|
Soyuz 38
Soyuz 38 was a human spaceflight mission conducted by the Soviet Union during September, 1980. The Soyuz spacecraft brought two visiting crew members to the Salyut 6 space station, one of whom was an Intercosmos cosmonaut from Cuba. Crew Backup crew Mission parameters *Mass: 6800 kg *Perigee: 199.7 km *Apogee: 273.5 km *Inclination: 51.63° *Period: 88.194 minutes Mission highlights 12th expedition to Salyut 6. 7th international crew. Carried Intercosmos cosmonaut from Cuba. The Soyuz 38 docking occurred in darkness. As the spacecraft approached Salyut 6, the crew on the space station could see only its “headlights.” Ryumin filmed ignition and operation of the transport's main engine. Arnaldo Tamayo Méndez of Cuba and Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Romanenko docked without incident. The purpose of the Soyuz 38 mission was to carry out nine experiments. They stimulated different areas of the brain to further understand the electrical activity in our brain. This wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 7K-T
The second generation of the Soyuz spacecraft, the ''Soyuz 7K-T'', comprised Soyuz 12 through Soyuz 40 (1973-1981). In the wake of the Soyuz 11 tragedy, the spacecraft was redesigned to accommodate two cosmonauts who would wear pressure suits at all times during launch, docking, undocking, and reentry. The place of the third cosmonaut was taken by extra life-support systems. Finally, the 7K-T, being intended purely as a space station ferry, had no solar panels, instead sporting two large whip antennas in their place. As a result, it relied on batteries which only provided enough power for two days of standalone flight. The idea was that the Soyuz would recharge while docked with a Salyut space station, but in the event of a docking or other mission failure (which ended up happening on several occasions), the crew was forced to power off everything except communications and life support systems until they could reenter. Two test flights of the 7K-T were conducted prior to comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
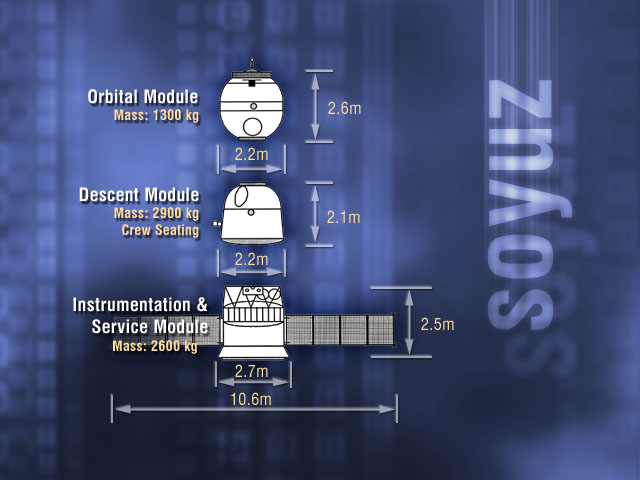
Soyuz (spacecraft)
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Between the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle and the 2020 demo flight of SpaceX Crew Dragon, the Soyuz served as the only means to ferry crew to or from the International Space Station, for which it remains heavily used. Although China did launch crewed Shenzhou flights during this time, none of them docked with the ISS. History The first Soyuz flight was uncrewed and started on 28 November 1966. The first Soyuz mission with a crew, Soyuz 1, launched on 23 April 1967 but ended with a crash due to a parachute failure, killing cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov. The following flight was uncrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1980 In Cuba
__NOTOC__ Year 198 (CXCVIII) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sergius and Gallus (or, less frequently, year 951 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 198 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire *January 28 **Publius Septimius Geta, son of Septimius Severus, receives the title of Caesar. **Caracalla, son of Septimius Severus, is given the title of Augustus. China *Winter – Battle of Xiapi: The allied armies led by Cao Cao and Liu Bei defeat Lü Bu; afterward Cao Cao has him executed. By topic Religion * Marcus I succeeds Olympianus as Patriarch of Constantinople (until 211). Births * Lu Kai (or Jingfeng), Chinese official and general (d. 269) * Quan Cong, Chinese general and advisor (d. 24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Launched By Soyuz-U Rockets
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Which Reentered In 1980
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Launched In 1980
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Salyut Expeditions
This is a chronological list of expeditions to the Salyut space stations. Initially these expeditions were not numbered, however the crews of Salyut 6 and Salyut 7 were numbered , where ''n'' is sequentially increased with each expedition to that particular station. Taxi crews are excluded from this list (see List of human spaceflights to Salyut space stations for details). Salyut commanders are listed in ''italics''. "Duration" refers to the crew and does not always correspond to "Flight up" or "Flight down". Missions which failed to reach or dock with the station are highlighted in red. The Salyut programme was a series of Soviet space stations launched during the 1970s and 1980s. Six Salyut space stations were crewed, whilst a number of other stations were not, either due to failures, or because they were prototypes and not designed to be crewed. Crewed flights as part of the Salyut programme ended in 1986, when Salyut was superseded by the Mir space station. See also * Salyut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Human Spaceflights To Salyut Space Stations
This is a chronological list of human spaceflights to the Salyut space stations. Prior to Salyut 6, flights were referred to by the designation of the Soyuz spacecraft that transported the crew to and from the station. Flights to Salyut 6 and Salyut 7 were numbered either for long-term expedition crews, or for short-term visiting or taxi crews, where ''n'' was sequentially increased with each flight of that type to that particular station. Salyut commanders are listed in ''italics''. "Duration" refers to the crew and does not always correspond to "Flight up" or "Flight down". Missions which failed to reach or dock with the station are listed in red. All cosmonauts are Soviet unless otherwise indicated. The Salyut programme was a series of Soviet space stations launched during the 1970s and 1980s. Six Salyut space stations were crewed in addition to a number of prototypes and failures. Crewed flights as part of the Salyut programme ended in 1986 as efforts were shifted to Mir. Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 35
Soyuz 35 (russian: Союз 35, ''Union 35'') was a 1980 Soviet crewed space flight to the Salyut 6 space station. It was the 10th mission to and eighth successful docking at the orbiting facility. The Soyuz 35 crew were the fourth long-duration crew to man the space station.The mission report is available here: http://www.spacefacts.de/mission/english/soyuz-35.htm Cosmonauts Leonid Popov and Valery Ryumin spent 185 days in space, setting a new space endurance record. Ryumin had completed a previous mission only eight months before. They hosted four visiting crews, including the first Hungarian, Cuban and Vietnamese cosmonauts. As long-duration crews now routinely swapped spacecraft with incoming crew, the Soyuz 35 craft was used to return the visiting Soyuz 36 crew to Earth, while the resident crew returned in Soyuz 37. Crew Backup crew Mission parameters *Mass: *Perigee: *Apogee: *Inclination: 51.65° *Period: 88.81 minutes Crew launch, station activation Soyuz 35 wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jose Lopez Falcon
Jose is the English transliteration of the Hebrew and Aramaic name ''Yose'', which is etymologically linked to ''Yosef'' or Joseph. The name was popular during the Mishnaic and Talmudic periods. * Jose ben Abin * Jose ben Akabya *Jose the Galilean *Jose ben Halafta *Jose ben Jochanan *Jose ben Joezer of Zeredah * Jose ben Saul Given name Male * Jose (actor), Indian actor * Jose C. Abriol (1918–2003), Filipino priest * Jose Advincula (born 1952), Filipino Catholic Archbishop * Jose Agerre (1889–1962), Spanish writer * Jose Vasquez Aguilar (1900–1980), Filipino educator * Jose Rene Almendras (born 1960), Filipino businessman * Jose T. Almonte (born 1931), Filipino military personnel * Jose Roberto Antonio (born 1977), Filipino developer * Jose Aquino II (born 1956), Filipino politician * Jose Argumedo (born 1988), Mexican professional boxer * Jose Aristimuño, American political strategist * Jose Miguel Arroyo (born 1945), Philippine lawyer * Jose D. Aspiras (1924–1999 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yevgeni Khrunov
Yevgeny Vasilyevich Khrunov (; 10 September 1933 – 20 May 2000) was a Soviet cosmonaut who flew on the Soyuz 5/Soyuz 4 mission. Early life Yevgeny Khrunov was born on 10 September 1933 to Vasily Yegorevich and Agrafena Nikolayevna. Nicknamed “Zhenya” he had five brothers and two sisters. Khrunov's family was a farming family. Khrunov married Svetlana Sokolyuk and had a son on 13 July 1959. He was born in Prudy, Tula Oblast, Russian SFSR. Education and career Khrunov began officially being schooled in 1941. Khrunov was initially interested in pursuing farming in studies. His interest in flying would soon follow after he watched the planes during wartime. Once he graduated from primary school he enrolled at Kashira Agricultural Secondary School on scholarship and would graduate from there in 1952. His teachers regularly spoke highly of him and considered him a hard working student. In 1952 Khrunov was also drafted into the Soviet Army where he would follow his interests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |