|
Soyuz 1
Soyuz 1 (, ''Union 1'') was a crewed spaceflight of the Soviet space program. Launched into orbit on 23 April 1967 carrying cosmonaut colonel Vladimir Komarov, Soyuz 1 was the first crewed flight of the Soyuz spacecraft. The flight was plagued with technical issues, and Komarov was killed when the descent module crashed into the ground due to a parachute failure. This was the first in-flight fatality in the history of spaceflight. The original mission plan was complex, involving a rendezvous with Soyuz 2 and an exchange of crew members before returning to Earth. However, the launch of Soyuz 2 was called off due to thunderstorms. Crew Backup crew Mission parameters * Mass: * Perigee: * Apogee: * Inclination: 50.8° * Period: 88.7 minutes Background Soyuz 1 was the first crewed flight of the first-generation Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft and Soyuz rocket, designed as part of the Soviet lunar program. It was the first Soviet crewed spaceflight in over two years, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
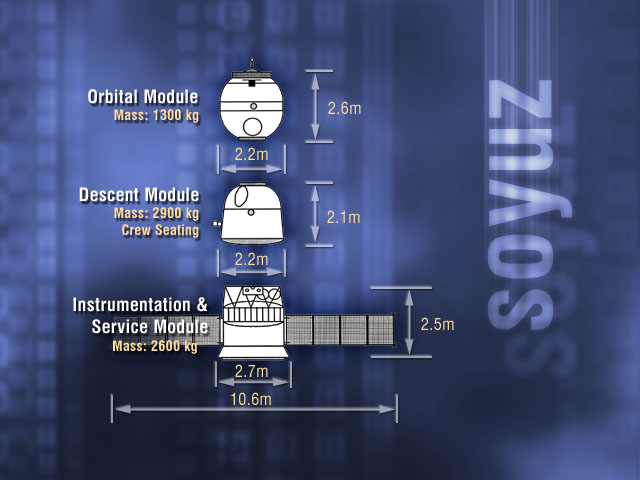
Soyuz (spacecraft)
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia (corporation), Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched atop the similarly named Soyuz (rocket family), Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Following the Soviet Union's dissolution, Roscosmos, the Russian space agency, continued to develop and utilize the Soyuz. Between the Space Shuttle retirement, Space Shuttle's 2011 retirement and the SpaceX Crew Dragon's 2020 debut, Soyuz was the sole means of crewed transportation to and from the International Space Station, a role it continues to fulfill. The Soyuz design has also influenced other spacecraft, including China's Shenzhou (spacecraft), Shenzhou and Russia's Progress (spacecraft), Progress cargo vehicle. The Soyu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Korolev
Sergei Pavlovich Korolev (14 January 1966) was the lead Soviet Aerospace engineering, rocket engineer and spacecraft designer during the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union in the 1950s and 1960s. He invented the R-7 Semyorka, R-7 Rocket, Sputnik 1, and was involved in the launching of Laika, Sputnik 3, the first luna 2, human-made object to make contact with another celestial body, Soviet space dogs#Belka and Strelka, Belka and Strelka, the first human being, Yuri Gagarin, into space, Voskhod 1, and the first person, Alexei Leonov, to conduct a Voskhod 2, spacewalk. Although Korolev trained as an aircraft designer, his greatest strengths proved to be in design integration, organization and strategic planning. Arrested on a false official charge as a "member of an anti-Soviet counter-revolutionary organization" (which would later be reduced to "saboteur of military technology"), he was imprisoned in 1938 for almost six years, including a few months in a K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Crewed Lunar Programs
The Soviet crewed lunar programs were a series of programs pursued by the Soviet Union to Moon landing, land humans on the Moon, Space Race, in competition with the United States Apollo program. The Soviet government publicly denied participating in such a competition, but secretly pursued two programs in the 1960s: crewed lunar flyby missions using Soyuz 7K-L1 (Zond) spacecraft launched with the Proton-K rocket, and a crewed lunar landing using Soyuz 7K-LOK and LK (spacecraft), LK spacecraft launched with the N1 (rocket), N1 rocket. Following the dual American successes of the first crewed lunar orbit on 24–25 December 1968 (Apollo 8) and the first Moon landing on July 20, 1969 (Apollo 11), and a series of catastrophic N1 failures, both Soviet programs were eventually brought to an end. The Proton-based Zond program was canceled in 1970, and the N1-L3 program was ''de facto'' terminated in 1974 and officially canceled in 1976. Details of both Soviet programs were kept secret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz Rocket
The Soyuz (, meaning "union", GRAU index 11A511) was a Soviet expendable carrier rocket designed in the 1960s by OKB-1 and manufactured by State Aviation Plant No. 1 in Kuybyshev, Soviet Union. It was commissioned to launch Soyuz spacecraft as part of the Soviet human spaceflight program, first with eight uncrewed test flights, followed by the first 19 crewed launches. The original Soyuz also propelled four test flights of the improved Soyuz 7K-T capsule between 1972 and 1974. It flew 30 successful missions over ten years and suffered two failures. The Soyuz 11A511 type, a member of the R-7 family of rockets, first flew in 1966 and was an attempt to standardize the R-7 family and get rid of the variety of models that existed up to that point. It was basically a Molniya 8K78M without the Blok L stage. It featured the 8D74M RD-107 and the RD-110 engines from the 8K78M, The new, uprated core stage and strap-ons became standard for all R-7 derived launch vehicles to replace the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets, exoplanets orbiting other stars, or binary stars. It may also refer to the time it takes a satellite orbiting a planet or moon to complete one orbit. For celestial objects in general, the orbital period is determined by a 360° revolution of one body around its primary, ''e.g.'' Earth around the Sun. Periods in astronomy are expressed in units of time, usually hours, days, or years. Its reciprocal is the orbital frequency, a kind of revolution frequency, in units of hertz. Small body orbiting a central body According to Kepler's Third Law, the orbital period ''T'' of two point masses orbiting each other in a circular or elliptic orbit is: :T = 2\pi\sqrt where: * ''a'' is the orbit's semi-major axis * ''G'' is the gravitationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Earth directly above the Equator, the plane of the satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that it is tilted, spending half an orbit over the northern hemisphere and half over the southern. If the orbit swung between 20° north latitude and 20° south latitude, then its orbital inclination would be 20°. Orbits The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually the plane containing the planet's equator. For pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apogee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values. Apsides pertaining to orbits around different bodies have distinct names to differentiate themselves from other apsides. Apsides pertaining to geocentric orbits, orbits around the Earth, are at the farthest point called the ''apogee'', and at the nearest point the ''perigee'', like with orbits of satellites and the Moon around Earth. Apsides pertaining to orbits around the Sun are named ''aphelion'' for the farthest and ''perihelion'' for the nearest point in a heliocentric orbit. Earth's two apsides are the farthest point, ''aphelion'', and the nearest point, ''perihelion'', of its orbit around the host Sun. The terms ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion'' apply in the same way to the orbits of Jupiter and the other planets, the comets, and the asteroids of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass
Mass is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic property of a physical body, body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the physical quantity, quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particle, elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple Mass in special relativity, definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure (mathematics), measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the Force, strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is Mass versus weight, not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuri Gagarin
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin; Gagarin's first name is sometimes transliterated as ''Yuriy'', ''Youri'', or ''Yury''. (9 March 1934 – 27 March 1968) was a Soviet pilot and cosmonaut who, aboard the first successful Human spaceflight, crewed spaceflight, became the first person to journey into outer space. Travelling on Vostok 1, Gagarin completed one orbit of Earth on 12 April 1961, with his flight taking 108 minutes. By achieving this major milestone for the Soviet Union amidst the Space Race, he became an international celebrity and was awarded many medals and titles, including his country's highest distinction: Hero of the Soviet Union. Hailing from the village of Klushino in the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR, Gagarin was a foundryman at a steel plant in Lyubertsy in his youth. He later joined the Soviet Air Forces as a pilot and was stationed at the Luostari/Pechenga (air base), Luostari Air Base, near the Norway–Russia border, Norway–Soviet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |