|
Southwestern Amazonian Moist Forests
The Southwest Amazon moist forests (NT0166) is an ecoregion located in the Upper Amazon basin. The forest is characterized by a relatively flat landscape with alluvial plains dissected by undulating hills or high terraces. The biota of the southwest Amazon moist forest is very rich because of these dramatic edaphic and topographical variations at both the local and regional levels. This ecoregion has the highest number of both mammals and birds recorded for the Amazonian biogeographic realm: 257 with 11 endemic species for mammals and 782 and 17 endemics for birds. The inaccessibility of this region, along with few roads, has kept most of the habitat intact. Also, there are a number of protected areas, which preserve this extremely biologically rich ecoregion. Location The southwest Amazon moist forest region covers an extensive area of the Upper Amazon Basin comprising four sub-basins: (1) both the Pastaza- Marañon and (2) Ucayali River sub-basins drain into the Upper Ama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
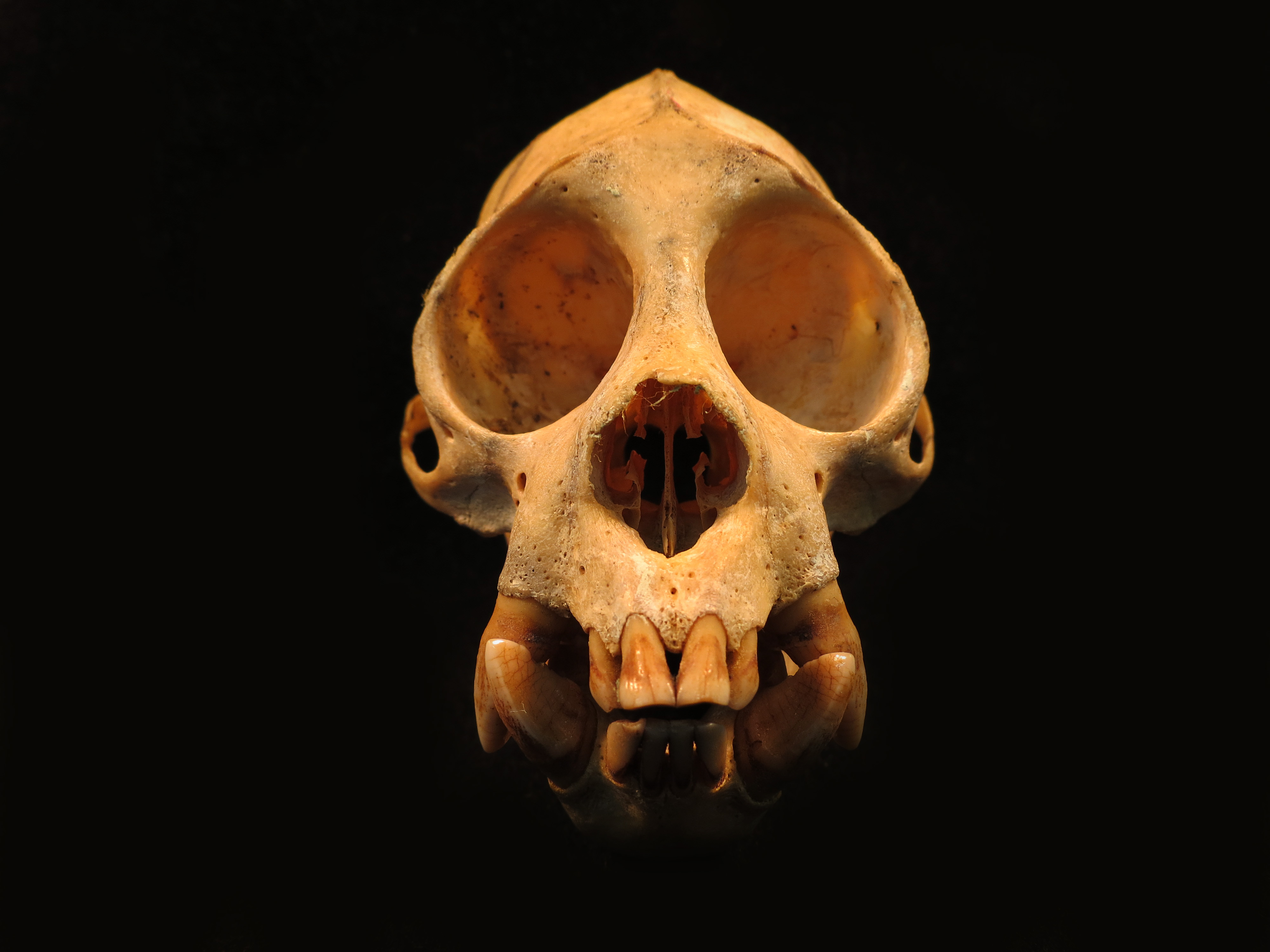
Bald Uakari
The bald uakari (''Cacajao calvus'') or bald-headed uakari is a small New World monkey characterized by a very short tail; bright, crimson face; a bald head; and long coat. The bald uakari is restricted to várzea forests and other wooded habitats near water in the western Amazon of Brazil and Peru. Taxonomy There are four recognized subspecies of the bald uakari, each of which is considered vulnerable to extinction: * White bald-headed uakari, ''Cacajao calvus calvus'' * Ucayali bald-headed uakari, ''Cacajao calvus ucayalii'' * Red bald-headed uakari, ''Cacajao calvus rubicundus'' * Novae's bald-headed uakari, ''Cacajao calvus novaesi'' Description The bald uakari weighs between 2.75 and 3.45 kg (6.1 and 7.6 lb), with head and body lengths average 45.6 cm (18.0 in) (male) and 44.0 cm (17.3 in) (female). In general, the bald uakari has a long, shaggy coat ranging from white in color to red and its head is bald. The tail is bob-like and rather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogeographic
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area.Brown University, "Biogeography." Accessed February 24, 2014. . Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals. Mycogeography is the branch that studies distribution of fungi, such as mushrooms. Knowledge of spatial variation in the numbers and types of organisms is as vital to us today as it was to our early human ancestors, as we adapt to heterogeneous but geographically predictable environments. Biogeography is an integrative field of inquiry that unites concepts and information from ecology, evolutionary biology, taxonomy, geology, physical geography, palaeontology, and climatology.Dansereau, Pierre. 1957. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serra Do Divisor National Park
The Serra do Divisor National Park ( pt, Parque Nacional da Serra do Divisor) is a national park on the westernmost point of Brazil, in the state of Acre, near the Peruvian border. It also has the highest point in that state, reaching 609 meters above sea level. It has been nominated by the Brazilian government as a Tentative World Heritage Site since 1998. Location The Serra do Divisor National Park is divided between the municipalities of Rodrigues Alves (13.45%), Porto Walter (26.99%), Marechal Thaumaturgo (4.73%), Mâncio Lima (31.71%) and Cruzeiro do Sul (23.12%) in the state of Acre. It has an area of . The park is bounded to the west by the border with Peru, which runs along the Serra Divisor mountain range. It adjoins the Alto Juruá Extractive Reserve along its southeast border. The Juruá River defines the eastern boundary of the southern section of the park. The Azul River defines the eastern boundary of the northern section. The conservation unit would be include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madeira River
The Madeira River ( pt, Rio Madeira, link=no ) is a major waterway in South America. It is estimated to be in length, while the Madeira-Mamoré is estimated near or in length depending on the measuring party and their methods. The Madeira is the biggest tributary of the Amazon, accounting for about 15% of the water in the basin. A map from Emanuel Bowen in 1747, held by the David Rumsey Map Collection, refers to the Madeira by the pre-colonial, indigenous name Cuyari. The River of Cuyari, called by the Portuguese Madeira or the Wood River, is formed by two great rivers, which join near its mouth. It was by this River, that the Nation of Topinambes passed into the River Amazon. Climate The mean inter-annual precipitations on the great basins vary from , the entire upper Madeira basin receiving . The greatest extremes of rainfall are between . Even just below the confluence that forms it, the Madeira is one of the largest rivers of the world, with a mean inter-annual discha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purus River
The Purus River (Portuguese: ''Rio Purus''; Spanish: ''Río Purús'') is a tributary of the Amazon River in South America. Its drainage basin is , and the mean annual discharge (hydrology), discharge is . The river shares its name with the Alto Purús National Park and the Purús Province (and its conformed Purús District), one of the four provinces of Peru in the Ucayali Region. Geography The Purus River rises in Peru. It defines the boundary between Peru and Brazil in the centre of the state of Acre (state), Acre, then runs for a short distance along the boundary of the Santa Rosa do Purus National Forest, a sustainable use conservation unit created in 2001 after it is joined by the Santa Rosa River (Acre), Santa Rosa River. It then flows north east through Manoel Urbano It runs through a continuous forest at the bottom of the great depression, lying between the Madeira River, which skirts the edge of the Brazilian sandstone plateau, and the Ucayali River, which hugs the ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juruá River
The Juruá River (Portuguese ''Rio Juruá''; Spanish ''Río Yuruá'') is a southern affluent river of the Amazon River west of the Purus River, sharing with this the bottom of the immense inland Amazon depression, and having all the characteristics of the Purus as regards curvature, sluggishness and general features of the low, half-flooded forest country it traverses. For most of its length the river flows through the Purus várzea ecoregion. This is surrounded by the Juruá-Purus moist forests ecoregion. It rises among the Ucayali highlands, and is navigable and unobstructed for a distance of above its junction with the Amazon. It has a total length of approximately , and is one of the longest tributaries of the Amazon. The Médio Juruá Extractive Reserve, created in 1997, is on the left bank of the river as it meanders in a generally northeast direction through the municipality of Carauari. The lower Juruá River forms the western boundary of the Baixo Juruá Extractiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beni River
The Beni River ( es, Río Beni) is a river in the north of Bolivia. It rises north of La Paz and flows northeast. The Madre de Dios River is where its mouth is at. In the upper portion of its course it flows through highland forest and rainforest, where the rapids of Cachuela Esperanza interrupt the upstream navigability of the river. The middle river runs through dense rainforest where it is joined by the Madidi River and the Tuichi River which flow through Madidi National Park. The Tuichi River joins the Beni River upstream from the town Rurrenabaque. North of Rurrenabaque, the Beni River runs through the Llanos de Moxos also known as the Beni Savanna, which is named from the river. It empties into the larger Madre de Dios at Riberalta. The Beni River has a number of minor tributaries, including intermittent streams such as the Emero River. In 1947, the CIA The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madre De Dios River
The Madre de Dios River () is a river shared by Bolivia and Peru which is homonymous to the Peruvian region it runs through. On Bolivian territory it receives the Beni River, close to the town of Riberalta, which later joins with the Mamore River to become the Madeira River after the confluence. The Madeira is a tributary to the Amazon River. The Madre de Dios is an important waterway for the department of Madre de Dios, particularly Puerto Maldonado, the largest town in the area, and the capital of the department. Mango farming and gold mining are among the many industries on its beaches. Other important industries the Madre de Dios provides are selective logging and farming, both of which are serious environmental problems. Along the length of the river there are several national parks and reserves, notably Tambopata-Candamo National Park, Manú National Park (also known as Manú Biosphere Reserve) and Bahuaja-Sonene National Park. Hydrography The Madre de Dios serves as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acre River
The Acre River (called Aquiry in the local Iñapari language; locally, ''Rio Acre'') is a long river in central South America. Course The river is born in Peru, and runs North-Eastwards, forming part of the border between Peru and Brazil and then part of the border between Bolivia and Brazil. It runs through the Brazilian states of Acre and Amazonas, before eventually running into the Purus River at Boca do Acre. It runs along the Bolivian frontier and flows northeastward to a junction with the Purus at 8° 45' South latitude. The name is also applied to a district situated on the same river and on the former boundary line of 1867, between Bolivia and Brazil. This region's area is estimated at about . It is navigable from the mouth until the Xapuri River (), even farther in the wet season from January until May. The river was an important transportation artery at the end of the 19th century due to newly discovered rubber tree forests. The Rio Acre Ecological Station lies i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazon River
The Amazon River (, ; es, Río Amazonas, pt, Rio Amazonas) in South America is the largest river by discharge volume of water in the world, and the disputed longest river system in the world in comparison to the Nile. The headwaters of the Apurímac River on Nevado Mismi had been considered for nearly a century as the Amazon basin's most distant source, until a 2014 study found it to be the headwaters of the Mantaro River on the Cordillera Rumi Cruz in Peru. The Mantaro and Apurímac rivers join, and with other tributaries form the Ucayali River, which in turn meets the Marañón River upstream of Iquitos, Peru, forming what countries other than Brazil consider to be the main stem of the Amazon. Brazilians call this section the Solimões River above its confluence with the Rio Negro forming what Brazilians call the Amazon at the Meeting of Waters ( pt, Encontro das Águas) at Manaus, the largest city on the river. The Amazon River has an average discharge of abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ucayali River
The Ucayali River ( es, Río Ucayali, ) is the main headstream of the Amazon River. It rises about north of Lake Titicaca, in the Arequipa region of Peru and becomes the Amazon at the confluence of the Marañón close to Nauta city. The city of Pucallpa is located on the banks of the Ucayali. Description The Ucayali, together with the Apurímac River, the Ene River and the Tambo River, is today considered the main headwater of the ''Amazon River'', totaling a length of from the source of the ''Apurímac'' at Nevado Mismi to the confluence of the Ucayali and Marañón Rivers: *Apurímac River (total length): *Ene River (total length): *Tambo River (total length): * Ucayali River (confluence with Tambo River to confluence with the Marañón): Exploration The Ucayali was first called ''San Miguel'', then ''Ucayali'', ''Ucayare'', ''Poro'', ''Apu-Poro'', ''Cocama'' and ''Rio de Cuzco''. Peru has organised many costly and ably-conducted expeditions to explore it. One of them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |