|
Sorbinil
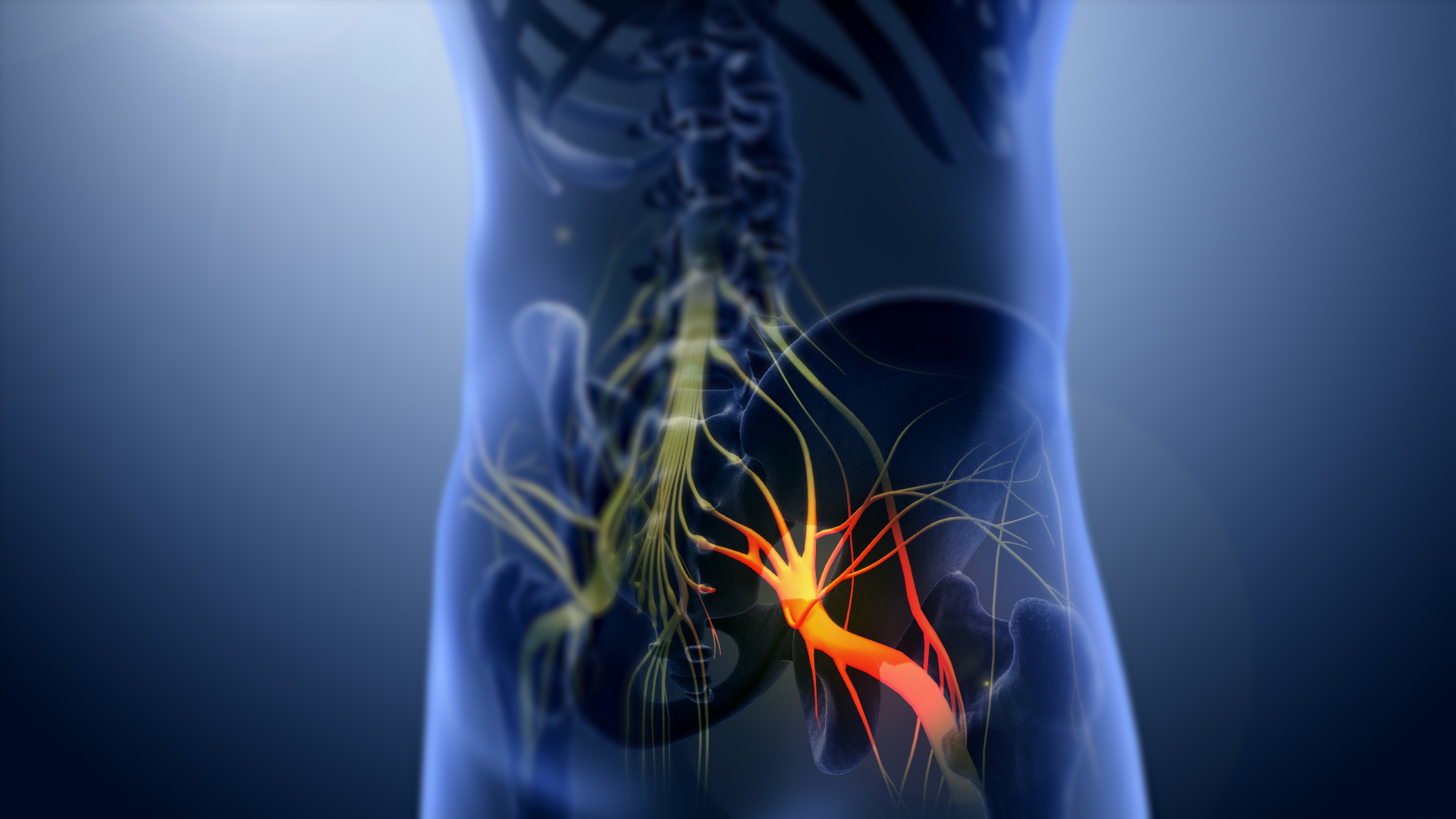
Sorbinil (INN) is an aldose reductase inhibitor being investigated for treatment of diabetic complications including neuropathy and retinopathy. Aldose reductase is an enzyme present in lens and brain that removes excess glucose by converting it to sorbitol. Sorbitol accumulation can lead to the development of cataracts in the lens and neuropathy in peripheral nerves. Sorbinil has been shown to inhibit aldose reductase in human brain and placenta and calf and rat lens. Sorbinil reduced sorbitol accumulation in rat lens and sciatic nerve The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals which is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the lower limb. It is the longest and widest si ... of diabetic rats orally administered 0.25 mg/kg sorbinil. References Aldose reductase inhibitors Hydantoins Fluoroarenes Pfizer brands Spiro compounds {{gastrointestinal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldose Reductase Inhibitor
Aldose reductase inhibitors are a class of drugs being studied as a way to prevent eye and nerve damage in people with diabetes. Mechanism Their target, aldose reductase, is an enzyme that is normally present in many other parts of the body, and catalyzes one of the steps in the polyol pathway, sorbitol(polyol) pathway that is responsible for fructose formation from glucose. Aldose reductase activity increases as the glucose concentration rises in diabetes Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ... in those tissues that are not insulin sensitive, which include the lens (anatomy), lenses, peripheral nerves and glomerulus. Sorbitol does not diffuse through cell membranes easily and therefore accumulates, causing osmotic damage which leads to retinopathy and neuropathy. Examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldose Reductase Inhibitors
Aldose reductase inhibitors are a class of drugs being studied as a way to prevent eye and nerve damage in people with diabetes. Mechanism Their target, aldose reductase, is an enzyme that is normally present in many other parts of the body, and catalyzes one of the steps in the sorbitol(polyol) pathway that is responsible for fructose formation from glucose. Aldose reductase activity increases as the glucose concentration rises in diabetes in those tissues that are not insulin sensitive, which include the lenses, peripheral nerves and glomerulus. Sorbitol does not diffuse through cell membranes easily and therefore accumulates, causing osmotic damage which leads to retinopathy and neuropathy. Examples File:Alrestatin.svg, Alrestatin File:Epalrestat.svg, Epalrestat File:Fidarestat structure.svg, Fidarestat File:Imirestat.svg, Imirestat File:Lidorestat.svg, Lidorestat File:Minalrestat.svg, Minalrestat File:Ponalrestat.svg, Ponalrestat File:Ranirestat.svg, Ranirestat File:Salfr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma-Aldrich
Sigma-Aldrich (formally MilliporeSigma) is an American chemical, life science, and biotechnology company that is owned by the German chemical conglomerate Merck Group. Sigma-Aldrich was created in 1975 by the merger of Sigma Chemical Company and Aldrich Chemical Company. It grew through various acquisitions until it had over 9,600 employees and was listed on the Fortune 1000. The company is headquartered in St. Louis and has operations in approximately 40 countries. In 2015, the German chemical conglomerate Merck Group acquired Sigma-Aldrich for $17 billion. The company is currently a part of Merck's life science business and in combination with Merck's earlier acquired Millipore Corporation, Millipore, operates as MilliporeSigma. History Sigma Chemical Company of St. Louis and Aldrich Chemical Company of Milwaukee were both American specialty chemical companies when they merged in August 1975. The company grew throughout the 1980s and 1990s, with significant expansion in fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cataracts
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and trouble seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognizing faces. Poor vision caused by cataracts may also result in an increased risk of falling and depression. Cataracts cause 51% of all cases of blindness and 33% of visual impairment worldwide. Cataracts are most commonly due to aging but may also occur due to trauma or radiation exposure, be present from birth, or occur following eye surgery for other problems. Risk factors include diabetes, longstanding use of corticosteroid medication, smoking tobacco, prolonged exposure to sunlight, and alcohol. The underlying mechanism involves accumulation of clumps of protein or yellow-brown pigment in the lens that reduces transmission of li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydantoins
Hydantoin, or glycolylurea, is a heterocyclic organic compound with the formula CH2C(O)NHC(O)NH. It is a colorless solid that arises from the reaction of glycolic acid and urea. It is an oxidized derivative of imidazolidine. In a more general sense, hydantoins can refer to a groups and a class of compounds with the same ring structure as the parent. For example, phenytoin (mentioned below) has two phenyl groups substituted onto the number 5 carbon in a hydantoin molecule. Synthesis Hydantoin was first isolated in 1861 by Adolf von Baeyer in the course of his study of uric acid. He obtained it by hydrogenation of allantoin, hence the name. : Friedrich Urech synthesized 5-methylhydantoin in 1873 from alanine sulfate and potassium cyanate in what is now known as the Urech hydantoin synthesis. The method is very similar to the modern route using alkyl and arylcyanates. The 5,5-dimethyl compound can also be obtained from acetone cyanohydrin (also discovered by Urech: see cyanohydri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sciatic Nerve
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals which is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect. The sciatic nerve has no cutaneous branches for the thigh. This nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for the skin of the lateral leg and the whole foot, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from spinal nerves L4 to S3. It contains fibers from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus. Structure In humans, the sciatic nerve is formed from the L4 to S3 segments of the sacral plexus, a collection of nerve fibres that emerge from the sacral part of the spinal cord. The lumbosacral trunk from the L4 and L5 roots descends between the sacral promontory and ala and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate maternal and fetal circulations, and is an important endocrine organ, producing hormones that regulate both maternal and fetal physiology during pregnancy. The placenta connects to the fetus via the umbilical cord, and on the opposite aspect to the maternal uterus in a species-dependent manner. In humans, a thin layer of maternal decidual (endometrial) tissue comes away with the placenta when it is expelled from the uterus following birth (sometimes incorrectly referred to as the 'maternal part' of the placenta). Placentas are a defining characteristic of placental mammals, but are also found in marsupials and some non-mammals with varying levels of development. Mammalian placentas probably first evolved about 150 million to 200 million years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Brain
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body. The brain is contained in, and protected by, the skull bones of the head. The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter, and an outer surface – the cerebral cortex – composed of grey matter. The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex, and an inner allocortex. The neocortex is made up of six neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each hemisphere is conventionally divided into four lobes – the frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerves
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon, within the nerve, is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called Nerve fascicle, fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Finally, the entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorbitol
Sorbitol (), less commonly known as glucitol (), is a sugar alcohol with a sweet taste which the human body metabolizes slowly. It can be obtained by reduction of glucose, which changes the converted aldehyde group (−CHO) to a primary alcohol group (−CH2OH). Most sorbitol is made from potato starch, but it is also found in nature, for example in apples, pears, peaches, and prunes. It is converted to fructose by sorbitol-6-phosphate 2-dehydrogenase. Sorbitol is an isomer of mannitol, another sugar alcohol; the two differ only in the orientation of the hydroxyl group on carbon 2.Kearsley, M. W.; Deis, R. C. Sorbitol and Mannitol. In Sweeteners and Sugar Alternatives in Food Technology; Ames: Oxford, 2006; pp 249-249-261. While similar, the two sugar alcohols have very different sources in nature, melting points, and uses. As an over-the-counter drug, sorbitol is used as a laxative to treat constipation. Synthesis Sorbitol may be synthesised via a glucose reduction reaction in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_PHIL_4284_lores.jpg)