|
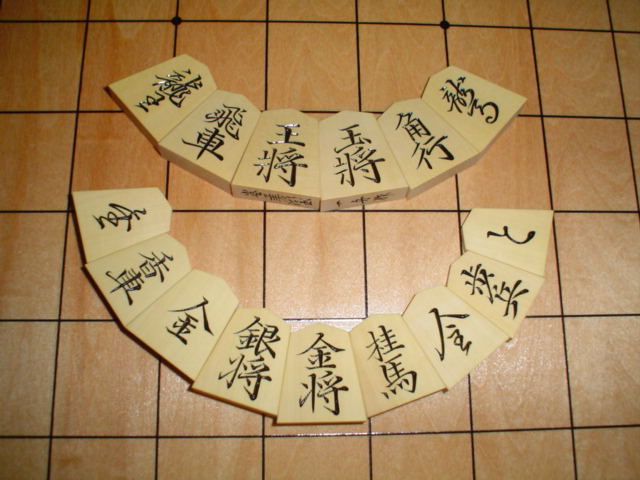
Space Shogi
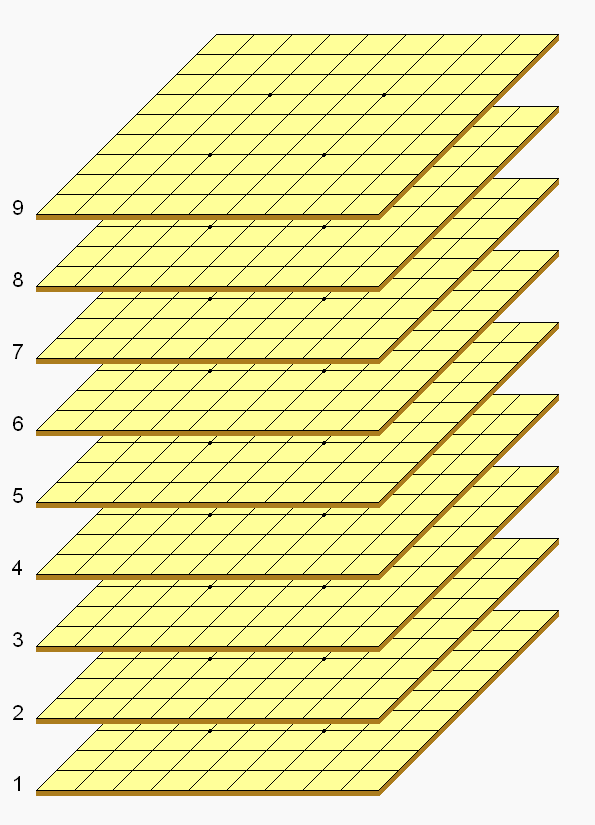
Space shogi is a three-dimensional shogi variant invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1987. The gamespace comprises nine 9×9 shogi boards stacked vertically. Each player controls a standard set of shogi pieces. Space shogi was included in ''World Game Review'' No. 10 edited by Michael Keller. Game rules Space shogi follows standard shogi conventions, including the same types and numbers of pieces, and a similar initial setup. All the normal shogi rules apply, including drops, promotion, check, checkmate, and impasse. But pieces have the freedom of three-dimensional movement. Starting setup Black starts the game occupying levels 1 through 3; White starts on levels 9 through 7. See also * Three-dimensional chess Three-dimensional chess (or 3‑D chess) is any chess variant that replaces the two-dimensional board with a three-dimensional array of cells between which the pieces can move. In practical play, this is usually achieved by boards representing ... * Also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shogi Gameboard
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum known as spacetime. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. Debates concerning the nature, essence and the mode of existence of space date back to antiquity; namely, to treatises like the ''Timaeus'' of Plato, or Socrates in his reflections on what the Greeks called ''khôra'' (i.e. "space"), or in the ''Physics'' of Aristotle (Book IV, Delta) in the definition of ''topos'' (i.e. place), or in the later "geometrical conception of place" as "sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-dimensional Space
Three-dimensional space (also: 3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a geometric setting in which three values (called ''parameters'') are required to determine the position (geometry), position of an element (i.e., Point (mathematics), point). This is the informal meaning of the term dimension. In mathematics, a tuple of Real number, numbers can be understood as the Cartesian coordinates of a location in a -dimensional Euclidean space. The set of these -tuples is commonly denoted \R^n, and can be identified to the -dimensional Euclidean space. When , this space is called three-dimensional Euclidean space (or simply Euclidean space when the context is clear). It serves as a model of the physical universe (when relativity theory is not considered), in which all known matter exists. While this space remains the most compelling and useful way to model the world as it is experienced, it is only one example of a large variety of spaces in three dimensions called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi Variant
A shogi variant is a game related to or derived from shogi (Japanese chess). Many shogi variants have been developed over the centuries, ranging from some of the largest chess-type games ever played to some of the smallest. A few of these variants are still regularly played, though none are as popular as shogi itself. The drop rule, often considered the most notable feature of shogi, is absent from most shogi variants, which therefore play more like other forms of chess, with the board becoming less crowded as pieces are exchanged. This is especially true for variants larger than shogi itself − in fact, the largest well-known variant that features the drop rule is the 11×11 game wa shogi. Predecessors of modern shogi Some form of chess had almost certainly reached Japan by the 9th century, if not earlier, but the earliest surviving Japanese description of the rules of chess dates from the early 12th century, during the Heian period. Unfortunately, this description does not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George R
George may refer to: People * George (given name) * George (surname) * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Washington, First President of the United States * George W. Bush, 43rd President of the United States * George H. W. Bush, 41st President of the United States * George V, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1910-1936 * George VI, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1936-1952 * Prince George of Wales * George Papagheorghe also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George Harrison, an English musician and singer-songwriter Places South Africa * George, Western Cape ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa * George, Missouri * George, Washington * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Characters * George (Peppa Pig), a 2-year-old pig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and '' janggi''. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Western chess is sometimes called (''Seiyō Shōgi'' ) in Japan. Shogi was the earliest chess-related historical game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the sixth century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in its present form was played as early as the 16th century, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Game
Board games are tabletop games that typically use . These pieces are moved or placed on a pre-marked board (playing surface) and often include elements of table, card, role-playing, and miniatures games as well. Many board games feature a competition between two or more players. To show a few examples: in checkers (British English name 'draughts'), a player wins by capturing all opposing pieces, while Eurogames often end with a calculation of final scores. '' Pandemic'' is a cooperative game where players all win or lose as a team, and peg solitaire is a puzzle for one person. There are many varieties of board games. Their representation of real-life situations can range from having no inherent theme, such as checkers, to having a specific theme and narrative, such as ''Cluedo''. Rules can range from the very simple, such as in snakes and ladders; to deeply complex, as in ''Advanced Squad Leader''. Play components now often include custom figures or shaped counters, and distin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and '' janggi''. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Western chess is sometimes called (''Seiyō Shōgi'' ) in Japan. Shogi was the earliest chess-related historical game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the sixth century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in its present form was played as early as the 16th century, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-dimensional Chess
Three-dimensional chess (or 3‑D chess) is any chess variant that replaces the two-dimensional board with a three-dimensional array of cells between which the pieces can move. In practical play, this is usually achieved by boards representing different layers being laid out next to each other. Three-dimensional variants have existed since at least the late 19th century, one of the oldest being ''Raumschach'' (), invented in 1907 by Ferdinand Maack and considered the classic 3‑D game. Maack founded a Raumschach club in Hamburg in 1919, which remained active until World War II. Chapter 25 of David Pritchard's ''The Classified Encyclopedia of Chess Variants'' discusses some 50 such variations extending chess to three dimensions as well as a handful of higher-dimensional variants. Chapter 11 covers variants using multiple boards normally set side by side which can also be considered to add an extra dimension to chess. "Three-dimensional chess" is used collo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexshogi
Hexshogi is a shogi variant for two players created by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. The gameboard comprises 85 hexagonal cells. The game is in all respects the same as shogi, except that piece moves have been transfigured for the hexagonal board-cell geometry. Hexshogi was included in ''World Game Review'' No. 10 edited by Michael Keller. Game rules Hexshogi has the same types and numbers of pieces as shogi, and all normal shogi rules apply, including a similar initial setup (see diagram), drops, promotion, check, checkmate, and impasse. As in shogi, pieces capture the same as they move. But the hexagonal geometry implies special move patterns for the pieces. Piece moves The diagrams show how the unpromoted pieces move. As in shogi, a dragon king (promoted rook) moves as a rook, or as a king. A dragon horse (promoted bishop) moves as a bishop or a king. See also * Gliński's hexagonal chess * Also by George Dekle: ** Trishogi – a variant with triangular cells ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trishogi
Trishogi is a shogi variant for two players created by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1987. The gameboard comprises 9×10 interlocking triangular cells. The game is in all respects the same as shogi, except that piece moves have been transfigured for the triangular board-cell geometry. Trishogi was included in ''World Game Review'' No. 10 edited by Michael Keller. Game rules Trishogi has the same types and numbers of pieces as shogi, and all normal shogi rules apply, including initial setup (see diagram), drops, promotion, check, and checkmate. As in shogi, pieces capture the same as they move. But the triangular geometry creates special move patterns for the pieces. Piece moves The diagrams show how the unpromoted pieces move. As in shogi, a dragon king (promoted rook) moves as a rook and as a king. A dragon horse (promoted bishop) moves as a bishop and king. See also * Shogi variants * Also by George Dekle: ** Hexshogi – a variant with hexagonal cells ** Masonic Shogi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Games Introduced In 1987
Board or Boards may refer to: Flat surface * Lumber, or other rigid material, milled or sawn flat ** Plank (wood) ** Cutting board ** Sounding board, of a musical instrument * Cardboard (paper product) * Paperboard * Fiberboard ** Hardboard, a type of fiberboard * Particle board, also known as ''chipboard'' ** Oriented strand board * Printed circuit board, in computing and electronics ** Motherboard, the main printed circuit board of a computer * A reusable writing surface ** Chalkboard ** Whiteboard Recreation * Board game **Chessboard **Checkerboard * Board (bridge), a device used in playing duplicate bridge * Board, colloquial term for the rebound statistic in basketball * Board track racing, a type of motorsport popular in the United States during the 1910s and 1920s * Boards, the wall around a bandy field or ice hockey rink * Boardsports * Diving board (other) Companies * Board International, a Swiss software vendor known for its business intelligence software tool ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |