|
Sowilō (rune)
Sowilo (*''sōwilō''), meaning "sun", is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic language name of the ''s''-rune (ᛊ, ᛋ). The letter is a direct adoption of Old Italic scripts, Old Italic (Etruscan or Latin) ''s'' (𐌔), ultimately from Greek sigma (Σ). It is present in the earliest inscriptions of the 2nd to 3rd century (Vimose inscriptions, Vimose, Spearhead of Kovel, Kovel). The name is attested for the same rune in all three Rune Poems. It appears as Old Norse and Old Icelandic Sól and as Old English Sigel. Name The Germanic words for "Sun" have the peculiarity of Alternation (linguistics), alternating between ''-l-'' and ''-n-'' stems, Proto-Germanic ''*sunnon'' (Old English ''sunne'', Old Norse, Old Saxon and Old High German ''sunna'') vs. *''sōwilō'' or *''sōwulō'' (Old Norse ''sól'', Gothic ''sauil'', also Old High German forms such as ''suhil''). This continues a Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European alternation ''*suwen-'' vs. '':wikt:Reconstruc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sól (sun)
Sól may refer to: *Sól (Germanic mythology), a goddess who personifies the sun in Germanic mythology *Sól, Lublin Voivodeship, east Poland *Sól, Masovian Voivodeship, east-central Poland *Sól, Silesian Voivodeship, south Poland *Sowilo rune or Sól See also *Sol (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma
Sigma ( ; uppercase Σ, lowercase σ, lowercase in word-final position ς; ) is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 200. In general mathematics, uppercase Σ is used as an operator (mathematics), operator for summation. When used at the end of a Letter case, letter-case word (one that does not use all caps), the final form (ς) is used. In ' (Odysseus), for example, the two lowercase sigmas (σ) in the center of the name are distinct from the word-final sigma (ς) at the end. The Latin alphabet, Latin letter S derives from sigma while the Cyrillic script, Cyrillic letter Es (Cyrillic), Es derives from a #Lunate sigma, lunate form of this letter. History The shape (Σς) and alphabetic position of sigma is derived from the Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician letter (Shin (letter), ''shin''). Sigma's original name may have been ''san'', but due to the complicated early history of the Greek Archaic Greek alphabets, epich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
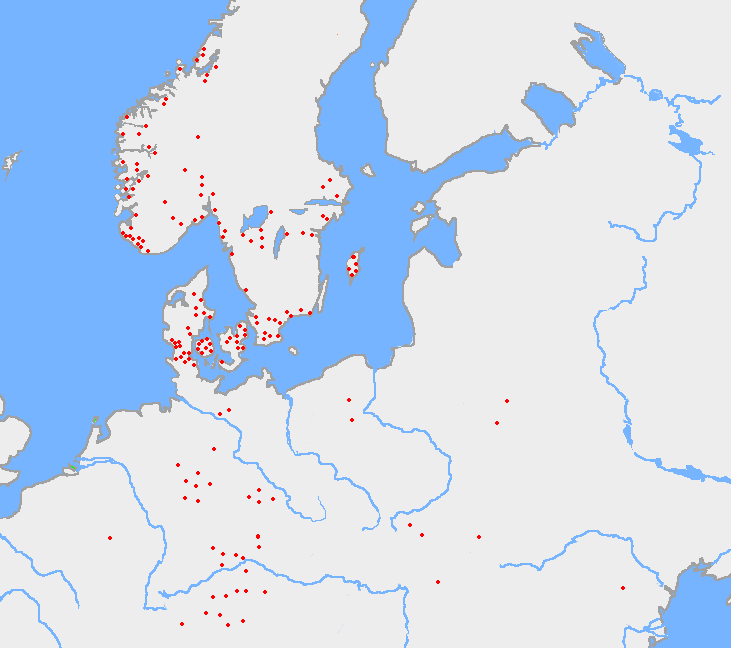
Elder Futhark
The Elder Futhark (or Fuþark, ), also known as the Older Futhark, Old Futhark, or Germanic Futhark, is the oldest form of the runic alphabets. It was a writing system used by Germanic peoples for Northwest Germanic dialects in the Migration Period. Inscriptions are found on artifacts including jewelry, amulets, plateware, tools, and weapons, as well as runestones, from the 2nd to the 8th centuries. In Scandinavia, beginning in the late 8th century, the script was simplified to the Younger Futhark, while the Anglo-Saxons and Frisians instead extended it, giving rise to the Anglo-Saxon runes, Anglo-Saxon futhorc. Both the Anglo-Saxon futhorc and the Younger Futhark remained in use during the Early Middle Ages, Early and the High Middle Ages respectively, but knowledge of how to read the Elder Futhark was forgotten until 1865, when it was deciphered by Norwegian scholar Sophus Bugge. Description The Elder Futhark is named after the initial phoneme of the first six rune names: /f/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution Of Sowilo Rune
Evolution is the change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more or less common within a population over successive generations. The process of evolution has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation. The scientific theory of evolution by natural selection was conceived independently by two British naturalists, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, in the mid-19th century as an explanation for why organisms are adapted to their physical and biological environments. The theory was first set out in detail in Darwin's book ''On the Origin of Species''. Evolution by natural selection is established by observable facts about living organisms: (1) more offspring are often produced than can possibly survive; (2) traits vary among individuals with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Bosworth
Joseph Bosworth (1788 – 27 May 1876) was an English scholar of the Anglo-Saxon language and compiler of the first major Anglo-Saxon dictionary. Biography Born in Derbyshire in 1788, Bosworth was educated at Repton School as a 'Poor Scholar' but left in his early teens and did not go to university. Despite the lack of a degree he somehow gained sufficient academic standing for the Church of England to allow him to become a priest. He became a curate in Bunny, Notts in 1814 and three years later became vicar of Little Horwood, Buckinghamshire. He was proficient in many European languages and made a particular study of Anglo-Saxon. This suggests that his years between leaving Repton and becoming a priest were spent working for someone whose own interests lay in these directions and who greatly encouraged Bosworth's academic development. There is no proof as to who this was but possible candidates are Sharon Turner (1768-1847), a London solicitor turned researcher or Alexander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Grimm
Jacob Ludwig Karl Grimm (4 January 1785 – 20 September 1863), also known as Ludwig Karl, was a German author, linguist, philologist, jurist, and folklorist. He formulated Grimm's law of linguistics, and was the co-author of the ''Deutsches Wörterbuch'', the author of ''Deutsche Mythologie'', and the editor of ''Grimms' Fairy Tales''. He was the older brother of Wilhelm Grimm; together, they were the literary duo known as the Brothers Grimm. Life and books Jacob Grimm was born 4 January 1785, in Hanau in Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel, Hesse-Kassel. His father, Philipp Grimm, was a lawyer who died while Jacob was a child, and his mother Dorothea Grimm, Dorothea was left with a very small income. Her sister was the lady of the chamber to the Landgravine of Hesse, and she helped to support and educate the family. Jacob was sent to the public school at Kassel in 1798 with his younger brother Wilhelm Grimm, Wilhelm. In 1802, he went to the University of Marburg, where he stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolian Languages
The Anatolian languages are an extinct branch of Indo-European languages that were spoken in Anatolia. The best known Anatolian language is Hittite, which is considered the earliest-attested Indo-European language. Undiscovered until the late 19th and early 20th centuries, they are often believed to be the earliest branch to have split from the Proto Indo-European family. Once discovered, the presence of laryngeal consonants ''ḫ'' and ''ḫḫ'' in Hittite and Luwian provided support for the laryngeal theory of Proto-Indo-European linguistics. While Hittite attestation ends after the Bronze Age, hieroglyphic Luwian survived until the conquest of the Neo-Hittite kingdoms by the Semitic Assyrian Empire, and alphabetic inscriptions in Anatolian languages are fragmentarily attested until the early first millennium AD, eventually succumbing to the Hellenization of Anatolia as a result of Greek colonisation. Origins The Anatolian branch is often considered the earliest to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heteroclitic
Proto-Indo-European nominals include nouns, adjectives, and pronouns. Their grammatical forms and meanings have been reconstructed by modern linguists, based on similarities found across all Indo-European languages. This article discusses nouns and adjectives; Proto-Indo-European pronouns are treated elsewhere. The Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) had eight or nine cases, three numbers (singular, dual and plural) and probably originally two genders (animate and neuter), with the animate later splitting into the masculine and the feminine. Nominals fell into multiple different declensions. Most of them had word stems ending in a consonant (called athematic stems) and exhibited a complex pattern of accent shifts and/or vowel changes (ablaut) among the different cases. Two declensions ended in a vowel (The asterisk (*) indicates that the form is not directly attested but has been reconstructed on the basis of other linguistic material.) and are called ''thematic''; they were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surya
Surya ( ; , ) is the Sun#Dalal, Dalal, p. 399 as well as the solar deity in Hinduism. He is traditionally one of the major five deities in the Smarta tradition, Smarta tradition, all of whom are considered as equivalent deities in the Panchayatana puja and a means to realise Brahman. Other names of Surya in ancient Indian literature include Āditya, Arka, Bhānu, Savitṛ, Pūṣan, Ravi, Mārtāṇḍa, Mitra, Bhāskara, Prabhākara, Kathiravan, and Vivasvat.#Dalal, Dalal, pp. 5, 311 The iconography of Surya is often depicted riding a chariot harnessed by horses, often seven in number which represent the seven colours of visible light, and the seven days of the week. During the medieval period, Surya was worshipped in tandem with Brahma during the day, Shiva at noon, and Vishnu in the evening. In some ancient texts and art, Surya is presented syncretically with Indra, Ganesha, and others. Surya as a deity is also found in the arts and literature of Buddhism and Jainism. Surya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |