|
Specific Volume
In thermodynamics, the specific volume of a substance (symbol: , nu) is the quotient of the substance's volume () to its mass (): :\nu = \frac It is a mass-specific intrinsic property of the substance. It is the reciprocal of density (rho) and it is also related to the molar volume and molar mass: :\nu = \rho^ = \frac The standard unit of specific volume is cubic meters per kilogram (m3/kg), but other units include ft3/lb, ft3/slug, or mL/g. Specific volume for an ideal gas is related to the molar gas constant () and the gas's temperature (), pressure (), and molar mass (): : \nu = \frac It's based on the ideal gas law, PV = , and the amount of substance In chemistry, the amount of substance (symbol ) in a given sample of matter is defined as a ratio () between the particle number, number of elementary entities () and the Avogadro constant (). The unit of amount of substance in the International ..., n = m/M Applications Specific volume is commonly applied to: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, Work (thermodynamics), work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of thermodynamics, which convey a quantitative description using measurable macroscopic physical quantity, physical quantities but may be explained in terms of microscopic constituents by statistical mechanics. Thermodynamics applies to various topics in science and engineering, especially physical chemistry, biochemistry, chemical engineering, and mechanical engineering, as well as other complex fields such as meteorology. Historically, thermodynamics developed out of a desire to increase the thermodynamic efficiency, efficiency of early steam engines, particularly through the work of French physicist Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot, Sadi Carnot (1824) who believed that engine efficiency was the key that could help France win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Gas
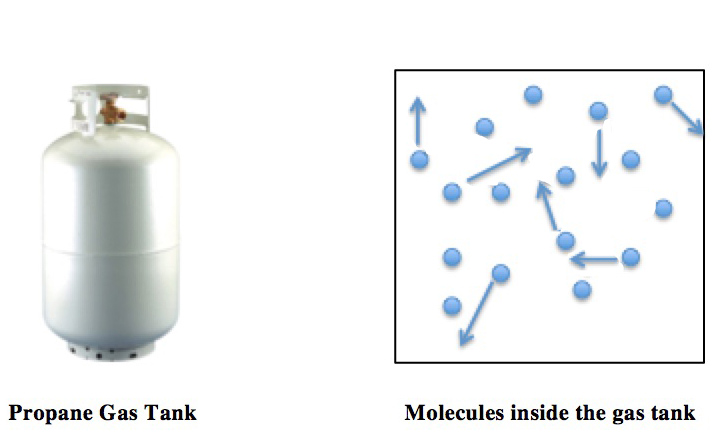
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of many randomly moving point particles that are not subject to interparticle interactions. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics. The requirement of zero interaction can often be relaxed if, for example, the interaction is perfectly elastic or regarded as point-like collisions. Under various conditions of temperature and pressure, many real gases behave qualitatively like an ideal gas where the gas molecules (or atoms for monatomic gas) play the role of the ideal particles. Many gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, noble gases, some heavier gases like carbon dioxide and mixtures such as air, can be treated as ideal gases within reasonable tolerances over a considerable parameter range around standard temperature and pressure. Generally, a gas behaves more like an ideal gas at higher temperature and lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volume
Volume is a measure of regions in three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). The definition of length and height (cubed) is interrelated with volume. The volume of a container is generally understood to be the capacity of the container; i.e., the amount of fluid (gas or liquid) that the container could hold, rather than the amount of space the container itself displaces. By metonymy, the term "volume" sometimes is used to refer to the corresponding region (e.g., bounding volume). In ancient times, volume was measured using similar-shaped natural containers. Later on, standardized containers were used. Some simple three-dimensional shapes can have their volume easily calculated using arithmetic formulas. Volumes of more complicated shapes can be calculated with integral calculus if a formula exists for the shape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic Properties
In thermodynamics, a physical property is any property that is measurable, and whose value describes a state of a physical system. Thermodynamic properties are defined as characteristic features of a system, capable of specifying the system's state. Some constants, such as the ideal gas constant, , do not describe the state of a system, and so are not properties. On the other hand, some constants, such as (the freezing point depression constant, or cryoscopic constant), depend on the identity of a substance, and so may be considered to describe the state of a system, and therefore may be considered physical properties. "Specific" properties are expressed on a per mass basis. If the units were changed from per mass to, for example, per mole, the property would remain as it was (i.e., intensive or extensive). Regarding work and heat Work and heat are not thermodynamic properties, but rather ''process quantities:'' flows of energy across a system boundary. Systems do not ''co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intensive And Extensive Properties
Physical or chemical properties of materials and systems can often be categorized as being either intensive or extensive, according to how the property changes when the size (or extent) of the system changes. The terms "intensive and extensive quantities" were introduced into physics by German mathematician Georg Helm in 1898, and by American physicist and chemist Richard C. Tolman in 1917. According to International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), an intensive property or intensive quantity is one whose magnitude is independent of the size of the system. An intensive property is not necessarily homogeneously distributed in space; it can vary from place to place in a body of matter and radiation. Examples of intensive properties include temperature, ''T''; refractive index, ''n''; density, ''ρ''; and hardness, ''η''. By contrast, an extensive property or extensive quantity is one whose magnitude is additive for subsystems. Examples include mass, volume and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Specific Volume
