|
Space Situational Awareness Programme
The Space Safety Programme, formerly the Space Situational Awareness (SSA) programme, is the European Space Agency's (ESA) initiative to monitor hazards from space, determine their risk, make this data available to the appropriate authorities and where possible, mitigate the threat. The SSA Programme was designed to support Europe's independent space access and utilization through the timely and accurate information delivery regarding the space environment, particularly hazards to both in-orbit and ground infrastructure. In 2019 it evolved into the present Space Safety Programme with an expanded focus, also including missions and activities to mitigate and prevent dangers from space. The programme is split into four main segments: * Space weather: monitoring the Sun, the solar wind, and in Earth's magnetosphere, ionosphere and thermosphere, that can affect spaceborne and ground-based infrastructure or endanger human life or health. This data is processed by thSpace Weather Service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Space Agency
, owners = , headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France , coordinates = , spaceport = Guiana Space Centre , seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png , seal_size = 130px , image = Views in the Main Control Room (12052189474).jpg , size = , caption = , acronym = , established = , employees = 2,200 , administrator = Director General Josef Aschbacher , budget = €7.2 billion (2022) , language = English and French (working languages) , website = , logo = European Space Agency logo.svg , logo_caption = Logo , image_caption = European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) Main Control Room The European Space Agency (ESA; french: Agence spatiale européenne , it, Agenzia Spaziale Europea, es, Agencia Espacial Europea ASE; german: Europäische Weltraumorganisation) is an intergovernmental organisation of 22 member states dedicated to the exploration of space. Established in 1975 and headquartered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
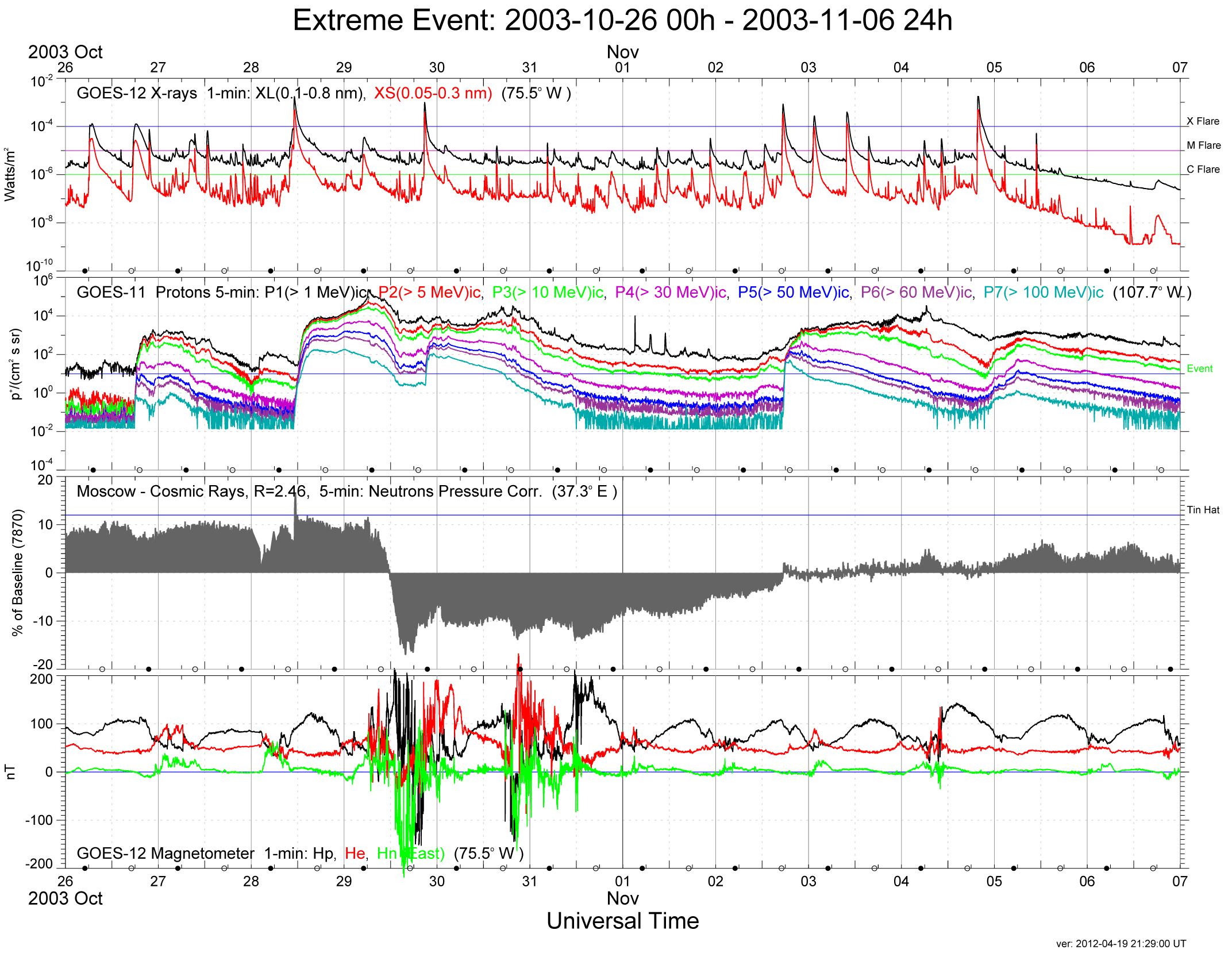
Space Weather
Space weather is a branch of space physics and aeronomy, or heliophysics, concerned with the time varying conditions within the Solar System, including the solar wind, emphasizing the space surrounding the Earth, including conditions in the magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Space weather is distinct from, but conceptually related to, the terrestrial weather of the atmosphere of Earth (troposphere and stratosphere). The term "space weather" was first used in the 1950s and came into common usage in the 1990s. Later, it was generalized to a " space climate" research discipline, which focuses on general behaviors of longer and larger-scale variabilities and effects. History For many centuries, the effects of space weather were noticed, but not understood. Displays of auroral light have long been observed at high latitudes. Genesis In 1724, George Graham reported that the needle of a magnetic compass was regularly deflected from magnetic north over the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Telescopes
An optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct visual inspection, to make a photograph, or to collect data through electronic image sensors. There are three primary types of optical telescope: * Refracting telescopes, which use lenses and less commonly also prisms (dioptrics) * Reflecting telescopes, which use mirrors ( catoptrics) * Catadioptric telescopes, which combine lenses and mirrors An optical telescope's ability to resolve small details is directly related to the diameter (or aperture) of its objective (the primary lens or mirror that collects and focuses the light), and its light-gathering power is related to the area of the objective. The larger the objective, the more light the telescope collects and the finer detail it resolves. People use optical telescopes (including monoculars and binoculars) for outdoor activities such as observation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Telescope
