|
Sparrow (bot)
Sparrow is a chatbot developed by the artificial intelligence research lab DeepMind, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. It is designed to answer users' questions correctly, while reducing the risk of unsafe and inappropriate answers. One motivation behind Sparrow is to address the problem of large language model, language models producing incorrect, biased or potentially harmful outputs. Sparrow is trained using human judgements, in order to be more “Helpful, Correct and Harmless” compared to baseline pre-trained language models. The development of Sparrow involved asking paid study participants to interact with Sparrow, and collecting their preferences to train a model of how useful an answer is. To improve accuracy and help avoid the problem of Hallucination (artificial intelligence), hallucinating incorrect answers, Sparrow has the ability to search the Internet using Google Search in order to find and cite evidence for any factual claims it makes. To make the model safer, its b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparrow Dialogue Blog Post
Sparrow may refer to: Birds * Old World sparrows, family Passeridae * New World sparrows, family Passerellidae * two species in the Passerine family Estrildidae: ** Java sparrow ** Timor sparrow * Hedge sparrow, also known as the dunnock or hedge accentor in the family Prunellidae People * Sparrow (surname) * Sparrow (American poet) (born 1953), American poet, activist, musician, and rabble-rouser * Alex Sparrow, also known as Alexey Vorobyov (born 1988), Russian singer and actor * Robert Brown (footballer, born 1856), Scottish footballer known by the nickname 'Sparrow' * The Little Sparrow (La Môme Piaf), the nickname of French singer Édith Piaf (1915 –1963) Media Films * ''The Sparrow'' (1914 film), a 1914 French silent film * ''Sparrows'' (1916 film), a Dutch film * ''Sparrows'' (1926 film), starring Mary Pickford * ''The Sparrow'' (1972 film), Arabic title ''Al Asfour'', a 1972 Egyptian film by director Youssef Chahine * ''Sparrow'' (1993 film), a 1993 Italian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AI Safety
AI is artificial intelligence, intellectual ability in machines and robots. Ai, AI or A.I. may also refer to: Animals * Ai (chimpanzee), an individual experimental subject in Japan * Ai (sloth) or the pale-throated sloth, northern Amazonian mammal species Arts, entertainment and media Works * ''Ai'' (album), a 2004 release by Seraphim * '' A.I. Artificial Intelligence'', a 2001 American film * ''A.I. Rising'', a 2018 Serbian film * '' AI: The Somnium Files'', a 2019 video game * ''American Idol'', televised singing contest * ''The American Interest'', a bimonthly magazine (2005–2020) * ''I'' (2015 film), an Indian Tamil film (initial title: ''Ai'') Other uses in arts and media * A.i. (band), a Californian rock–electroclash group * All in (poker), wagering one's entire stake * Appreciation Index, a British measure of broadcast programme approval * The Art Institutes, a chain of American art schools * Non-player character, in gaming (colloquially, ''an AI'') Business ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Modeling
A language model is a probability distribution over sequences of words. Given any sequence of words of length , a language model assigns a probability P(w_1,\ldots,w_m) to the whole sequence. Language models generate probabilities by training on text corpora in one or many languages. Given that languages can be used to express an infinite variety of valid sentences (the property of digital infinity), language modeling faces the problem of assigning non-zero probabilities to linguistically valid sequences that may never be encountered in the training data. Several modelling approaches have been designed to surmount this problem, such as applying the Markov assumption or using neural architectures such as recurrent neural networks or transformers. Language models are useful for a variety of problems in computational linguistics; from initial applications in speech recognition to ensure nonsensical (i.e. low-probability) word sequences are not predicted, to wider use in machine tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chatbots
A chatbot or chatterbot is a software application used to conduct an on-line chat conversation via text or text-to-speech, in lieu of providing direct contact with a live human agent. Designed to convincingly simulate the way a human would behave as a conversational partner, chatbot systems typically require continuous tuning and testing, and many in production remain unable to adequately converse, while none of them can pass the standard Turing test. The term "ChatterBot" was originally coined by Michael Mauldin (creator of the first Verbot) in 1994 to describe these conversational programs. Chatbots are used in dialog systems for various purposes including customer service, request routing, or information gathering. While some chatbot applications use extensive word-classification processes, natural-language processors, and sophisticated AI, others simply scan for general keywords and generate responses using common phrases obtained from an associated library or database. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prompt Engineering
Prompt engineering is a concept in artificial intelligence, particularly natural language processing (NLP). In prompt engineering, the description of the task is embedded in the input, e.g., as a question instead of it being implicitly given. Prompt engineering typically works by converting one or more tasks to a prompt-based dataset and training a language model with what has been called "prompt-based learning" or just "prompt learning". Prompt engineering may work from a large "frozen" pretrained language model and where only the representation of the prompt is learned (i.e., optimized), using methods such as "prefix-tuning" or "prompt tuning". The GPT-2 and GPT-3 language models were important steps in prompt engineering. In 2021, multitask prompt engineering using multiple NLP datasets showed good performance on new tasks. Prompts that include a chain of thought in few-shot learning examples show better indication of reasoning in language models. In zero-shot learning prepend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is an interdisciplinary subfield of linguistics, computer science, and artificial intelligence concerned with the interactions between computers and human language, in particular how to program computers to process and analyze large amounts of natural language data. The goal is a computer capable of "understanding" the contents of documents, including the contextual nuances of the language within them. The technology can then accurately extract information and insights contained in the documents as well as categorize and organize the documents themselves. Challenges in natural language processing frequently involve speech recognition, natural-language understanding, and natural-language generation. History Natural language processing has its roots in the 1950s. Already in 1950, Alan Turing published an article titled " Computing Machinery and Intelligence" which proposed what is now called the Turing test as a criterion of intelligence, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethics Of Artificial Intelligence
The ethics of artificial intelligence is the branch of the ethics of technology specific to artificially intelligent systems. It is sometimes divided into a concern with the moral behavior of ''humans'' as they design, make, use and treat artificially intelligent systems, and a concern with the behavior of ''machines,'' in machine ethics. It also includes the issue of a possible singularity due to superintelligent AI. Ethics fields' approaches Robot ethics The term "robot ethics" (sometimes "roboethics") refers to the morality of how humans design, construct, use and treat robots. Robot ethics intersect with the ethics of AI. Robots are physical machines whereas AI can be only software. Not all robots function through AI systems and not all AI systems are robots. Robot ethics considers how machines may be used to harm or benefit humans, their impact on individual autonomy, and their effects on social justice. Machine ethics Machine ethics (or machine morality) is the field ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonsense Reasoning
In artificial intelligence (AI), commonsense reasoning is a human-like ability to make presumptions about the type and essence of ordinary situations humans encounter every day. These assumptions include judgments about the nature of physical objects, taxonomic properties, and peoples' intentions. A device that exhibits commonsense reasoning might be capable of drawing conclusions that are similar to humans' folk psychology (humans' innate ability to reason about people's behavior and intentions) and naive physics (humans' natural understanding of the physical world). Definitions and characterizations Some definitions and characterizations of common sense from different authors include: * "Commonsense knowledge includes the basic facts about events (including actions) and their effects, facts about knowledge and how it is obtained, facts about beliefs and desires. It also includes the basic facts about material objects and their properties." * "Commonsense knowledge differs from e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reinforcement Learning From Human Feedback
In machine learning, reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) or reinforcement learning from human preferences is a technique that trains a "reward model" directly from human feedback and uses the model as a reward function to optimize an agent's policy using reinforcement learning (RL) through an optimization algorithm like Proximal Policy Optimization. The reward model is trained in advance to the policy being optimized to predict if a given output is good (high reward) or bad (low reward). RLHF can improve the robustness and exploration of RL agents, especially when the reward function is sparse or noisy. Human feedback is collected by asking humans to rank instances of the agent's behavior. These rankings can then be used to score outputs, for example with the Elo rating system. RLHF has been applied to various domains of natural language processing, such as conversational agents, text summarization, and natural language understanding. Ordinary reinforcement learnin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chatbot
A chatbot or chatterbot is a software application used to conduct an on-line chat conversation via text or text-to-speech, in lieu of providing direct contact with a live human agent. Designed to convincingly simulate the way a human would behave as a conversational partner, chatbot systems typically require continuous tuning and testing, and many in production remain unable to adequately converse, while none of them can pass the standard Turing test. The term "ChatterBot" was originally coined by Michael Mauldin (creator of the first Verbot) in 1994 to describe these conversational programs. Chatbots are used in dialog systems for various purposes including customer service, request routing, or information gathering. While some chatbot applications use extensive word-classification processes, natural-language processors, and sophisticated AI, others simply scan for general keywords and generate responses using common phrases obtained from an associated library or database. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinchilla AI
Chinchilla is a family of large language models developed by the research team at DeepMind, presented in March 2022. It is named "chinchilla" because it is a further development over a previous model family named Gopher. Both model families were trained in order to investigate the scaling laws of large language models. It claimed to outperform GPT-3. It considerably simplifies downstream utilization because it requires much less computer power for inference and fine-tuning. Based on the training of previously employed language models, it has been determined that if one doubles the model size, one must also have twice the number of training tokens. This hypothesis has been used to train Chinchilla by DeepMind DeepMind Technologies is a British artificial intelligence subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. and research laboratory founded in 2010. DeepMind was List of mergers and acquisitions by Google, acquired by Google in 2014 and became a wholly owned subsid .... Similar to Gopher in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
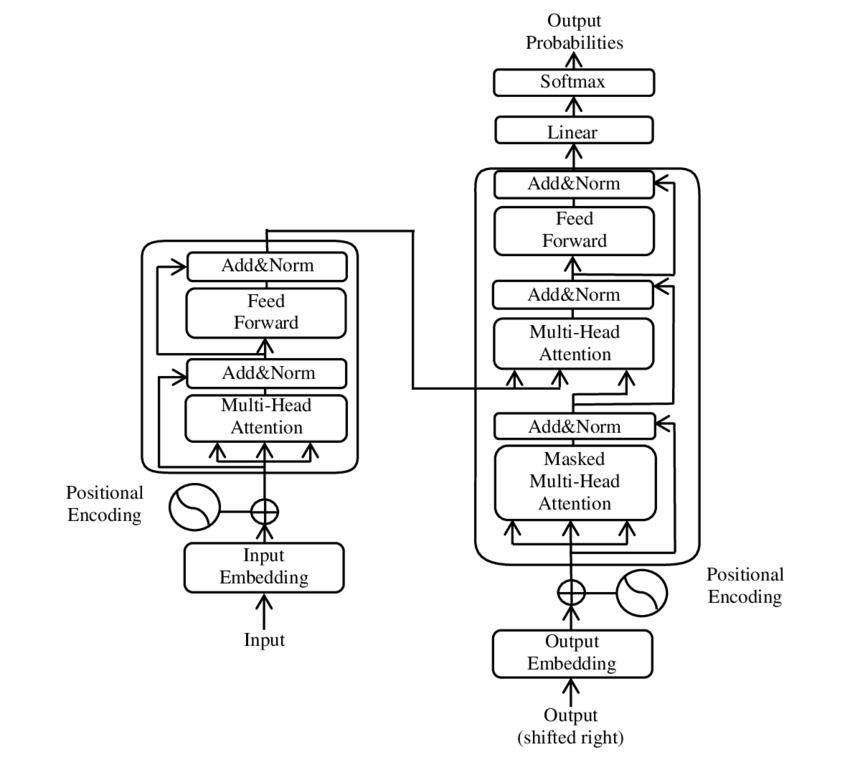
Transformer (machine Learning Model)
A transformer is a deep learning model that adopts the mechanism of self-attention, differentially weighting the significance of each part of the input data. It is used primarily in the fields of natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision (CV). Like recurrent neural networks (RNNs), transformers are designed to process sequential input data, such as natural language, with applications towards tasks such as translation and text summarization. However, unlike RNNs, transformers process the entire input all at once. The attention mechanism provides context for any position in the input sequence. For example, if the input data is a natural language sentence, the transformer does not have to process one word at a time. This allows for more parallelization than RNNs and therefore reduces training times. Transformers were introduced in 2017 by a team at Google Brain and are increasingly the model of choice for NLP problems, replacing RNN models such as long short-term me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |