|
Sonata No. 6 (Scriabin)
The Piano Sonata No. 6, Op. 62, by Alexander Scriabin was composed in 1911. Although it was named the sixth sonata, the piece was preceded by the Sonata No. 7. As it is one of the late piano sonatas of Scriabin's career, the music consists of a single movement and is almost atonal, although it is sometimes listed as being in the key of G. Scriabin reportedly never played the sonata in public, because he feared its darkness. It received its premiere on 19 March 1912 in Moscow by Elena Bekman-Shcherbina. Structure and content The piece consists of a single movement, typically lasting around 11–12 minutes, and is marked as follows: #Modéré: mystérieux, concentré The mood of the piece is marked "mystérieux" by the composer, but most striking are the sudden moments of horror that interrupt its dreamlike atmosphere, explicitly marked "l'épouvante surgit" (surge of terror) by Scriabin. The final passages are colourful and languid, like an elaborate Debussy prelude, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opus Number
In musicology, the opus number is the "work number" that is assigned to a musical composition, or to a set of compositions, to indicate the chronological order of the composer's production. Opus numbers are used to distinguish among compositions with similar titles; the word is abbreviated as "Op." for a single work, or "Opp." when referring to more than one work. To indicate the specific place of a given work within a music catalogue, the opus number is paired with a cardinal number; for example, Beethoven's Piano Sonata No. 14 in C-sharp minor (1801, nicknamed ''Moonlight Sonata'') is "Opus 27, No. 2", whose work-number identifies it as a companion piece to "Opus 27, No. 1" ( Piano Sonata No. 13 in E-flat major, 1800–01), paired in same opus number, with both being subtitled ''Sonata quasi una Fantasia'', the only two of the kind in all of Beethoven's 32 piano sonatas. Furthermore, the ''Piano Sonata, Op. 27 No. 2, in C-sharp minor'' is also catalogued as "Sonata No. 14", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elektra Chord
The ''Elektra'' chord is a "complexly dissonant signature- chord"Lawrence Kramer. "Fin-de-siècle Fantasies: ''Elektra'', Degeneration and Sexual Science", ''Cambridge Opera Journal'', Vol. 5, No. 2. (Jul., 1993), pp. 141-165. and motivic elaboration used by composer Richard Strauss to represent the title character of his opera '' Elektra'' that is a "bitonal synthesis of E major and C-sharp major" and may be regarded as a polychord related to conventional chords with added thirds,H. H. Stuckenschmidt; Piero Weiss. "Debussy or Berg? The Mystery of a Chord Progression", ''The Musical Quarterly'', Vol. 51, No. 3. (Jul., 1965), pp. 453-459. in this case an eleventh chord. It is enharmonically equivalent to a 7#9 chord : D-F-A-C-E and a 6b9 chord : E-G#-B-C#-F. In ''Elektra'' the chord, Elektra's "harmonic signature" is treated various ways betraying "both tonal and bitonal leanings...a dominant 4/2 over a nonharmonic bass." It is associated as well with its seven note comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dover Publications
