|
Sophiology
Sophiology (russian: Софиология, by detractors also called ''Sophianism'' or ''Sophism'' ) is a controversial school of thought in Russian Orthodoxy which holds that Divine Wisdom (or Sophia) is to be identified with God's essence, and that the Divine Wisdom is in some way expressed in the world as 'creaturely' wisdom. This notion has often been understood or misunderstood (depending upon one's point of view) as introducing a feminine "fourth hypostasis" into the Trinity. History Antecedents Personified representations of Holy Wisdom (Ἁγία Σοφία) or the "Wisdom of God" refer in Orthodox theology to the person of Jesus Christ, as illustrated in the Acts of the Seventh Ecumenical Council (Nicaea II, 787): "Our Lord Jesus Christ, our true God, the self-existent Wisdom of God the Father, Who manifested Himself in the flesh, and by His great and divine dispensation (lit. economy) freed us from the snares of idolatry, clothing Himself in our nature, restor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Wisdom (1812, Russian Museum)
Holy Wisdom (Greek: , la, Sancta Sapientia, russian: Святая София Премудрость Божия, translit=Svyataya Sofiya Premudrost' Bozhiya "Holy Sophia, Divine Wisdom") is a concept in Christian theology. Christian theology received the Old Testament personification of Wisdom (Hebrew ''Chokhmah'') as well as the concept of Wisdom (''Sophia'') from Greek philosophy, especially Platonism. In Christology, Christ the Logos as God the Son was identified with Divine Wisdom from earliest times. The identification of Holy Wisdom with God the Son remains particularly pronounced in Eastern Orthodoxy, while the Latin Rite has placed more emphasis of the identification of God the Son with the Logos. There has also been a minority position which identified Wisdom with the Holy Spirit instead. Furthermore, in mystical interpretations forwarded in Russian Orthodoxy, known as Sophiology, Holy Wisdom as a feminine principle came to be identified with the Theotokos (M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Bulgakov
Sergei Nikolaevich Bulgakov (; russian: Серге́й Никола́евич Булга́ков; – 13 July 1944) was a Russian Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox theologian, priest, philosopher, and economist. Biography Early life: 1871–1898 Sergei Nikolaevich Bulgakov was born on 16 July 1871 to the family of an Russian Orthodox Church, Orthodox priest (Nikolai Bulgakov) in the town of Livny, Oryol guberniya, in Russia. The family produced Orthodox priests for six generations, beginning in the sixteenth century with their ancestor Bulgak, a Tatars, Tatar from whom the family name derives. Metropolitan bishop, Metropolitan Macarius Bulgakov (1816–1882), one of the major Eastern Orthodox theologians of his days, and one of the most important Russian church historians, was a distant relative. At the age of fourteen, after three years at the local parish school, Bulgakov entered the seminary in Orel. In 1888, however, Bulgakov quit the seminary after a loss of his faith. Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophia (wisdom)
Sophia ( grc-koi, σοφία ''sophía'' "wisdom") is a central idea in Hellenistic philosophy and religion, Platonism, Gnosticism and Christian theology. Originally carrying a meaning of "cleverness, skill", the later meaning of the term, close to the meaning of ''Phronesis'' ("wisdom, intelligence"), was significantly shaped by the term ''philosophy'' ("love of wisdom") as used by Plato. In the Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church, the feminine personification of divine wisdom as Holy Wisdom ( ''Hagía Sophía'') can refer either to Jesus Christ the Word of God (as in the dedication of the church of Hagia Sophia in Constantinople) or to the Holy Spirit. References to ''Sophia'' in Koine Greek translations of the Hebrew Bible translate to the Hebrew term ''Chokhmah''. Greek and Hellenistic tradition The Ancient Greek word ''Sophia'' (, ) is the abstract noun of (), which variously translates to "clever, skillful, intelligent, wise". These words share the same Proto- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavel Florensky
Pavel Alexandrovich Florensky (also P. A. Florenskiĭ, Florenskii, Florenskij; russian: Па́вел Алекса́ндрович Флоре́нский; hy, Պավել Ֆլորենսկի, Pavel Florenski; – December 8, 1937) was a Russian Orthodox theologian, priest, philosopher, mathematician, physicist, electrical engineer, inventor, polymath and neomartyr. Biography Early life Pavel Aleksandrovich Florensky was born on in the town of Yevlakh in Elisabethpol Governorate (in present-day western Azerbaijan) into the family of a railroad engineer, Aleksandr Florensky. His father came from a family of Russian Orthodox priests while his mother Olga (Salomia) Saparova (Saparyan, Sapharashvili) was of the Tbilisi Armenian nobility in Georgia.Natalino Valentini, (ed.) Pavel Florenskij, ''La colonna e il fondamento della verità'', San Paolo editore, 2010, p. lxxi. His maternal grandmother Sofia Paatova (Paatashvili) was from an Armenian family from Karabakh, living in Bolnisi, Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Solovyov (philosopher)
Vladimir Sergeyevich Solovyov (russian: Влади́мир Серге́евич Соловьёв; also romanized as Soloviev; – ), a Russian philosopher, theologian, poet, pamphleteer, and literary critic, played a significant role in the development of Russian philosophy and poetry at the end of the 19th century and in the spiritual renaissance of the early-20th century. Life and work Vladimir Solovyov was born in Moscow; the son of the historian Sergey Mikhaylovich Solovyov (1820–1879); his elder brother Vsevolod (1849-1903), became a historical novelist, and his younger sister, Polyxena (1867-1924), became a poet. Vladimir Solovyov's mother Polyxena Vladimirovna belonged to a family of Polish origin and had, among her ancestors, philosopher Gregory Skovoroda (1722–1794). In his teens, he renounced Eastern Orthodoxy for nihilism, but later his disapproval of positivism saw him begin to express views that were in line with those of the Orthodox Church. From 1869 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Wisdom (iconography)
In Russian Orthodox tradition, Holy Wisdom (Russian: "Holy Sophia, Divine Wisdom") is a conventional topos of iconography, attested since at least the late 14th century. The "Novgorod type" is named for the icon of Holy Wisdom in Saint Sophia Cathedral in Novgorod (16th century), but represented by the older icon in the Cathedral of the Annunciation, Moscow, dated to the early 15th century. Also known as "fire-winged" (огнекрылой), this type shows Holy Wisdom as a fiery angel with wings, seated on a throne and flanked by the Theotokos and by Saint Cosmas of Maiuma. A related but highly divergent type is known as "Wisdom hath builded her Home" (). The name is a quotation of Proverbs 9:1 and references the incarnation of Christ the Logos, identified with Holy Wisdom, the "house" being the Theotokos. The earliest icon known under this title is a late-14th-century fresco in the Church of the Assumption in Volotovo Field, Veliky Novgorod, but its most notable representat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CrossCurrents
''CrossCurrents'' is a quarterly academic journal published by the Association for Public Religion and Intellectual Life (before 1990, it was published by the Convergence). Now published as a peer-reviewed academic journalAccording to the journal'sinstructions for authors on the Wiley website "CrossCurrents connects the wisdom of the heart with the life of the mind and the experiences of the body. The journal is operated through its parent organization, the Association for Public Religion and Intellectual Life (APRIL), an interreligious network of academics, activists, artists, and community leaders seeking to engage the many ways religion meets the public. Contributions to the journal exist at the nexus of religion, education, the arts, and social justice. Work in the journal is supplemented by our online magazine, The Commons.)" Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the following databases: * Academic ASAP * Academic Search Elite * America: History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feminist Theology
Feminist theology is a movement found in several religions, including Buddhism, Hinduism, Sikhism, Neopaganism, Baháʼí Faith, Judaism, Islam and New Thought, to reconsider the traditions, practices, scriptures, and theologies of those religions from a feminist perspective. Some of the goals of feminist theology include increasing the role of women among clergy and religious authorities, reinterpreting patriarchal (male-dominated) imagery and language about God, determining women's place in relation to career and motherhood, studying images of women in the religions' sacred texts, and matriarchal religion. Methodology Development of feminist theology While there is no specific date to pinpoint the beginning of this movement, its origins can be traced back to the 1960s article, “The Human Situation: A Feminine View,” written by Valerie Saiving (Goldstein). Her piece of work questioned theologies written by men for men in a modern perspective to then dismantle what it ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meditations On The Tarot
''Meditations on the Tarot: A Journey into Christian Hermeticism'' (french: Méditations sur les 22 arcanes majeurs du Tarot) is an esoteric Christian book originally written in French with the date of 21 May 1967 given by the author at the end of the last chapter, and published posthumously and anonymously in 1980. This was followed by translation into German (''Die großen Arcana des Tarot : Meditationen'', ). An English translation was then published in 1985, with Robert A. Powell basing his rendering on the author's original French manuscript, whereas the published French edition () does not always follow the French original manuscript. The author is known, but requested to remain anonymous. It is included in the bibliography of books ascribed to Valentin Tomberg. The afterword states that "The author wished to remain anonymous in order to allow the work to speak for itself, to avoid the interposition of any kind of personal element between the work and the reader - reasons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
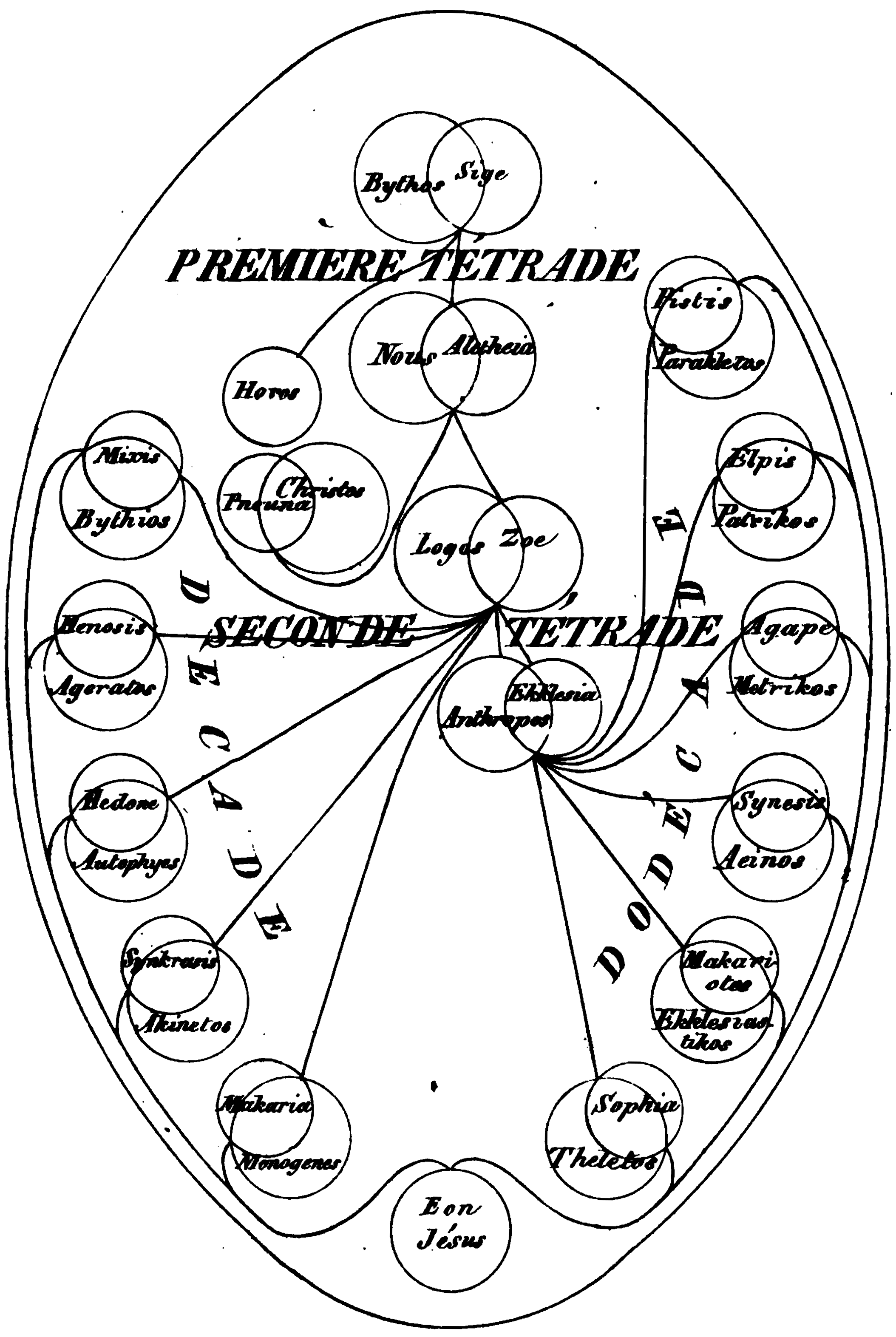
Sophia (Gnosticism)
Sophia ( grc-koi, Σοφíα "Wisdom", cop, ⲧⲥⲟⲫⲓⲁ "the Sophia") is a major theme, along with Knowledge ( ''gnosis'', Coptic ), among many of the early Christian knowledge-theologies grouped by the heresiologist Irenaeus as (), ‘knowing’ or ‘men that claimed to have deeper wisdom’. Gnosticism is a 17th-century term expanding the definition of Irenaeus' groups to include other syncretic and mystery religions. In Gnosticism, Sophia is a feminine figure, analogous to the human soul but also simultaneously one of the feminine aspects of God. Gnostics held that she was the ''syzygy'' (female twin Aeon (Gnosticism), divine Aeon) of Jesus (i.e. the Bride of Christ), and Holy Spirit of the Trinity. She is occasionally referred to by the Hebrew language, Hebrew equivalent of (, he, חכמה ) and as (). In the Nag Hammadi library, Nag Hammadi texts, Sophia is the lowest Aeon, or anthropic expression of the emanation of the light of God. She is considered to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gender Of God
The gender of God can be viewed as a literal or as an allegorical aspect of a deity. In polytheistic religions, gods often have genders which would enable them to sexually interact with each other, and even with humans. Abrahamic religions worship a single God, which in most interpretations of Yahweh, Allah, and God the Father, is not believed to have a physical body. Though often referred to with gendered pronouns, many Abrahamic denominations use "divine gender" primarily as an analogy to better relate to the concept of God, with no sexual connotation. In Christian traditions with the concept of the Trinity, Jesus is believed to be a physical manifestation called God the Son, who is male. In Mormonism, God the Father is male and is married to the female Heavenly Mother. Abrahamic religions In the Hebrew and Christian Bible, God is usually described in male terms in biblical sources, Pagels, Elaine H. 1976.What Became of God the Mother? Conflicting Images of God in Earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





.jpg)