|
Spartan (chemistry Software)
Spartan is a molecular modelling and computational chemistry application from Wavefunction. It contains code for molecular mechanics, semi-empirical methods, ''ab initio'' models, density functional models, post-Hartree–Fock models, and thermochemical recipes including G3(MP2) and T1. Quantum chemistry calculations in Spartan are powered by Q-Chem. Primary functions are to supply information about structures, relative stabilities and other properties of isolated molecules. Molecular mechanics calculations on complex molecules are common in the chemical community. Quantum chemical calculations, including Hartree–Fock method molecular orbital calculations, but especially calculations that include electronic correlation, are more time-consuming in comparison. Quantum chemical calculations are also called upon to furnish information about mechanisms and product distributions of chemical reactions, either directly by calculations on transition states, or based on Hammond's po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spartan20logo
Sparta (Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density Functional Theory
Density-functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics, chemistry and materials science to investigate the electronic structure (or nuclear structure) (principally the ground state) of many-body systems, in particular atoms, molecules, and the condensed phases. Using this theory, the properties of a many-electron system can be determined by using functionals, i.e. functions of another function. In the case of DFT, these are functionals of the spatially dependent electron density. DFT is among the most popular and versatile methods available in condensed-matter physics, computational physics, and computational chemistry. DFT has been very popular for calculations in solid-state physics since the 1970s. However, DFT was not considered accurate enough for calculations in quantum chemistry until the 1990s, when the approximations used in the theory were greatly refined to better model the exchange and correlation interactions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
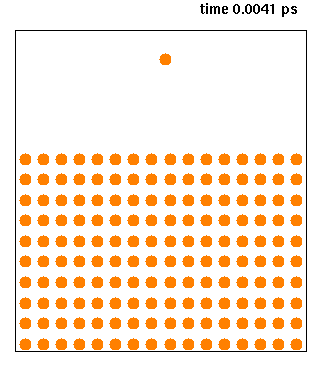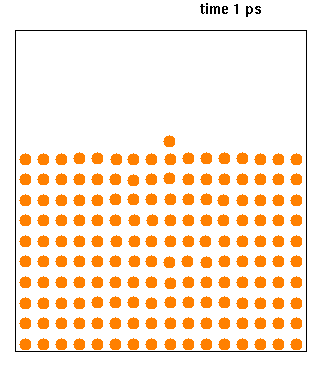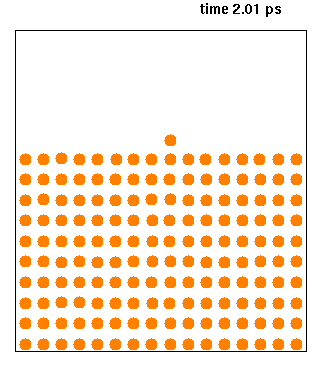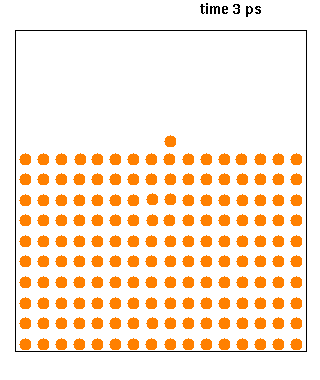
Molecular Dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamic "evolution" of the system. In the most common version, the trajectories of atoms and molecules are determined by numerically solving Newton's equations of motion for a system of interacting particles, where forces between the particles and their potential energies are often calculated using interatomic potentials or molecular mechanical force fields. The method is applied mostly in chemical physics, materials science, and biophysics. Because molecular systems typically consist of a vast number of particles, it is impossible to determine the properties of such complex systems analytically; MD simulation circumvents this problem by using numerical methods. However, long MD simulations are mathematically ill-conditioned, generating cumulative errors in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantitative Structure-activity Relationship
Quantitative may refer to: * Quantitative research, scientific investigation of quantitative properties * Quantitative analysis (other) * Meter (poetry), Quantitative verse, a metrical system in poetry * Statistics, also known as quantitative analysis * Numerical data, also known as quantitative data * Quantification (science) See also *Qualitative (other), Qualitative {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes charged matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative'' (commonly carried by protons and electrons respectively). Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. An object with an absence of net charge is referred to as neutral. Early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still accurate for problems that do not require consideration of quantum effects. Electric charge is a conserved property; the net charge of an isolated system, the amount of positive charge minus the amount of negative charge, cannot change. Electric charge is carried by subatomic particles. In ordinary matter, negative charge is carried by electrons, and positive charge is carried by the protons in the nuclei of atoms. If there are more electrons than protons in a piece of matter, it will have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs. A chemical mechanism is a theoretical conjecture that tries to describe in detail what takes place at each stage of an overall chemical reaction. The detailed steps of a reaction are not observable in most cases. The conjectured mechanism is chosen because it is thermodynamically feasible, and has experimental support in isolated intermediates (see next section) or other quantitative and qualitative characteristics of the reaction. It also describes each reactive intermediate, activated complex, and transition state, and which bonds are broken (and in what order), and which bonds are formed (and in what order). A complete mechanism must also explain the reason for the reactants and catalyst used, the stereochemistry observed in reactants and products, all products formed and the amount of each. The electron or arrow pushing method is often used in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition State Theory
In chemistry, transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes. TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ''H''‡, also written Δ‡''H''ɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ''S''‡ or Δ‡''S''ɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ''G''‡ or Δ‡''G''ɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest ''at the transition state''; Δ''H''‡ is the difference between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammond's Postulate
Hammond's postulate (or alternatively the Hammond–Leffler postulate), is a hypothesis in physical organic chemistry which describes the geometric structure of the transition state in an organic chemical reaction. First proposed by George Hammond in 1955, the postulate states that: If two states, as, for example, a transition state and an unstable intermediate, occur consecutively during a reaction process and have nearly the same energy content, their interconversion will involve only a small reorganization of the molecular structures. Therefore, the geometric structure of a state can be predicted by comparing its energy to the species neighboring it along the reaction coordinate. For example, in an ''exothermic'' reaction the transition state is closer in energy to the reactants than to the products. Therefore, the transition state will be more geometrically similar to the reactants than to the products. In contrast, however, in an ''endothermic'' reaction the transition st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition State
In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate. It is often marked with the double dagger ‡ symbol. As an example, the transition state shown below occurs during the SN2 reaction of bromoethane with a hydroxide anion: The activated complex of a reaction can refer to either the transition state or to other states along the reaction coordinate between reactants and products, especially those close to the transition state.Peter Atkins and Julio de Paula, ''Physical Chemistry'' (8th ed., W.H. Freeman 2006), p.809 According to the transition state theory, once the reactants have passed through the transition state configuration, they always continue to form products. History of concept The concept of a transition state has been important in many theories of the rates at which chemical reactions occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulation to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules, groups of molecules, and solids. It is essential because, apart from relatively recent results concerning the hydrogen molecular ion (dihydrogen cation, see references therein for more details), the quantum many-body problem cannot be solved analytically, much less in closed form. While computational results normally complement the information obtained by chemical experiments, it can in some cases predict hitherto unobserved chemical phenomena. It is widely used in the design of new drugs and materials. Examples of such properties are structure (i.e., the expected positions of the constituent atoms), absolute and relative (interaction) energies, electronic charge density distributions, dipoles and higher multipole moments, vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Correlation
Electronic correlation is the interaction between electrons in the electronic structure of a quantum system. The correlation energy is a measure of how much the movement of one electron is influenced by the presence of all other electrons. Atomic and molecular systems Within the Hartree–Fock method of quantum chemistry, the antisymmetric wave function is approximated by a single Slater determinant. Exact wave functions, however, cannot generally be expressed as single determinants. The single-determinant approximation does not take into account Coulomb correlation, leading to a total electronic energy different from the exact solution of the non-relativistic Schrödinger equation within the Born–Oppenheimer approximation. Therefore, the Hartree–Fock limit is always above this exact energy. The difference is called the ''correlation energy'', a term coined by Löwdin. The concept of the correlation energy was studied earlier by Wigner. A certain amount of electron c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hartree–Fock Method
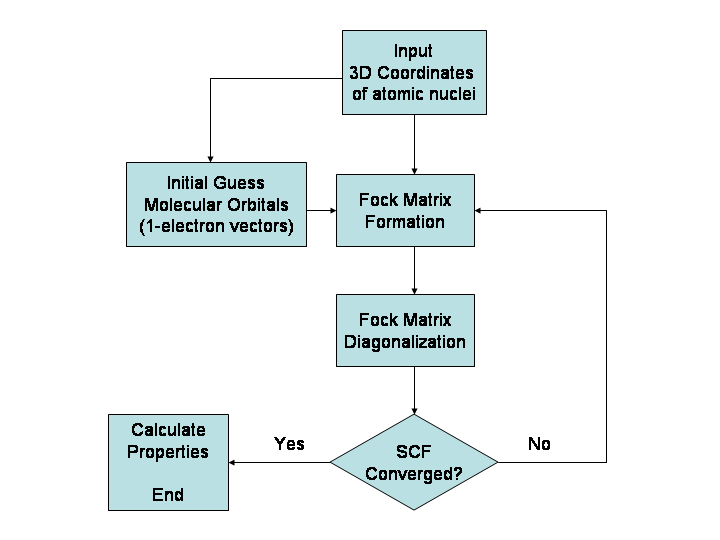
In computational physics and chemistry, the Hartree–Fock (HF) method is a method of approximation for the determination of the wave function and the energy of a quantum many-body system in a stationary state. The Hartree–Fock method often assumes that the exact ''N''-body wave function of the system can be approximated by a single Slater determinant (in the case where the particles are fermions) or by a single permanent (in the case of bosons) of ''N'' spin-orbitals. By invoking the variational method, one can derive a set of ''N''-coupled equations for the ''N'' spin orbitals. A solution of these equations yields the Hartree–Fock wave function and energy of the system. Especially in the older literature, the Hartree–Fock method is also called the self-consistent field method (SCF). In deriving what is now called the Hartree equation as an approximate solution of the Schrödinger equation, Hartree required the final field as computed from the charge distribution to be "s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |