Whitley, an heir of the Greenall Whitley brewers.Clark J. Biochemical Journal Centenary (2006) (accessed 30 September 2007) The two served as the first editors and the journal was initially published by the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fingolimod
Fingolimod, sold under the brand name Gilenya, is an immunomodulating medication, mostly used for treating multiple sclerosis (MS). Fingolimod is a sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator, which sequesters lymphocytes in lymph nodes, preventing them from contributing to an autoimmune reaction. It has been reported to reduce the rate of relapses in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis by approximately one-half over a two-year period. Medical uses Fingolimod is used in the treatment of the relapsing form of multiple sclerosis. Its effect in those with primary progressive MS is not clear. It may also be used in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Adverse effects The most common side effects of fingolimod have been head colds, headache, increased gamma-glutamyl transfer (≤15%), diarrhea (13%), nausea (13%), abdominal pain (11%) and fatigue. A few cases of skin cancer have been reported, which has also been reported in patients taking natalizumab (Tysabri), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylsphingosine
''N'',''N''-Dimethylsphingosine (also known as DMS) is an inhibitor of sphingosine kinase. In rats with neuropathic pain, the natural metabolite DMS is unregulated in the dorsal horn. Furthermore, DMS induces mechanical hypersensitivity when injected into rats. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Dimethylsphingosine, N,N- Diols Lipids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide
Flavin may refer to: Placename * Flavin, Aveyron, a commune in southern France Surname * Adrian Flavin (born 1979), a professional rugby player * Christopher Flavin, president of the Worldwatch Institute * Dan Flavin (1933–1996), a minimalist artist famous for using fluorescent light fixtures * Dan Flavin (politician), Louisiana politician * James Flavin (1906–1976), an American character actor * Jennifer Flavin (born 1968), a former model and wife of actor Sylvester Stallone * Martin Flavin (1883–1967), an American playwright and novelist * Martin Flavin (politician) (1841–1917), Irish Nationalist politician, Member of Parliament (MP) for Cork, 1891–1892 * Michael Joseph Flavin (1866-1944), Irish Nationalist politician, Member of Parliament (MP) for North Kerry, 1896-1918 * Mick Flavin, an Irish country singer Biochemistry * Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), a redox cofactor * Flavin-containing amine oxidoreductase, a family of amine oxidases * Flavin-containing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydrosphingosine
Safingol is a lyso-sphingolipid protein kinase inhibitor. It has the molecular formula C18H39NO2 and is a colorless solid. Medicinally, safingol has demonstrated promising anticancer potential as a modulator of multi-drug resistance and as an inducer of necrosis. The administration of safingol alone has not been shown to exert a significant effect on tumor cell growth.Schwartz, G. K., Haimovitz-Friedman, A., Dhupar, S. K., Ehleiter, D., Maslak, P., Lai, L., ... & Albino, A. P. (1995). Potentiation of apoptosis by treatment with the protein kinase C-specific inhibitor safingol in mitomycin C-treated gastric cancer cells. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 87(18), 1394-1399. However, preclinical and clinical studies have shown that combining safingol with conventional chemotherapy agents such as fenretinide, vinblastine, irinotecan and mitomycin C can dramatically potentiate their antitumor effects. Currently in Phase I clinical trials, it is believed to be safe to co-admin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent ('hydrogen source'). It is used by all forms of cellular life. NADPH is the reduced form of NADP. NADP differs from NAD by the presence of an additional phosphate group on the 2' position of the ribose ring that carries the adenine moiety. This extra phosphate is added by NAD+ kinase and removed by NADP+ phosphatase. Biosynthesis NADP In general, NADP+ is synthesized before NADPH is. Such a reaction usually starts with NAD+ from either the de-novo or the salvage pathway, with NAD+ kinase adding the extra phosphate group. ADP-ribosyl cyclase allows for synthesis from nicotinamide in the salvage pathway, and NADP+ phosphatase can convert NADPH back to NADH to maintain a balance. Some forms of the NAD+ kinas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphingosine Synthesis Corrected
Sphingosine (2-amino-4-trans-octadecene-1,3-diol) is an 18-carbon amino alcohol with an unsaturated hydrocarbon chain, which forms a primary part of sphingolipids, a class of cell membrane lipids that include sphingomyelin, an important phospholipid. Functions Sphingosine can be phosphorylated in vivo via two kinases, sphingosine kinase type 1 and sphingosine kinase type 2. This leads to the formation of sphingosine-1-phosphate, a potent signaling lipid. Sphingolipid metabolites, such as ceramides, sphingosine and sphingosine-1-phosphate, are lipid signaling molecules involved in diverse cellular processes. Biosynthesis Sphingosine is synthesized from palmitoyl CoA and serine in a condensation required to yield dihydrosphingosine. Dehydrosphingosine is then reduced by NADPH to dihydrosphingosine (sphinganine), acylated to dihydroceramide finally oxidized by FAD to ceramide. Sphingosine is then solely formed via degradation of sphingolipid in the lysosome. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the naturally occurring proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L-stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, ''sericum''. Serine's structure was estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |