|
SoxC Group
SoxC group is group C of Sry-related HMG box proteins transcription factors. SoxC genes play an important role in determining the cell fate of neuronal mesenchymal progenitor cells in many developmental processes.Huang, J. et al. The transcription factor sry-related HMG box-4 (SOX4) is required for normal renal development in vivo. ''Dev. Dynamics'' 2013, ''242,'' no p.n/ref> In ''Drosophila melanogaster'' (fly), ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' (worm), and other lower animals SoxC is made up of only one member, but humans, mice and most other vertebrates have three members of the SoxC group.Dy, P. et al. The three SoxC proteins–Sox4, Sox11 and Sox12–exhibit overlapping expression patterns and molecular properties. ''Nucleic Acids Research'' 2008, ''36'', 3101–311/ref> The three are Sox4, Sox11, and Sox12. These three are extremely similar to one another, more so than other proteins, but they are all highly distinct in the way that they bind DNA and active Transcription (genetics) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testis Determining Factor
Sex-determining region Y protein (SRY), or Testis-determining factor (TDF), is a DNA-binding protein (also known as gene-regulatory protein/transcription factor) encoded by the ''SRY'' gene that is responsible for the initiation of male sex determination in therian mammals (placental mammals and marsupials). SRY is an intronless sex-determining gene on the Y chromosome. Mutations in this gene lead to a range of disorders of sex development with varying effects on an individual's phenotype and genotype. TDF is a member of the SOX (SRY-like box) gene family of DNA-binding proteins. When complexed with the SF1 protein, TDF acts as a transcription factor that causes upregulation of other transcription factors, most importantly SOX9. Its expression causes the development of primary sex cords, which later develop into seminiferous tubules. These cords form in the central part of the yet-undifferentiated gonad, turning it into a testis. The now-induced Leydig cells of the testis t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
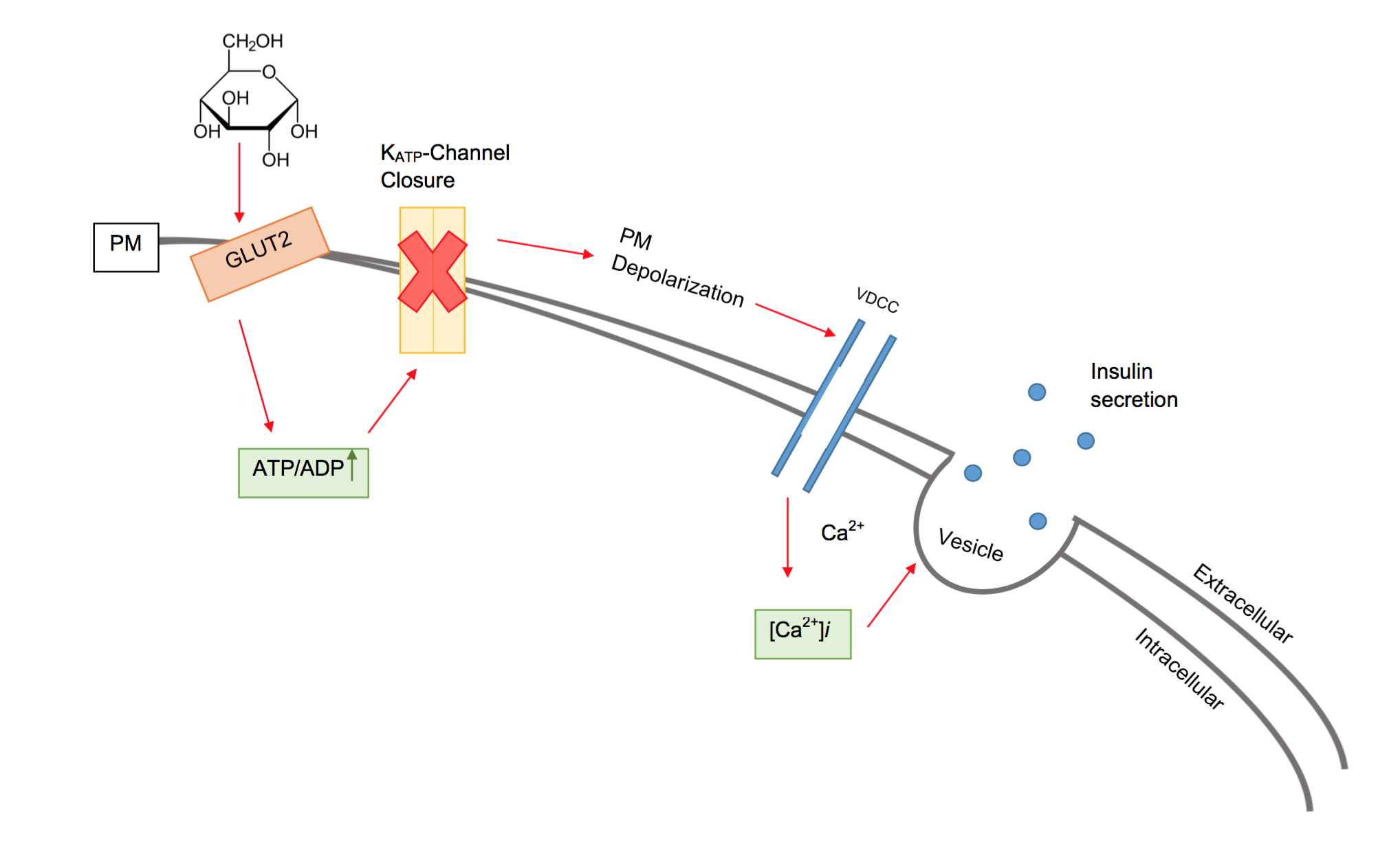
Beta Cells
Beta cells (β-cells) are a type of cell found in pancreatic islets that synthesize and secrete insulin and amylin. Beta cells make up 50–70% of the cells in human islets. In patients with Type 1 diabetes, beta-cell mass and function are diminished, leading to insufficient insulin secretion and hyperglycemia. Function The primary function of a beta cell is to produce and release insulin and amylin. Both are hormones which reduce blood glucose levels by different mechanisms. Beta cells can respond quickly to spikes in blood glucose concentrations by secreting some of their stored insulin and amylin while simultaneously producing more. Primary cilia on beta cells regulate their function and energy metabolism. Cilia deletion can lead to islet dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Insulin synthesis Beta cells are the only site of insulin synthesis in mammals. As glucose stimulates insulin secretion, it simultaneously increases proinsulin biosynthesis, mainly through translational cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoblasts
Osteoblasts (from the Greek language, Greek combining forms for "bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cell (biology), cells with a single Cell nucleus, nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the process of bone formation, osteoblasts function in groups of connected cells. Individual cells cannot make bone. A group of organized osteoblasts together with the bone made by a unit of cells is usually called the osteon. Osteoblasts are specialized, terminally differentiated products of mesenchymal stem cells. They synthesize dense, crosslinked collagen and specialized proteins in much smaller quantities, including osteocalcin and osteopontin, which compose the organic matrix of bone. In organized groups of disconnected cells, osteoblasts produce hydroxylapatite, the bone mineral, that is deposited in a highly regulated manner, into the organic matrix forming a strong and dense mineralized tissues, mineralized tissue, the mineralized mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adaptive immunity), and B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity). They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte". Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells. Types The three major types of lymphocyte are T cells, B cells and natural killer (NK) cells. Lymphocytes can be identified by their large nucleus. T cells and B cells T cells (thymus cells) and B cells ( bone marrow- or bursa-derived cells) are the major cellular components of the adaptive immune response. T cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity, whereas B cells are primarily responsible for humoral immunity (relating to antibodies). The function of T cells and B cells is to recognize specif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleft Palate
