|
Southport War Memorial
Southport War Memorial is in London Square, Lord Street, Southport, Merseyside, England. It consists of an obelisk flanked by two colonnades in the form of Greek temples. Outside the colonnades are memorial gardens, each containing a Pool of Remembrance and fountains. The memorial was designed by the local architects Grayson and Barnish, and the carving was executed by Herbert Tyson Smith. It was unveiled in 1923 by the Earl of Derby. Following the Second World War and subsequent conflicts further inscriptions and names have been added. The memorial is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade II* listed building. History As a result of a meeting on 14 February 1919 a War Memorial Committee was established to raise money by public subscription for a monument, to extend the hospital, and to provide grants for bereaved children. The monument was to be sited in London Square as part of a scheme to remodel the centre of the town. A total of £3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Memorial, Southport - Geograph
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular or irregular military forces. Warfare refers to the common activities and characteristics of types of war, or of wars in general. Total war is warfare that is not restricted to purely legitimate military targets, and can result in massive civilian or other non-combatant suffering and casualties. While some war studies scholars consider war a universal and ancestral aspect of human nature, others argue it is a result of specific socio-cultural, economic or ecological circumstances. Etymology The English word ''war'' derives from the 11th-century Old English words ''wyrre'' and ''werre'', from Old French ''werre'' (also ''guerre'' as in modern French), in turn from the Frankish *''werra'', ultimately deriving from the Prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite. Marble is typically not Foliation (geology), foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphosed limestone, but its use in stonemasonry more broadly encompasses unmetamorphosed limestone. Marble is commonly used for Marble sculpture, sculpture and as a building material. Etymology The word "marble" derives from the Ancient Greek (), from (), "crystalline rock, shining stone", perhaps from the verb (), "to flash, sparkle, gleam"; Robert S. P. Beekes, R. S. P. Beekes has suggested that a "Pre-Greek origin is probable". This Stem (linguistics), stem is also the ancestor of the English language, English word "marmoreal," meaning "marble-like." While the English term "marble" resembles the French language, French , most other European languages (with words like "marmoreal") more closely resemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cast Iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impurities which allow cracks to pass straight through, grey cast iron has graphite flakes which deflect a passing crack and initiate countless new cracks as the material breaks, and ductile cast iron has spherical graphite "nodules" which stop the crack from further progressing. Carbon (C), ranging from 1.8 to 4 wt%, and silicon (Si), 1–3 wt%, are the main alloying elements of cast iron. Iron alloys with lower carbon content are known as steel. Cast iron tends to be brittle, except for malleable cast irons. With its relatively low melting point, good fluidity, castability, excellent machinability, resistance to deformation and wear resistance, cast irons have become an engineering material with a wide range of applications and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coffer
A coffer (or coffering) in architecture is a series of sunken panels in the shape of a square, rectangle, or octagon in a ceiling, soffit or vault. A series of these sunken panels was often used as decoration for a ceiling or a vault, also called ''caissons'' ("boxes"), or ''lacunaria'' ("spaces, openings"), so that a coffered ceiling can be called a ''lacunar'' ceiling: the strength of the structure is in the framework of the coffers. History The stone coffers of the ancient Greeks and Romans are the earliest surviving examples, but a seventh-century BC Etruscan chamber tomb in the necropolis of San Giuliano, which is cut in soft tufa-like stone reproduces a ceiling with beams and cross-beams lying on them, with flat panels filling the ''lacunae''. For centuries, it was thought that wooden coffers were first made by crossing the wooden beams of a ceiling in the Loire Valley châteaux of the early Renaissance. In 2012, however, archaeologists working under the Packard Humani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
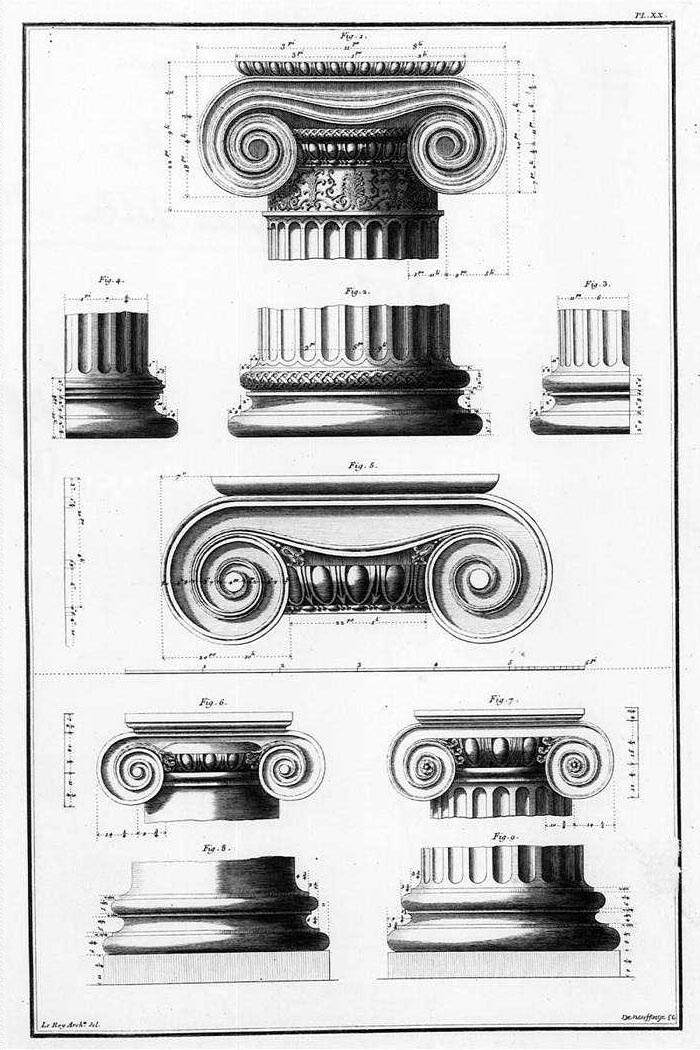
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entablature
An entablature (; nativization of Italian , from "in" and "table") is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and are commonly divided into the architrave (the supporting member immediately above; equivalent to the lintel in post and lintel construction), the frieze (an unmolded strip that may or may not be ornamented), and the cornice (the projecting member below the pediment). The Greek and Roman temples are believed to be based on wooden structures, the design transition from wooden to stone structures being called petrification. Overview The structure of an entablature varies with the orders of architecture. In each order, the proportions of the subdivisions (architrave, frieze, cornice) are defined by the proportions of the column. In Roman and Renaissance interpretations, it is usually approximately a quarter of the height of the column. Varian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenotaph
A cenotaph is an empty tomb or a monument erected in honour of a person or group of people whose remains are elsewhere. It can also be the initial tomb for a person who has since been reinterred elsewhere. Although the vast majority of cenotaphs honour individuals, many noted cenotaphs are instead dedicated to the memories of groups of individuals, such as the lost soldiers of a country or of an empire. Etymology The word "cenotaph" in the English Language is derived from the Greek el, κενοτάφιον, kenotaphion, label=none. It is a compound word that is created from the morphological combination of two root words: # el, κενός, kenos, label=none meaning "empty" # el, τάφος, taphos, label=none meaning "tomb", from el, θαπτω, thapto, I bury, label=none History Cenotaphs were common in the ancient world. Many were built in Ancient Egypt, Ancient Greece and across Northern Europe (in the shape of Neolithic barrows). The cenotaph in Whitehall, Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay (architecture)
In architecture, a bay is the space between architectural elements, or a recess or compartment. The term ''bay'' comes from Old French ''baie'', meaning an opening or hole."Bay" ''Online Etymology Dictionary''. http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?allowed_in_frame=0&search=bay&searchmode=none accessed 3/10/2014 __NOTOC__ Examples # The spaces between posts, columns, or buttresses in the length of a building, the division in the widths being called aisles. This meaning also applies to overhead vaults (between ribs), in a building using a vaulted structural system. For example, the Gothic architecture period's Chartres Cathedral has a nave (main interior space) that is '' "seven bays long." '' Similarly in timber framing a bay is the space between posts in the transverse direction of the building and aisles run longitudinally."Bay", n.3. def. 1-6 and "Bay", n.5 def 2. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) © Oxford University Press 2009 # Where there a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doric Order
The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of columns. Originating in the western Doric region of Greece, it is the earliest and, in its essence, the simplest of the orders, though still with complex details in the entablature above. The Greek Doric column was fluted or smooth-surfaced, and had no base, dropping straight into the stylobate or platform on which the temple or other building stood. The capital was a simple circular form, with some mouldings, under a square cushion that is very wide in early versions, but later more restrained. Above a plain architrave, the complexity comes in the frieze, where the two features originally unique to the Doric, the triglyph and gutta, are skeuomorphic memories of the beams and retaining pegs of the wooden constructions that preceded stone Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluting (architecture)
Fluting in architecture consists of shallow grooves running along a surface. The term typically refers to the grooves (flutes) running vertically on a column shaft or a pilaster, but need not necessarily be restricted to those two applications. If the hollowing out of material meets in a point, the point (sharp ridge) is called an arris. If the raised ridge between two flutes is blunt, the ridge is a . Purpose Fluting promotes a play of light on a column which helps the column appear more perfectly round than a smooth column. As a strong vertical element it also has the visual effect of minimizing any horizontal joints. Greek architects viewed rhythm as an important design element. As such, fluting was often used on buildings and temples to increase the sense of rhythm. It may also be incorporated in columns to make them look thinner, lighter, and more elegant. There is debate as to whether fluting was originally used in imitation of ancient woodworking practices, mimicking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barry Pain
Barry Eric Odell Pain (28 September 18645 May 1928) was an English journalist, poet, humorist and writer. Biography Born in Cambridge, Barry Pain was educated at Sedbergh School and Corpus Christi College, Cambridge. He became a prominent contributor to '' The Granta''. He was known as a writer of parody and lightly humorous stories. In 1889, ''Cornhill Magazines editor, James Payn, published his story "The Hundred Gates", and shortly afterwards Pain became a contributor to ''Punch'' and '' The Speaker'', and joined the staffs of the ''Daily Chronicle'' and ''Black and White''. Pain supposedly "owes his discovery to Robert Louis Stevenson, who compares him to De Maupassant". From 1896 to 1928 he was a regular contributor to ''The Windsor Magazine''. He died in Bushey, in Hertfordshire and is buried in Bushey churchyard. Pain's works include : * ''In a Canadian Canoe'' (1891), papers reprinted from ''The Granta''; * ''Playthings and Parodies'' (1892); * ''The Redemption of Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)