Dover Publications, also known as Dover Books, is an American book publisher founded in 1941 by Hayward and Blanche Cirker. It primarily reissues books that are out of print from their original publishers. These are often, but not always, books in the public domain. The original published editions may be scarce or historically significant. Dover republishes these books, making them available at a significantly reduced cost. Classic reprints Dover reprints classic works of literature, classical sheet music, and public-domain images from the 18th and 19th centuries. Dover also publishes an extensive collection of mathematical, scientific, and engineering texts. It often targets its reprints at a niche market, such as woodworking. Starting in 2015, the company branched out into graphic novel reprints, overseen by Dover acquisitions editor and former comics writer and editor Drew Ford. Most Dover reprints are photo facsimiles of the originals, retaining the original pagination and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
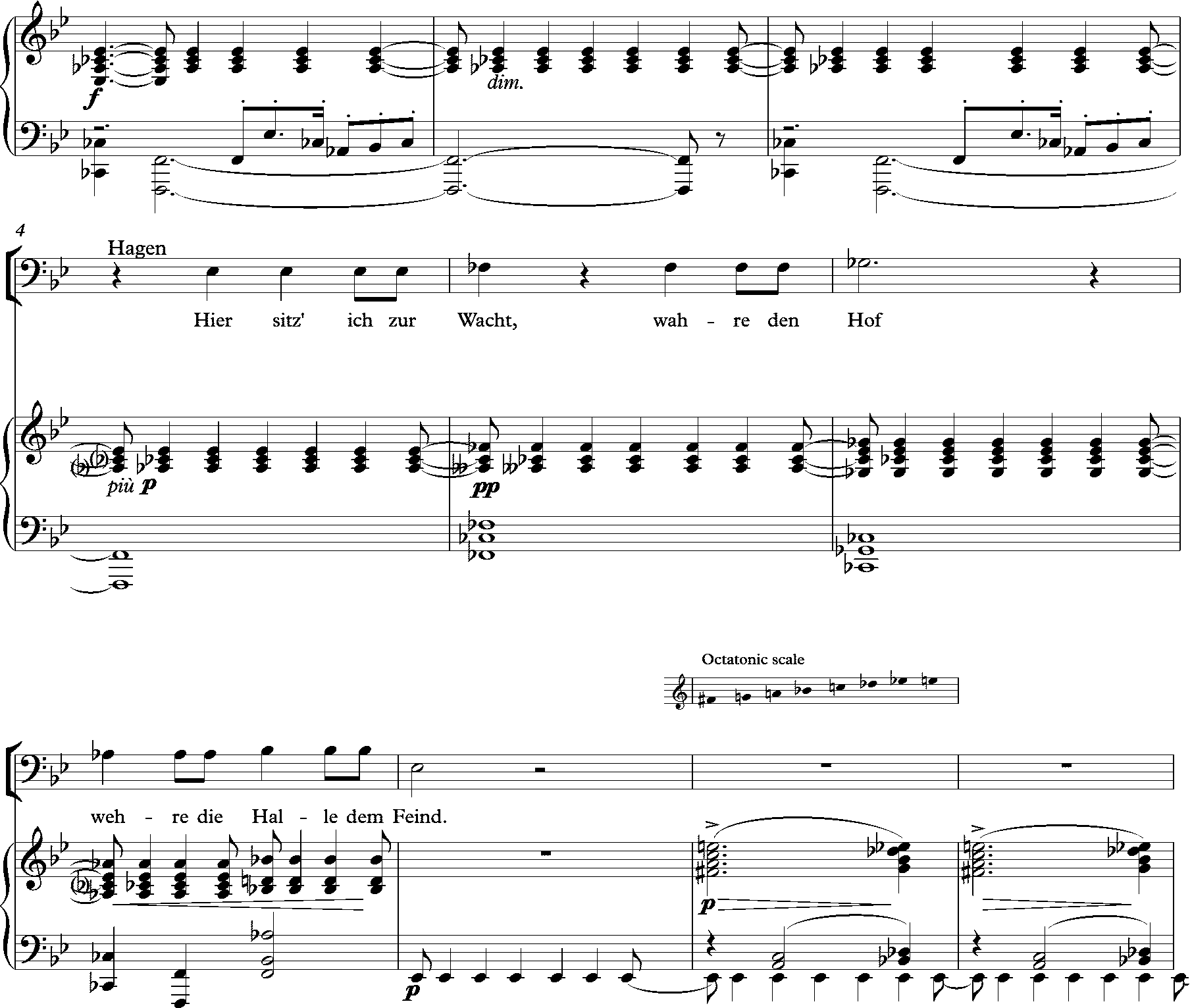
Octatonic Scale
An octatonic scale is any eight-note musical scale. However, the term most often refers to the symmetric scale composed of alternating whole and half steps, as shown at right. In classical theory (in contrast to jazz theory), this symmetrical scale is commonly called the ''octatonic scale'' (or the ''octatonic collection''), although there are a total of 42 enharmonically non-equivalent, transpositionally non-equivalent eight-note sets. The earliest systematic treatment of the octatonic scale was in Edmond de Polignac's unpublished treatise "Étude sur les successions alternantes de tons et demi-tons (Et sur la gamme dite majeure-mineure)" (''Study of the Succession of Alternating Whole Tones and Semitones (and of the so-called Major-Minor Scale)'') from c. 1879, which preceded Vito Frazzi's ''Scale alternate per pianoforte'' of 1930 by a full half-century. Nomenclature In Saint Petersburg at the turn of the 20th century, this scale had become so familiar in the circle of comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decca Records
Decca Records is a British record label established in 1929 by Edward Lewis (Decca), Edward Lewis. Its U.S. label was established in late 1934 by Lewis, Jack Kapp, American Decca's first president, and Milton Rackmil, who later became American Decca's president. In 1937, anticipating Nazi Germany, Nazi aggression leading to World War II, Lewis sold American Decca and the link between the U.K. and U.S. Decca labels was broken for several decades. The British label was renowned for its development of recording methods, while the American company developed the concept of cast albums in the musical genre. Both wings are now part of the Universal Music Group. The U.S. Decca label was the foundation company that evolved into UMG (Universal Music Group). Label name The name dates back to a portable phonograph, gramophone called the "Decca Dulcephone" patented in 1914 by musical instrument makers Barnett Samuel and Sons. The name "Decca" was coined by Wilfred S. Samuel by merging the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Ashkenazy
Vladimir Davidovich Ashkenazy (russian: Влади́мир Дави́дович Ашкена́зи, ''Vladimir Davidovich Ashkenazi''; born 6 July 1937) is an internationally recognized solo pianist, chamber music performer, and conductor. He is originally from Russia and has held Icelandic citizenship since 1972. He has lived in Switzerland since 1978. Ashkenazy has collaborated with well-known orchestras and soloists. In addition, he has recorded a large repertoire of classical and romantic works. His recordings have earned him five Grammy awards and Iceland's Order of the Falcon. Early life Vladimir Ashkenazy was born in Gorky, Soviet Union (now Nizhny Novgorod, Russia), to pianist and composer David Ashkenazi and to actress Yevstolia Grigorievna (born Plotnova). His father was Jewish and his mother came from a Russian Orthodox family. Ashkenazy was christened in a Russian Orthodox church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Heinz Stuckenschmidt
Hans Heinz Stuckenschmidt (1 November 1901 – 15 August 1988) was a German composer, musicologist, and historian and critic of music. Life Stuckenschmidt was born in Strasbourg. At as early an age as 19, he was the Berlin-based music critic/correspondent for the Prague-based periodical ''Bohemia'', and lived as a freelance music writer in Hamburg, Vienna, Paris, Berlin and Prague, becoming personally acquainted with numerous composers of avant-garde music. Amongst his most prominent musical productions were the "new music" concert cycle in Hamburg, and the 1927-8 concerts of the Berlin ''November Group'' with Max Butting. In 1929, Stuckenschmidt became the successor to Adolf Weissmans as the music critic at the ''Berliner Zeitung am Mittag''. Due to political pressure owing to the newly empowered Nazi regime, he left the paper, later moving to Prague. At the end of the 1930s, he was conscripted into the armed forces as an interpreter. After the end of the war, Stuckensc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mystic Chord
In music, the mystic chord or Prometheus chord is a six-note synthetic chord and its associated scale, or pitch collection; which loosely serves as the harmonic and melodic basis for some of the later pieces by Russian composer Alexander Scriabin. Scriabin, however, did not use the chord directly but rather derived material from its transpositions. When rooted in C, the mystic chord consists of the pitch classes: C, F, B, E, A, D. This is often interpreted as a quartal hexachord consisting of an augmented fourth, diminished fourth, augmented fourth, and two perfect fourths. However, the chord may be spelled in a variety of ways, and it is related to other pitch collections, such as being a hexatonic subset of the overtone scale, lacking the perfect fifth. Nomenclature The term "mystic chord" appears to derive from Alexander Scriabin's intense interest in Theosophy, and the chord is imagined to reflect this mysticism. It was coined by Arthur Eaglefield Hull in 1916."Skryab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Strauss
Richard Georg Strauss (; 11 June 1864 – 8 September 1949) was a German composer, conductor, pianist, and violinist. Considered a leading composer of the late Romantic and early modern eras, he has been described as a successor of Richard Wagner and Franz Liszt. Along with Gustav Mahler, he represents the late flowering of German Romanticism, in which pioneering subtleties of orchestration are combined with an advanced harmonic style. Strauss's compositional output began in 1870 when he was just six years old and lasted until his death nearly eighty years later. While his output of works encompasses nearly every type of classical compositional form, Strauss achieved his greatest success with tone poems and operas. His first tone poem to achieve wide acclaim was ''Don Juan'', and this was followed by other lauded works of this kind, including ''Death and Transfiguration'', ''Till Eulenspiegel's Merry Pranks'', ''Also sprach Zarathustra'', ''Don Quixote'', ''Ein Heldenleben' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Scriabin
Alexander Nikolayevich Scriabin (; russian: Александр Николаевич Скрябин ; – ) was a Russian composer and virtuoso pianist. Before 1903, Scriabin was greatly influenced by the music of Frédéric Chopin and composed in a relatively tonal, late Romantic idiom. Later, and independently of his influential contemporary, Arnold Schoenberg, Scriabin developed a much more dissonant musical language that had transcended usual tonality but was not atonal, which accorded with his personal brand of metaphysics. Scriabin found significant appeal in the concept of Gesamtkunstwerk as well as synesthesia, and associated colours with the various harmonic tones of his scale, while his colour-coded circle of fifths was also inspired by theosophy. He is often considered the main Russian Symbolist composer and a major representative of the Russian Silver Age. Scriabin was an innovator as well as one of the most controversial composer-pianists of the early 20th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Debussy
(Achille) Claude Debussy (; 22 August 1862 – 25 March 1918) was a French composer. He is sometimes seen as the first Impressionist composer, although he vigorously rejected the term. He was among the most influential composers of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Born to a family of modest means and little cultural involvement, Debussy showed enough musical talent to be admitted at the age of ten to France's leading music college, the Conservatoire de Paris. He originally studied the piano, but found his vocation in innovative composition, despite the disapproval of the Conservatoire's conservative professors. He took many years to develop his mature style, and was nearly 40 when he achieved international fame in 1902 with the only opera he completed, '' Pelléas et Mélisande''. Debussy's orchestral works include ''Prélude à l'après-midi d'un faune'' (1894), ''Nocturnes'' (1897–1899) and ''Images'' (1905–1912). His music was to a considerable extent a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tempo
In musical terminology, tempo (Italian, 'time'; plural ''tempos'', or ''tempi'' from the Italian plural) is the speed or pace of a given piece. In classical music, tempo is typically indicated with an instruction at the start of a piece (often using conventional Italian terms) and is usually measured in beats per minute (or bpm). In modern classical compositions, a "metronome mark" in beats per minute may supplement or replace the normal tempo marking, while in modern genres like electronic dance music, tempo will typically simply be stated in BPM. Tempo may be separated from articulation and meter, or these aspects may be indicated along with tempo, all contributing to the overall texture. While the ability to hold a steady tempo is a vital skill for a musical performer, tempo is changeable. Depending on the genre of a piece of music and the performers' interpretation, a piece may be played with slight tempo rubato or drastic variances. In ensembles, the tempo is often ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)