|
Spa Road Railway Station
Spa Road railway station in Bermondsey, south-east London, was the original terminus of the capital's first railway, the London and Greenwich Railway (L&GR). It was also the first railway terminus in what is now Greater London. First opened in 1836, the station went through several changes of ownership, was rebuilt several times, changed its name and was relocated a couple of hundred yards away from its original site before it closed in 1915 due to cost-saving measures during the First World War. The disused station building is today part of a light industrial estate. A number of elements of the original station – including the ticket office and remnants of the platforms – are still visible. History First station (1836–1838) In 1833 an Act of Parliament granted the L&GR the rights to build a viaduct from the south end of London Bridge to Greenwich and to run trains along it. However, the line was partially opened to the public well before its full length had been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
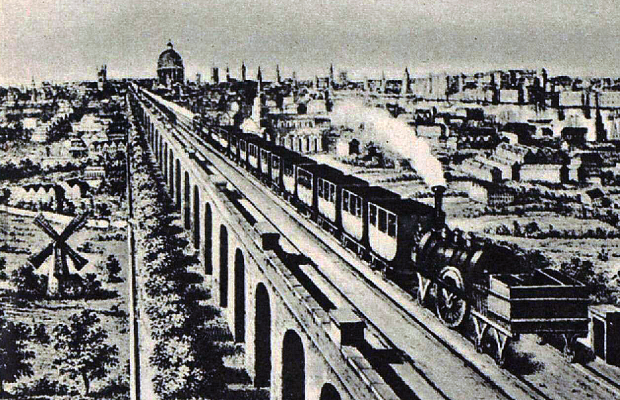
London And Greenwich Railway
The London and Greenwich Railway (L&GR) was opened in London between 1836 and 1838. It was the first steam railway in the capital, the first to be built specifically for passengers, and the first entirely elevated railway. Origins The idea for the line came from Colonel George Thomas Landmann, until 1824 a Royal Engineer, and George Walter, and the company was floated at a meeting on 25 November 1831. It would run from close to London Bridge, convenient for journeys to the City. It would be some long, on a viaduct of 878 brick arches, some of them skew (see London Bridge-Greenwich Railway Viaduct), to avoid level crossings over the many streets which were already appearing in the south of London. Landmann planned to rent the arches out as workshops. The intention had been to descend to ground level after the Grand Surrey Canal but this was opposed by Parliament. The first Act of Parliament was obtained in 1833 for a line from Tooley Street (now London Bridge) to London Street, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charing Cross Railway Station
Charing Cross railway station (also known as London Charing Cross) is a central London railway terminus between the Strand and Hungerford Bridge in the City of Westminster. It is the terminus of the South Eastern Main Line to Dover via Ashford. All trains are operated by Southeastern, which provides the majority of commuter and regional services to south-east London and Kent. It is connected to Charing Cross Underground station and is near to Embankment Underground station and Embankment Pier. The station was originally opened by the South Eastern Railway in 1864. It takes its name from its proximity to the road junction Charing Cross, the notional "centre of London" from which distances from the city are measured. During the 19th century the station became the main London terminus for continental traffic via boat trains, and served several prestigious international services. It was badly damaged by an engineering accident in 1905 and extensively rebuilt, subsequently beco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Opened In 1836
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenwich Line
The Greenwich line is a short railway line in South London that follows part of the route of the London and Greenwich Railway, which was the first railway line in London. The line diverges from the South Eastern Main Line at North Kent East junction and runs as far as Charlton junction where it connects with the North Kent Line. Stations * * * * History The line was electrified with the other SE&CR local routes to Dartford on 6 June 1926 by Southern Railway. From 12 January 2015, services using the Greenwich line were no longer able to serve London Charing Cross. This is due to the Thameslink Programme work, which removed the diamond crossing at Spa Road Junction, located between London Bridge and Deptford. As a result of this, trains using the Greenwich line could no longer reach the lines going into Charing Cross. To compensate for the loss of this, London Cannon Street was given revised service times, with it being open seven days a week and until the end of service. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neal's Yard Dairy
Neal's Yard Dairy is a London artisanal cheese retailer, wholesaler and (formerly) cheesemaker in London, which was founded in 1979. It has been described as "London's foremost cheese store." History Neal's Yard Dairy was founded in 1979 by Nicholas Saunders and Randolph Hodgson as a cheesemaker's shop. The original store, located in Neal's Yard, Covent Garden, London, is considered an important part of the revival of the immediate area. The shop moved around the corner to 17 Shorts Gardens in 1992. One of the first customers was Monty Python's John Cleese. The new owners were still learning how to make cheese, and "had only managed yoghurt that day, so it all rather descended into a Monty Python sketch". Despite this rocky start, the store grew from a cheesemaker into a retailer of artisanal, mostly British and Irish cheeses (including farmhouse Cheddar cheese and varieties such as Stinking Bishop), spinning off the cheesemaking operation as ''Neal's Yard Creamery'' in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monmouth Coffee Company
Monmouth Coffee Company is a coffee roaster, retailer and wholesaler in London, which was founded in 1978. It played an important role in regenerating Neal's Yard and Borough Market. It has remained focused on roasting and selling coffee beans and was one of the foundations for the third wave of coffee in London after the year 2000. History Monmouth Coffee was founded in 1978 by Nick Saunders and Anita Le Roy. Le Roy later took over the business. Together with Neal's Yard Dairy and Saunders' other businesses, Monmouth Coffee transformed the run down area around Neal's Yard in Covent Garden, central London. The original shop is at 27 Monmouth Street (), a grade II listed 18th-century terraced house. The basement was used to roast coffee and the ground floor as a tasting room. In its early years, the shop sold three or four kinds of green or roast coffee beans in sacks containing one, three, seven or ten pounds. Le Roy wanted to buy coffee from individual farmers, but that was no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spa Road Junction Rail Crash
The Spa Road Junction rail crash was an accident on the British railway system which occurred during the peak evening rush hour of 8 January 1999 at Spa Road Junction in Bermondsey, in South East London. The incident On a dark and wet evening, a Connex South Eastern train from Dover Priory to Charing Cross collided with a Thameslink train from Brighton to Bedford causing derailment to both trains. The accident resulted in no fatalities and four injuries. The Thameslink train had been held at a danger (red) signal until the route was set for it to cross from the Brighton Main Line onto the London Bridge Up Loop Line, and the signal then cleared. The Connex train, which was approaching from behind, passed a preliminary caution (double yellow) signal then a caution (yellow) signal and then a danger (red) signal. It continued for 283 metres (309 yards) past the red signal until the point where the two lines converged. It was travelling at an estimated speed of when it collided w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Cross Station
New Cross railway station serves New Cross in south-east London, England. It is down the line from and is in London fare zone 2. The platforms are lettered rather than numbered to avoid confusion with those at by staff who worked at both stations before privatisation of the stations in 1997. Platform D is used exclusively by London Overground services. Ticket barriers control access to all platforms. History In the early Victorian railway boom two companies constructed lines through the area. The London and Croydon Railway (L&CR) built a station on the New Cross Road close to Hatcham in 1839. On 14 October 1844 a large fire that broke out in a paint shop destroyed carriage and engine sheds and workshops adjacent to the station. The fire was witnessed by Louis Philippe I, King of France who was travelling from the station to Dover. On 30 July 1849 the South Eastern Railway (SER) opened a station at North Kent Junction when the North Kent line opened linking Strood with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British railway companies, and was privatised in stages between 1994 and 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. The period of nationalisation saw sweeping changes in the railway. A process of dieselisation and electrification took place, and by 1968 steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction, except for the Vale of Rheidol Railway (a narrow-gauge tourist line). Passengers replaced freight as the main source of business, and one-third of the network was closed by the Beeching cuts of the 1960s in an effort to reduce rail subsidies. On privatis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
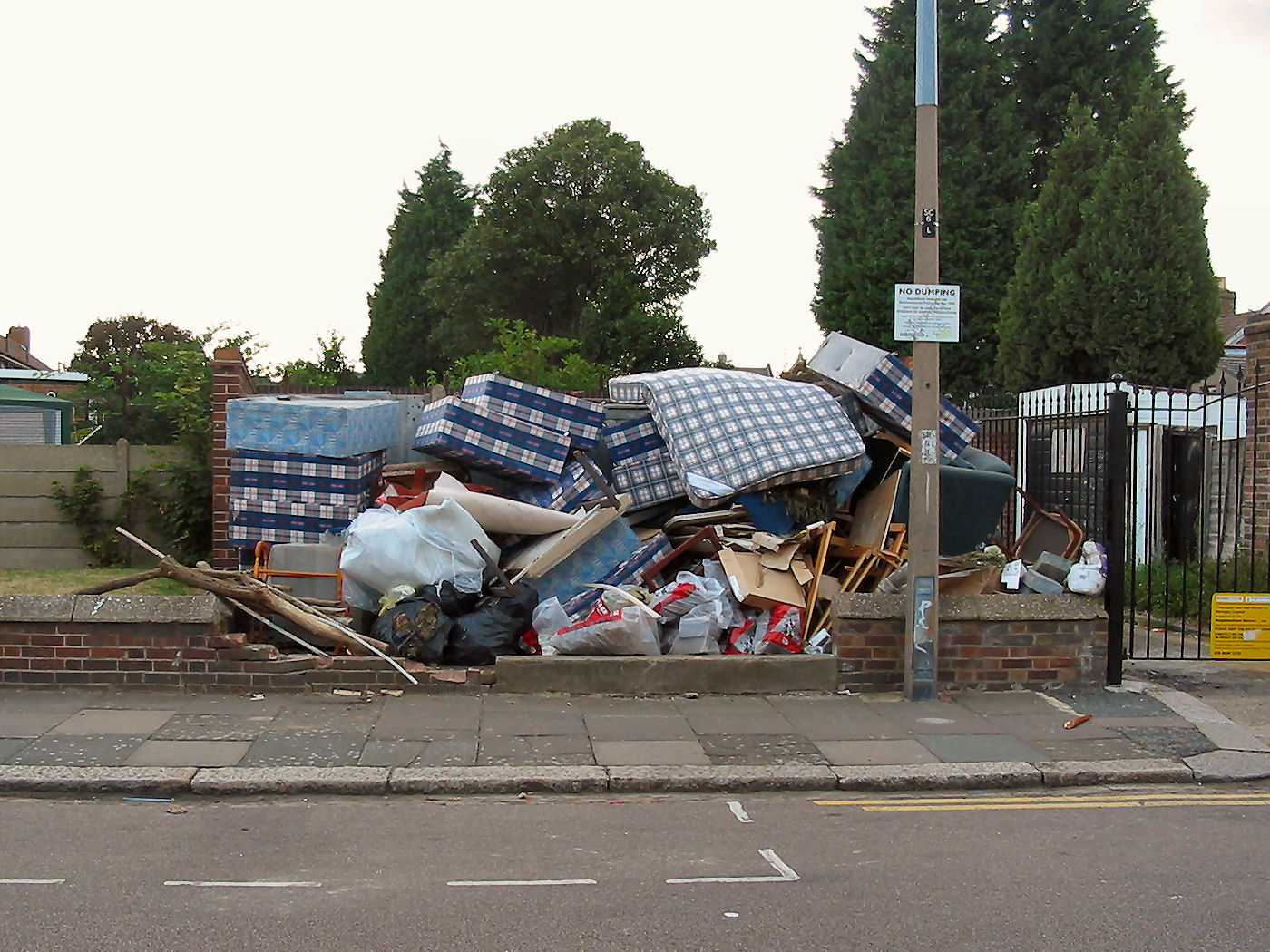
Illegal Dumping
Illegal dumping, also called fly dumping or fly tipping ( UK), is the dumping of waste illegally instead of using an authorized method such as curbside collection or using an authorized rubbish dump. It is the illegal deposit of any waste onto land, including waste dumped or tipped on a site with no license to accept waste. The United States Environmental Protection Agency developed a “profile” of the typical illegal dumper. Characteristics of offenders include local residents, construction and landscaping contractors, waste removers, scrap yard operators, and automobile and tire repair shops. Terminology Illegal dumping is typically distinguished from littering by the type and amount of material and/or the manner in which it is discarded. An example of littering could be throwing a cigarette on the ground. However, emptying a rubbish bin with no permission in a public or private area can be classified as illegal dumping. The term ''fly tipping'' is derived from the verb '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwark Park Railway Station
Southwark Park was a railway station in Bermondsey, south-east London, on the Greenwich Line between and . It was opened by the South Eastern and Chatham Railway on 1 October 1902, on approximately the same site as the then long-closed Commercial Dock railway station. It was close to the southern end of Southwark Park, from which it took its name. South Bermondsey railway station, on the South London Line, is nearby. The station was constructed on a section of extra wide arches running from west of Rotherhithe New Road to east of the road. Two loop lines ran through the station, which was controlled by the Corbetts Lane Signal Cabin (later renamed Southwark Park Station Signal Cabin). Passengers boarded trains from two island platforms, reached from ground level via ramped approaches. Each platform was long, with waiting rooms and a roof long. A booking hall and station offices stood at ground level. The station did not attract much traffic, as an electric tramway ran nea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


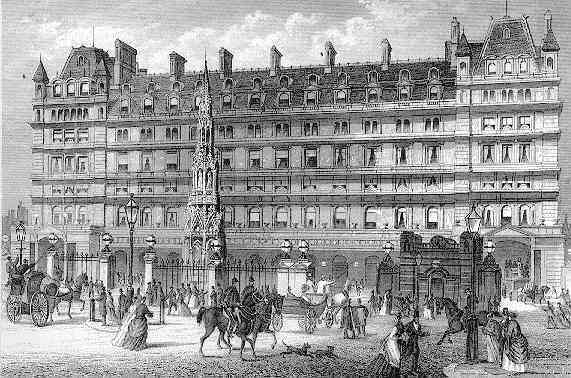


.jpg)