The partial specific volume \bar, express the variation of the extensive volume of a mixture in respect to composition of the masses. It is the partial derivative of volume with respect to the mass of the component of interest. :V=\sum _^n m_i \bar, where \bar is the partial specific volume of a component i defined as: :\bar=\left( \frac \right)_. The PSV is usually measured in milliLiters (mL) per gram (g), proteins > 30 kDa can be assumed to have a partial specific volume of 0.708 mL/g. Experimental determination is possible by measuring the natural frequency of a U-shaped tube filled successively with air, buffer and protein solution. Properties The weighted sum of partial specific volumes of a mixture or solution is an inverse of density of the mixture namely the specific volume of the mixture. :v = \sum_i w_i\cdot \bar = \frac :\sum_i \rho_i \cdot \bar = 1 See also * Partial molar property *Apparent molar property In thermodynamics, an apparent molar property of a sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Molar Volume
In thermodynamics, a partial molar property is a quantity which describes the variation of an extensive property of a solution or mixture with changes in the molar composition of the mixture at constant temperature and pressure. It is the partial derivative of the extensive property with respect to the amount (number of moles) of the component of interest. Every extensive property of a mixture has a corresponding partial molar property. Definition The partial molar volume is broadly understood as the contribution that a component of a mixture makes to the overall volume of the solution. However, there is more to it than this: When one mole of water is added to a large volume of water at 25 °C, the volume increases by 18 cm3. The molar volume of pure water would thus be reported as 18 cm3 mol−1. However, addition of one mole of water to a large volume of pure ethanol results in an increase in volume of only 14 cm3. The reason that the increase is diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volume (thermodynamics)
In thermodynamics, the volume of a system is an important extensive parameter for describing its thermodynamic state. The '' specific volume'', an intensive property, is the system's volume per unit mass. Volume is a function of state and is interdependent with other thermodynamic properties such as pressure and temperature. For example, volume is related to the pressure and temperature of an ideal gas by the ideal gas law. The physical region covered by a system may or may not coincide with a ''control volume'' used to analyze the system. Overview The volume of a thermodynamic system typically refers to the volume of the working fluid, such as, for example, the fluid within a piston. Changes to this volume may be made through an application of work, or may be used to produce work. An isochoric process however operates at a constant-volume, thus no work can be produced. Many other thermodynamic processes will result in a change in volume. A polytropic process, in parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molar Volume
In chemistry and related fields, the molar volume, symbol ''V''m, or \tilde V of a substance is the ratio of the volume (''V'') occupied by a substance to the amount of substance (''n''), usually at a given temperature and pressure. It is also equal to the molar mass (''M'') divided by the mass density (''ρ''): V_ = \frac = \frac The molar volume has the SI unit of cubic metres per mole (m3/mol), although it is more typical to use the units cubic decimetres per mole (dm3/mol) for gases, and cubic centimetres per mole (cm3/mol) for liquids and solids. Definition The molar volume of a substance ''i'' is defined as its molar mass divided by its density ''ρ''''i''0: V_ = For an ideal mixture containing ''N'' components, the molar volume of the mixture is the weighted sum of the molar volumes of its individual components. For a real mixture the molar volume cannot be calculated without knowing the density: V_ = \frac There are many liquid–liquid mixtures, for instance mix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amount Of Substance
In chemistry, the amount of substance (symbol ) in a given sample of matter is defined as a ratio () between the particle number, number of elementary entities () and the Avogadro constant (). The unit of amount of substance in the International System of Units is the Mole (unit), mole (symbol: mol), a SI base unit, base unit. p. 134 Since 2019, the mole has been defined such that the value of the Avogadro constant is exactly , defining a macroscopic unit convenient for use in laboratory-scale chemistry. The elementary entities are usually molecules, atoms, ions, or Ion pair, ion pairs of a specified kind. The particular chemical substance, substance sampled may be specified using a subscript or in parentheses, e.g., the amount of sodium chloride (NaCl) could be denoted as or . Sometimes, the amount of substance is referred to as the chemical amount or, informally, as the "number of moles" in a given sample of matter. The amount of substance in a sample can be calculated from mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Gas Law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The ideal gas law is often written in an empirical form: pV = nRT where p, V and T are the pressure, volume and Thermodynamic temperature, temperature respectively; n is the amount of substance; and R is the ideal gas constant. It can also be derived from the microscopic kinetic theory of gases, kinetic theory, as was achieved (independently) by August Krönig in 1856 and Rudolf Clausius in 1857. Equation The state function, state of an amount of gas is determined by its pressure, volume, and temperature. The modern form of the equation relates these simply in two main forms. The temperature us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various #Units, units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the International System of Units, SI unit of pressure, the Pascal (unit), pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton (unit), newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the Pound (force), pound-force per square inch (Pound per square inch, psi, symbol lbf/in2) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial units, imperial and United States customary units, US customary systems. Pressure ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |