|
Speed Of The Wind
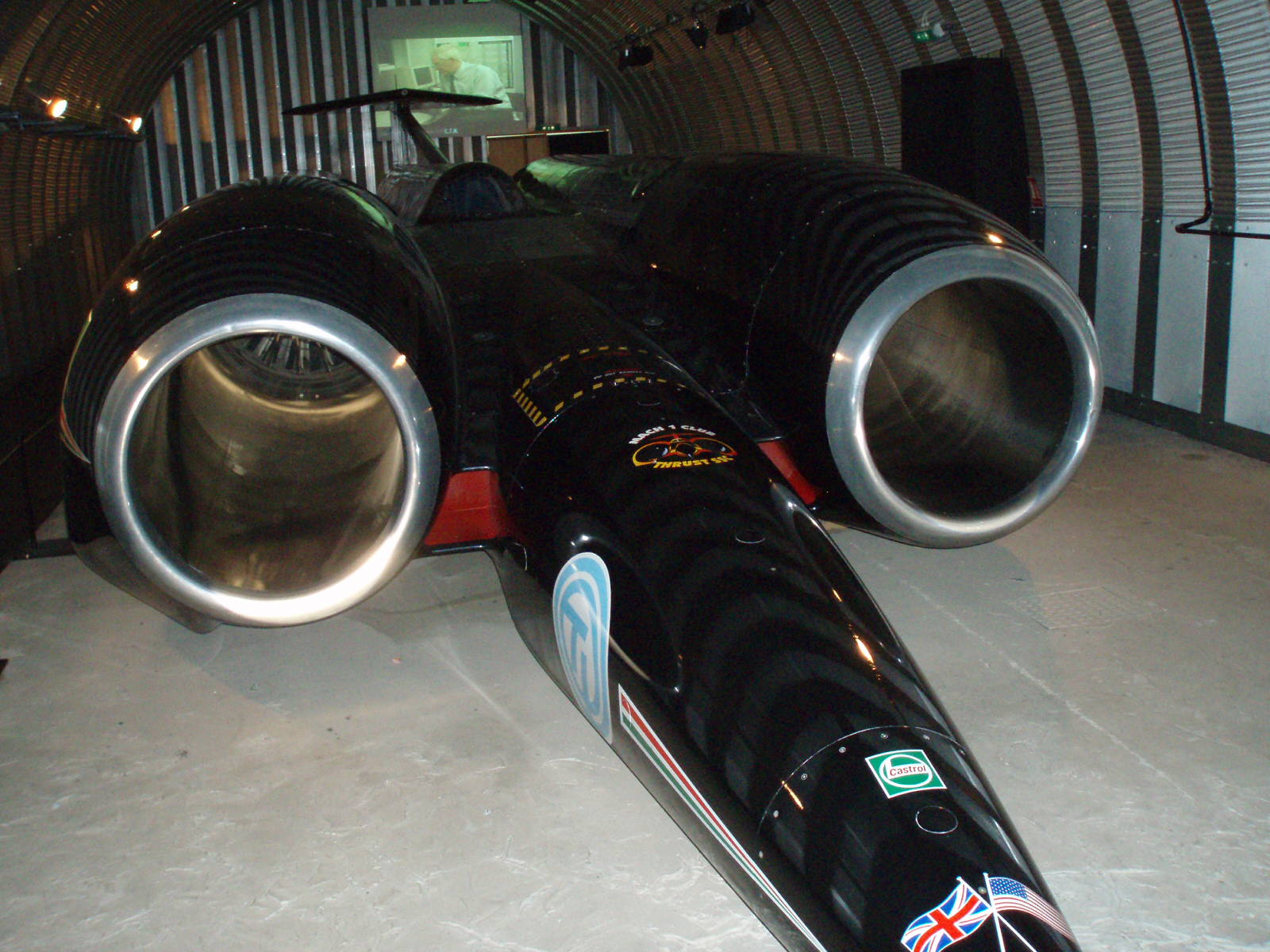
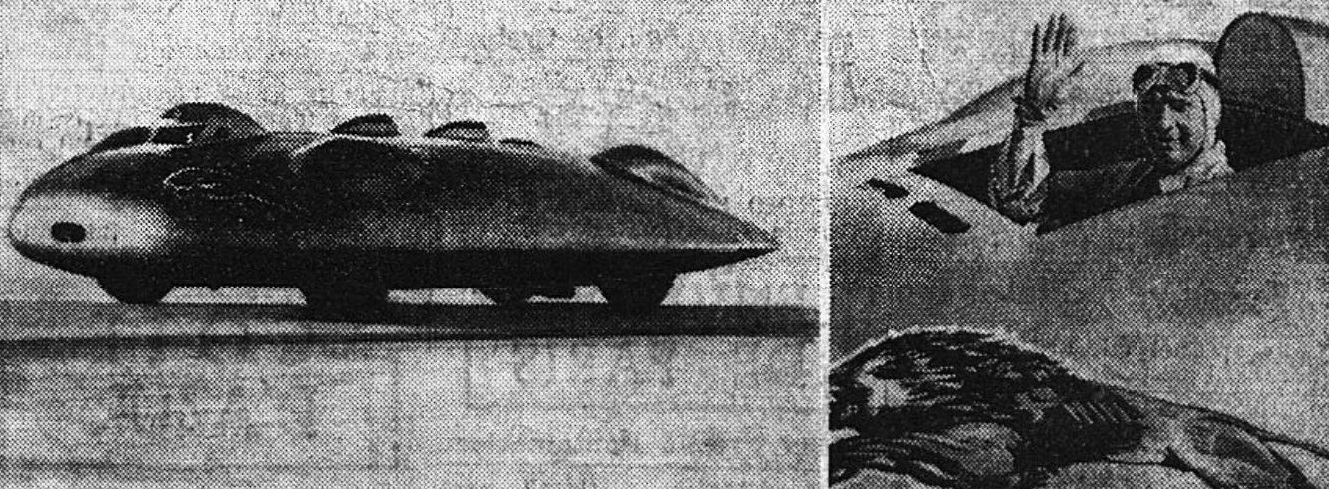
Speed of the Wind was a record-breaking car of the 1930s, built for and driven by Captain George Eyston. The car was designed by Eyston and E A D Eldridge, then built by the father of Tom Delaney (racing driver), Tom Delaney It was powered by an unsupercharged version of the V-12 Rolls-Royce Kestrel aero engine. The car was too large and heavy for circuit racing and was already underpowered by the standards of the absolute speed record breakers. This car was designed for ''endurance'', more than peak power. Running a supercharged engine with the fuel and materials technology of the day would never have lasted the duration. This particular engine was obtained second-hand from Rolls-Royce Limited, Rolls-Royce, where it had previously powered an airflow fan in an engine test cell. Having always been intended for long-term use at ground level, it had been built without the Kestrel's usual supercharger. For streamlining, distinctive features of the car are the two small "nostrils", he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Speed Record
The land speed record (or absolute land speed record) is the highest speed achieved by a person using a vehicle on land. There is no single body for validation and regulation; in practice the Category C ("Special Vehicles") flying start regulations are used, officiated by regional or national organizations under the auspices of the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The land speed record (LSR) is standardized as the speed over a course of fixed length, averaged over two runs (commonly called "passes"). Two runs are required in opposite directions within one hour, and a new record mark must exceed the previous one by at least one percent to be validated. History The first regulator was the ''Automobile Club de France'', which proclaimed itself arbiter of the record in about 1902. Until 1903, trains held the land speed record for fastest vehicles in which people could travel. Different clubs had different standards and did not always recognize the same wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mormon Meteor
The ''Mormon Meteor I'' and ''III'' were two land speed record cars built in the 1930s by Ab Jenkins. Duesenberg Special The ''Duesenberg Special'' was a one-off speed record car. It was built in 1935 on a supercharged Duesenberg Model J rolling chassis with a standard wheelbase of , a dropped front axle, wheels instead of the standard wheels, and a non-standard 3:1 rear axle ratio. The engine was highly tuned by August Duesenberg, with the compression ratio raised to 7.5:1 and different engine bearings being used. High performance parts developed for the Special, especially the "ram's horn" twin-carburetor inlet manifold, would be used on later supercharged Js (or "SJ"s as they were called by the public). Financing for the Duesenberg Special came from sponsorship solicited by Ab Jenkins from oil companies and accessory manufacturers and distributors. Jenkins guaranteed his sponsors that he would break established speed records with the car. He delivered on his guarantee in O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinky Toys
Dinky Toys was the brand name for a range of die-cast toy, die-cast zamak zinc alloy scale model model car, vehicles produced by British toy company Meccano Ltd. They were made in England from 1934 to 1979, at a factory in Binns Road in Liverpool. Dinky Toys were among the most popular die-cast vehicles ever made – pre-dating other popular die-cast marques, including Corgi Toys, Corgi, Matchbox (brand), Matchbox and Mattel's Hot Wheels. Vehicles commercialised under the "Dinky" name include model car, cars, model commercial vehicle, trucks, model aircraft, aircraft, model military vehicle, military, model ship, ships. Pre-war history Frank Hornby established Meccano Ltd. in 1908 to make metal construction sets. The company later moved into model railways, with its O scale, O gauge clockwork trains appearing in 1920. In the early 1930s, Meccano made many types of tinplate and other metal cars, such as its Morgan and Birmingham Small Arms Company, BSA three-wheelers, mostl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of The Wind Dinky Toy 23E
In everyday use and in kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a scalar quantity. The average speed of an object in an interval of time is the distance travelled by the object divided by the duration of the interval; the instantaneous speed is the limit of the average speed as the duration of the time interval approaches zero. Speed is not the same as velocity. Speed has the dimensions of distance divided by time. The SI unit of speed is the metre per second (m/s), but the most common unit of speed in everyday usage is the kilometre per hour (km/h) or, in the US and the UK, miles per hour (mph). For air and marine travel, the knot is commonly used. The fastest possible speed at which energy or information can travel, according to special relativity, is the speed of light in a vacuum ''c'' = metres per second (approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marriott Library
The J. Willard Marriott Library is the main academic library of the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, Utah. The university library has had multiple homes since the first University of Utah librarian was appointed in 1850. The current building was opened in 1968 and named for J. Willard Marriott, founder of Marriott International, in 1969. After two major renovations, the building is more than and houses more than 4.5 million volumes. The University of Utah Press and Red Butte Press are divisions of the Marriott Library. History The first University of Utah librarian was appointed in 1850, the same year the school was founded. University president John R. Park opened a library and reading room stocked with his personal collection of books on loan to the university in 1874. The library moved to the LeRoy Cowles Building in 1900 and the George Thomas Library Building in 1935, both on Presidents Circle. The current five-story building was opened in 1968 and was named for J. Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napier-Railton
The Napier-Railton is an aero-engined racing car built in 1933, designed by Reid Railton to a commission by John Cobb, and built by Thomson & Taylor. It was driven by Cobb, mainly at the Brooklands race track where it holds the all-time lap record () which was set in 1935. The circuit was appropriated for military purposes during the Second World War, and never reopened in that form for racing. It has a W12 engine with 3 different exhaust systems. History Between 1933 and 1937, the Napier-Railton broke 47 world speed records at Brooklands, Autodrome de Linas-Montlhéry and Bonneville Salt Flats in Utah. (photo of the Napier-Railton at Bonneville) The car is powered by the high compression version (6.1:1) (RAF specification) of the naturally aspirated Napier Lion, a W12 of capacity, producing at 2585 revolutions per minute (recorded at 5,000ft - performance at ground level may be different), and of torque. The 12 cylinders are in three banks of four (broad-arrow configura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Cobb (motorist)
John Rhodes Cobb (2 December 1899 – 29 September 1952) was an early to mid 20th century English racing motorist. He was three times holder of the World Land Speed Record, in 1938, 1939 and 1947, set at Bonneville Speedway in Utah, US. He was awarded the Segrave Trophy in 1947. He was killed in 1952 whilst piloting a jet powered speedboat attempting to break the World Water Speed Record on Loch Ness water in Scotland. Early life Cobb was born in Esher, Surrey, on 2 December 1899, near the Brooklands motor racing track which he frequented as a boy. He was the son of Florence and Rhodes Cobb, a wealthy furs broker in the City of London. He received his formal education at Eton College and Trinity Hall, Cambridge, before joining his father's firm and pursuing a successful career as the managing director of a number of companies in the trade, the personal financial resources from which he used to fund a passion for large capacity motor high speed racing. In 1924 he acquired a Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brooklands
Brooklands was a motor racing circuit and aerodrome built near Weybridge in Surrey, England, United Kingdom. It opened in 1907 and was the world's first purpose-built 'banked' motor racing circuit as well as one of Britain's first airfields, which also became Britain's largest aircraft manufacturing centre by 1918, producing military aircraft such as the Wellington and civil airliners like the Viscount and VC-10. The circuit hosted its last race in August 1939 and today part of it forms the Brooklands Museum, a major aviation and motoring museum, as well as a venue for vintage car, motorcycle and other transport-related events. History Brooklands motor circuit The Brooklands motor circuit was the brainchild of Hugh Fortescue Locke-King, and was the first purpose-built banked motor race circuit in the world. Following the Motor Car Act 1903, Britain was subject to a blanket speed limit on public roads: at a time when nearly 50% of the world's new cars were produced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duesenberg
Duesenberg Automobile and Motors Company, Inc. was an American race car, racing and luxury car, luxury automobile manufacturer founded in Indianapolis, Indiana, by brothers Fred Duesenberg, Fred and August Duesenberg in 1920. The company is known for popularizing the straight-eight engine and four-wheel hydraulic brakes. A Duesenberg car was the first American car to win a Grand Prix race, winning the 1921 French Grand Prix. Duesenbergs won the Indianapolis 500 in 1924, 1925, and 1927. Transportation executive Errett Lobban Cord acquired the Duesenberg corporation in 1926. The company was sold and dissolved in 1937. History Fred Duesenberg, Fred and August Duesenberg began designing engines in the early 1900s after Fred became involved with bicycle racing. The brothers designed a vehicle in 1905 and in 1906, formed the Mason Motor Car Company with funds from lawyer Edward R. Mason in Des Moines, Iowa. Frederick Louis Maytag I, F.L. and Elmer Henry Maytag, Elmer Maytag acqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtiss Conqueror
The Curtiss V-1570 Conqueror was a 12-cylinder vee liquid-cooled aircraft engine. Representing a more powerful version of the Curtiss D-12, the engine entered production in 1926 and flew in numerous aircraft.Gunston 1989, p. 46. Design and development Designed in 1924 as a military successor to the Curtiss D-12, initially named the Conqueror, it was later given the military designation of V-1570 based on its displacement of 1,570 cubic inches (26 L). The engine featured open-ended cylinder liners (advanced technology for the period) and pressurized liquid cooling. Developments including the use of a supercharger gradually increased power output until reliability problems due to overheating and coolant leaks became apparent. Military funding for further development of the Conqueror was cut in 1932, efforts by Curtiss to market the engine for civil airliners failed and the line was dropped from production. Variants ;V-1570-1 ;V-1570-5 ;V-1570-7 ;GV-1570-7: geared -7 ;V-1570-9 ;V- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)