A radio telescope is a specialized antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum emitted by astronomical objects, just as optical telescopes are the main observing instrument used in traditional optical astronomy which studies the light wave portion of the spectrum coming from astronomical objects. Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can be used in the daytime as well as at night. Since astronomical radio sources such as planets, stars, nebulas and galaxies are very far away, the radio waves coming from them are extremely weak, so radio telescopes require very large antennas to collect enough radio energy to study them, and extremely sensitive receiving equipment. Radio telescopes are typically large parabolic ("dish") antennas similar to those employed in tracking an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ESA Centre For Earth Observation
The ESA Centre for Earth Observation (also known as the European Space Research Institute or ESRIN) is a research centre belonging to the European Space Agency (ESA), located in Frascati (Rome) Italy. It is dedicated to research involving earth observation data taken from satellites, among other specialised activities. The establishment currently hosts the European Space Agency's development team for the Vega launcher. History ESLAR, a laboratory for advanced research was created in 1966 mainly to break the political deadlock over the location of ESLAB. Later renamed ESRIN, an acronym for European Space Research Institute, ESLAR was based in Frascati (Italy). The ESRO Convention describes ESRINs' role in the following manner: The facility began acquiring data from environmental satellites within Earthnet programme in the 1970s. See also * European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) * European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC) * European Space Astronomy Centre (ESAC) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-Earth Object Coordination Centre
The Near-Earth Object Coordination Centre (NEOCC) is the main centre of the Planetary Defence Office of the European Space Agency (ESA). The NEOCC, which is based at ESRIN The ESA Centre for Earth Observation (also known as the European Space Research Institute or ESRIN) is a research centre belonging to the European Space Agency (ESA), located in Frascati (Rome) Italy. It is dedicated to research involving ear ... in Frascati, Italy, coordinates observations of small bodies such as asteroids and comets in the Solar System in order to evaluate and monitor the threat posed by those potentially hazardous. The Coordination Centre also conducts studies with the purpose of improving near-Earth object warning services. These are necessary to give real-time alerts to different organizations, scientific bodies, and decision-makers. References Planetary defense organizations {{ESA-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEOSTEL
The Near Earth Object Survey TELescope (NEOSTEL - also known as "Flyeye") is an astronomical survey and early-warning system for detecting near-Earth objects sized and above a few weeks before they impact Earth. NEOSTEL is a project founded by the European Space Agency (ESA), starting with an initial prototype currently under construction at OHB in Milan, Italy. The telescope is of a new "fly-eye" design inspired by the wide field of vision from a fly's eye. The design combines a single objective reflector with multiple sets of optics and CCDs, giving a very wide field of view (around , or 220 times the area of the full moon). When complete it will have one of the widest fields of view of any telescope and be able to survey the majority of the visible sky in a single night. If the initial prototype is successful, three more telescopes are planned, in complementary positions around the globe close to the equator. In terms of light gathering power, the size of the primary mirr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OGS Telescope
The ESA Optical Ground Station (''OGS Telescope'' or ''ESA Space Debris Telescope'') is the European Space Agency's ground based observatory at the Teide Observatory on Tenerife, Spain, built for the observation of space debris. OGS is part of the Artemis experiment and is operated by the IAC (Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias) and Ataman Science S.L.U. The telescope is a 1-metre Coudé telescope with field of view of 0.7 degrees, supported by an English cross-axial mount inside a dome 12.5-metre in diameter. Its main purposes are: # to be the optical ground station of the Artemis telecommunications satellite (the project from which the telescope takes its name) # to make surveys of space debris in different orbits around the Earth, # to make surveys and follow-up observations of near-Earth objects as part of ESA's Space Situational Awareness programme, and # to make scientific astronomical night observations. It is equipped with a cryogenically cooled mosaic CCD-Camera o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Event
An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or meteoroids and have minimal effect. When large objects impact terrestrial planets such as the Earth, there can be significant physical and biospheric consequences, though atmospheres mitigate many surface impacts through atmospheric entry. Impact craters and Impact structure, structures are dominant landforms on many of the Solar System's solid objects and present the strongest empirical evidence for their frequency and scale. Impact events appear to have played a significant role in the Formation and evolution of the Solar System, evolution of the Solar System since its formation. Major impact events have significantly shaped History of the Earth, Earth's history, and have been implicated in the giant impact theory, formation of the Earth� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-Earth Object
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body whose orbit brings it into proximity with Earth. By convention, a Solar System body is a NEO if its closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 astronomical units (AU). If a NEO's orbit crosses the Earth's orbit, and the object is larger than across, it is considered a potentially hazardous object (PHO). Most known PHOs and NEOs are asteroids, but a small fraction are comets. There are over 30,503 known near-Earth asteroids (NEAs) and over a hundred known short-period near-Earth comets (NECs). A number of solar-orbiting meteoroids were large enough to be tracked in space before striking the Earth. It is now widely accepted that collisions in the past have had a significant role in shaping the geological and biological history of the Earth. Asteroids as small as in diameter can cause significant damage to the local environment and human populations. Larger asteroids penetrate the atmosphere to the surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to the southwest, and the North Sea to the northwest. It covers an area of and has a population of more than 11.5 million, making it the 22nd most densely populated country in the world and the 6th most densely populated country in Europe, with a density of . Belgium is part of an area known as the Low Countries, historically a somewhat larger region than the Benelux group of states, as it also included parts of northern France. The capital and largest city is Brussels; other major cities are Antwerp, Ghent, Charleroi, Liège, Bruges, Namur, and Leuven. Belgium is a sovereign state and a federal constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. Its institutional organization is complex and is structured on both regional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redu Station
Redu Station is an ESTRACK radio Antenna (electronics), antenna station for communication with spacecraft. The station is located in Wallonia, about one kilometre away from the village of Redu, Belgium. The ground terminals provide tracking capabilities in C band (IEEE), C band, L-band, S-band, Ku band, Ku band, and Ka band, Ka band as well as provide in-orbit tests of Communications satellite, telecommunication satellites. External links ESA webpage on ESTRACK, including links to all stationsESA/ESTRACK Redu station pageESA Redu ground station gallery European Space Agency ESTRACK facilities Buildings and structures in Luxembourg (Belgium) Libin, Belgium {{space-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |