|
SpaceX Mars Program
The SpaceX Mars program is a set of projects through which the aerospace company SpaceX hopes to facilitate the colonization of Mars. The company claims that this is necessary for the long-term survival of the human species and that its Mars program, including the ongoing development of the SpaceX Starship, will reduce space transportation costs, thereby making travel to Mars a more realistic possibility. Elon Musk, who founded SpaceX, first presented his goal of enabling Mars colonization in 2001 as a member of the Mars Society's board of directors. In the 2000s and early 2010s, SpaceX made many vehicle concepts for delivering payloads and crews to Mars, including space tugs, heavy-lift launch vehicles, ''Red Dragon'' capsules. The company's current Mars plan was first formally proposed in 2016 International Astronautical Congress alongside a fully-reusable launch vehicle, the Interplanetary Transport System. Since then, the launch vehicle proposal was altered and renamed to " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerospace Engineering
Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is similar, but deals with the electronics side of aerospace engineering. "Aeronautical engineering" was the original term for the field. As flight technology advanced to include vehicles operating in outer space, the broader term "aerospace engineering" has come into use. Aerospace engineering, particularly the astronautics branch, is often colloquially referred to as "rocket science". Overview Flight vehicles are subjected to demanding conditions such as those caused by changes in atmospheric pressure and temperature, with structural loads applied upon vehicle components. Consequently, they are usually the products of various technological and engineering disciplines including aerodynamics, Air propulsion, avionics, materials science, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vice (magazine)
''Vice'' (stylized in all caps) is a Canadian-American magazine focused on lifestyle, arts, culture, and news/politics. Founded in 1994 in Montreal as an alternative punk magazine, the founders later launched the youth media company Vice Media, which consists of divisions including the printed magazine as well as a website, broadcast news unit, a film production company, a record label, and a publishing imprint. As of February 2015, the magazine's editor-in-chief is Ellis Jones. History Founded by Suroosh Alvi, Gavin McInnes, and Shane Smith (the latter two being childhood friends), the magazine was launched in 1994 as the ''Voice of Montreal'' with government funding. The intention of the founders was to provide work and a community service. When the editors later sought to dissolve their commitments with the original publisher, Alix Laurent, they bought him out and changed the name to ''Vice'' in 1996. Richard Szalwinski, a Canadian software millionaire, acquired the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as Computer program, programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the Computer hardware, hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of Programmable logic controller, industrial and Consumer electronics, consumer products use computers as control systems. Simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls are included, as are factory devices like industrial robots and computer-aided design, as well as general-purpose devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, and Health promotion, promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention (medical), prevention and therapy, treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, medical genetics, genetics, and medical technology to diagnosis (medical), diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, splint (medicine), external splints and traction, medical devices, biologic medical product, biologics, and Radiation (medicine), ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since Prehistoric medicine, prehistoric times, and for most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Research
Space research is scientific study carried out in outer space, and by studying outer space. From the use of space technology to the observable universe, space research is a wide research field. Earth science, materials science, biology, medicine, and physics all apply to the space research environment. The term includes scientific payloads at any altitude from deep space to low Earth orbit, extended to include sounding rocket research in the upper atmosphere, and high-altitude balloons. Space exploration is also a form of space research. History Rockets Chinese rockets were used in ceremony and as weaponry since the 13th century, but no rocket would overcome Earth's gravity until the latter half of the 20th century. Space-capable rocketry appeared simultaneously in the work of three scientists, in three separate countries. In Russia, Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, in the United States, Robert H. Goddard, and in Germany, Hermann Oberth. The United States and the Soviet Union c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid Mining
Asteroid mining is the hypothetical exploitation of materials from asteroids and other minor planets, including near-Earth objects. Notable asteroid mining challenges include the high cost of spaceflight, unreliable identification of asteroids which are suitable for mining, and the challenges of extracting usable material in a space environment. Asteroid sample return research missions (see completed missions '' Hayabusa'' and ''Hayabusa2'' and in-progress '' OSIRIS-REx'') illustrate the challenges of collecting ore from space using current technology. As of 2021, less than 1 gram of asteroid material has been successfully returned to Earth from space. In progress missions promise to increase this amount to approximately 60 grams (two ounces). Asteroid research missions are complex endeavors and return a tiny amount of material (less than 1 milligram ''Hayabusa'', 100 milligrams ''Hayabusa2'', 60 grams planned ''OSIRIS-REx'') relative to the size and expense of these project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
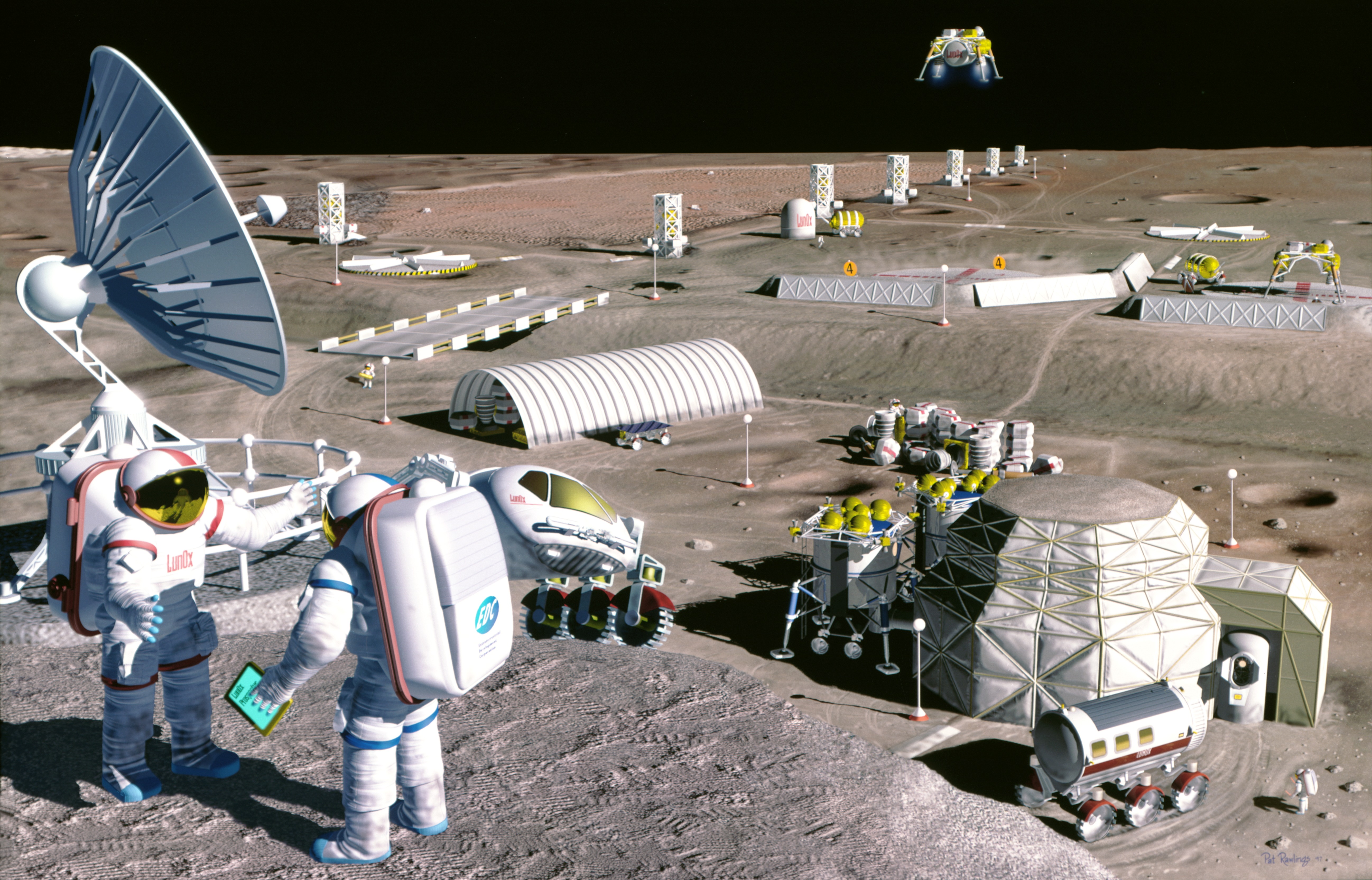
Space Colonization
Space colonization (also called space settlement or extraterrestrial colonization) is the use of outer space or celestial bodies other than Earth for permanent habitation or as extraterrestrial territory. The inhabitation and territorial use of extraterrestrial space has been proposed to be realized by for example building space settlements or extraterrestrial mining enterprises. To date, no permanent space settlement other than temporary space habitats have been set up, nor any extraterrestrial territory or land has been legally claimed. Making territorial claims in space is prohibited by international space law, defining space as a common heritage. International space law has had the goal to prevent colonial claims and militarization of space, advocating the installation of international regimes to regulate access to and sharing of space, particularly for specific locations such as the limited space of geostationary orbit or the Moon. Many arguments both for an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space-based Economy
Space-based economy is economic activity in outer space, including asteroid mining, space manufacturing, space trade, construction performed in space such as the building of space stations, space burial, and space advertising. Space-based industrial efforts are presently in their infancy. Most such concepts would require a considerable long-term human presence in space and relatively low-cost access to space. The majority of proposals would also require technological or engineering developments in areas such as robotics, solar energy, and life support systems. Some analysts have argued for creating an International Bank, to support deep space exploration. See also * NewSpace * Space colonization Space colonization (also called space settlement or extraterrestrial colonization) is the use of outer space or celestial bodies other than Earth for permanent habitation or as extraterrestrial territory. The inhabitation and territor ... References {{s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Exploration Of Mars
The idea of sending humans to Mars has been the subject of aerospace engineering and scientific studies since the late 1940s as part of the broader exploration of Mars. Some have also considered exploring the Martian moons of Phobos and Deimos. Long-term proposals have included sending settlers and terraforming the planet. Proposals for human missions to Mars came from e.g. NASA, Russia, Boeing, and SpaceX. As of 2022, only robotic landers and rovers have been on Mars. The farthest humans have been beyond Earth is the Moon. Conceptual proposals for missions that would involve human explorers started in the early 1950s, with planned missions typically being stated as taking place between 10 and 30 years from the time they are drafted. The list of crewed Mars mission plans shows the various mission proposals that have been put forth by multiple organizations and space agencies in this field of space exploration. The plans for these crews have varied—from scientific expedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Zubrin
Robert Zubrin (; born April 9, 1952) is an American aerospace engineer, author, and advocate for human exploration of Mars. He and his colleague at Martin Marietta, David Baker, were the driving force behind Mars Direct, a proposal in a 1990 research paper intended to produce significant reductions in the cost and complexity of such a mission. The key idea was to use the Martian atmosphere to produce oxygen, water, and rocket propellant for the surface stay and return journey. A modified version of the plan was subsequently adopted by NASA as their "design reference mission". He questions the delay and cost-to-benefit ratio of first establishing a base or outpost on an asteroid or another Apollo program-like return to the Moon, as neither would be able to provide all of its own oxygen, water, or energy; these resources are producible on Mars, and he expects people would be there thereafter. Disappointed with the lack of interest from government in Mars exploration and after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'', also widely referred to as ''Science Magazine'', is the peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature'' cover the full ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national "newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)







.png)