A cleft lip contains an opening in the upper lip that may extend into the nose. The opening may be on one side, both sides, or in the middle. A cleft palate occurs when the palate (the roof of the mouth) contains an opening into the nose. The term orofacial cleft refers to either condition or to both occurring together. These disorders can result in feeding problems, speech problems, hearing problems, and frequent ear infections. Less than half the time the condition is associated with other disorders. Cleft lip and palate are the result of tissues of the face not joining properly during development. As such, they are a type of birth defect. The cause is unknown in most cases. Risk factors include smoking during pregnancy, diabetes, obesity, an older mother, and certain medications (such as some used to treat seizures). Cleft lip and cleft palate can often be diagnosed during pregnancy with an ultrasound exam. A cleft lip or palate can be successfully treated with surgery. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malformations
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at childbirth, birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disability, disabilities that may be physical disability, physical, intellectual disability, intellectual, or developmental disability, developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic disorder, metabolic and degenerative disease, degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic disorder, genetic or chromosome abnormality, chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain vertically transmitted infection, infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Genetics
Conservation genetics is an interdisciplinary subfield of population genetics that aims to understand the dynamics of genes in populations principally to avoid extinction. Therefore, it applies genetic methods to the conservation and restoration of biodiversity. Researchers involved in conservation genetics come from a variety of fields including population genetics, molecular ecology, biology, evolutionary biology, and systematics. Genetic diversity is one of the three fundamental levels of biodiversity, so it is directly important in conservation. Genetic variability influences both the health and long-term survival of populations because decreased genetic diversity has been associated with reduced fitness, such as high juvenile mortality, diminished population growth, reduced immunity, and ultimately, higher extinction risk. Genetic diversity Genetic diversity is the variability of genes in a species. A number of means can express the level of genetic diversity: observed hete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-translational Modification
Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. This process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signaling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones. Post-translational modifications can occur on the amino acid side chains or at the protein's C- or N- termini. They can extend the chemical repertoire of the 20 standard amino acids by modifying an existing functional group or introducing a new one such as phosphate. Phosphorylation is a highly effective mechanism for regulating the activity of enzymes and is the most common post-translational modification. Many eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins also have carbohydrate molecules attached to them in a process called glycosyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminal
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Mobility Group
High-Mobility Group or HMG is a group of chromosomal proteins that are involved in the regulation of DNA-dependent processes such as transcription, replication, recombination, and DNA repair. Families The HMG proteins are subdivided into 3 superfamilies each containing a characteristic functional domain: * HMGA – contains an AT-hook domain ** HMGA1 ** HMGA2 * HMGB – contains a HMG-box domain ** HMGB1 ** HMGB2 ** HMGB3 ** HMGB4 * HMGN – contains a nucleosomal binding domain ** HMGN1 ** HMGN2 ** HMGN3 ** HMGN4 ** HMGN5 Proteins containing any of these embedded in their sequence are known as HMG motif proteins. HMG-box proteins are found in a variety of eukaryotic organisms. They were originally isolated from mammalian cells, and named according to their electrophoretic mobility in polyacrylamide gels. Other families with HMG-box domain * SOX gene family ** Sex-Determining Region Y Protein ** SOX1, SOX2, etc. * TCF/LEF family (T cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Domain
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins. Background The concept of the domain was first proposed in 1973 by Wetlaufer aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |