|
Somnolent
Somnolence (alternatively sleepiness or drowsiness) is a state of strong desire for sleep, or sleeping for unusually long periods (compare hypersomnia). It has distinct meanings and causes. It can refer to the usual state preceding falling asleep, the condition of being in a drowsy state due to circadian rhythm disorders, or a symptom of other health problems. It can be accompanied by lethargy, weakness and lack of mental agility. Somnolence is often viewed as a symptom rather than a disorder by itself. However, the concept of somnolence recurring at certain times for certain reasons constitutes various disorders, such as excessive daytime sleepiness, shift work sleep disorder, and others; and there are medical codes for somnolence as viewed as a disorder. Sleepiness can be dangerous when performing tasks that require constant concentration, such as driving a vehicle. When a person is sufficiently fatigued, microsleeps may be experienced. In individuals deprived of sleep, somnol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychiatry
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of mental disorders. These include various maladaptations related to mood, behaviour, cognition, and perceptions. See glossary of psychiatry. Initial psychiatric assessment of a person typically begins with a case history and mental status examination. Physical examinations and psychological tests may be conducted. On occasion, neuroimaging or other neurophysiological techniques are used. Mental disorders are often diagnosed in accordance with clinical concepts listed in diagnostic manuals such as the ''International Classification of Diseases'' (ICD), edited and used by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the widely used '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM), published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). The fifth edition of the DSM (DSM-5) was published in May 2013 which re-organized the larger categories of various diseases and expanded upon the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
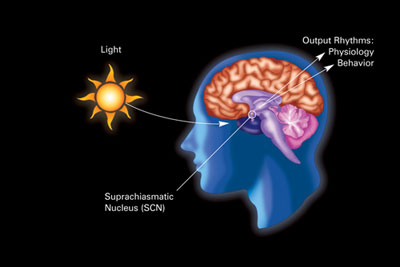
Irregular Sleep–wake Rhythm
Irregular sleep–wake rhythm (ISWD) is a rare form of circadian rhythm sleep disorder. It is characterized by numerous naps throughout the 24-hour period, no main nighttime sleep episode, and irregularity from day to day. Affected individuals have no pattern of when they are awake or asleep, may have poor quality sleep, and often may be very sleepy while they are awake. The total time asleep per 24 hours is normal for the person's age. The disorder is serious—an invisible disability. It can create social, familial, and work problems, making it hard for a person to maintain relationships and responsibilities, and may make a person home-bound and isolated. Causes ISWD has various causes, including neurological disorders such as dementia (particularly Alzheimer's Disease), brain damage, or intellectual disabilities. It is thought that those affected have a weak circadian clock. The risk for the disorder increases with age, but only due to increased prevalence of co-morbid medical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or altered consciousness, nausea, vomiting, and an inability to tolerate light or loud noises. Young children often exhibit only nonspecific symptoms, such as irritability, drowsiness, or poor feeding. A non-blanching rash (a rash that does not fade when a glass is rolled over it) may also be present. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria or other microorganisms. Non-infectious causes include malignancy (cancer), subarachnoid haemorrhage, chronic inflammatory disease (sarcoidosis) and certain drugs. Meningitis can be life-threatening because of the inflammation's proximity to the brain and spinal cord; therefore, the condition is classified as a medical emergency. A lumbar puncture, in which a needle is inserte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
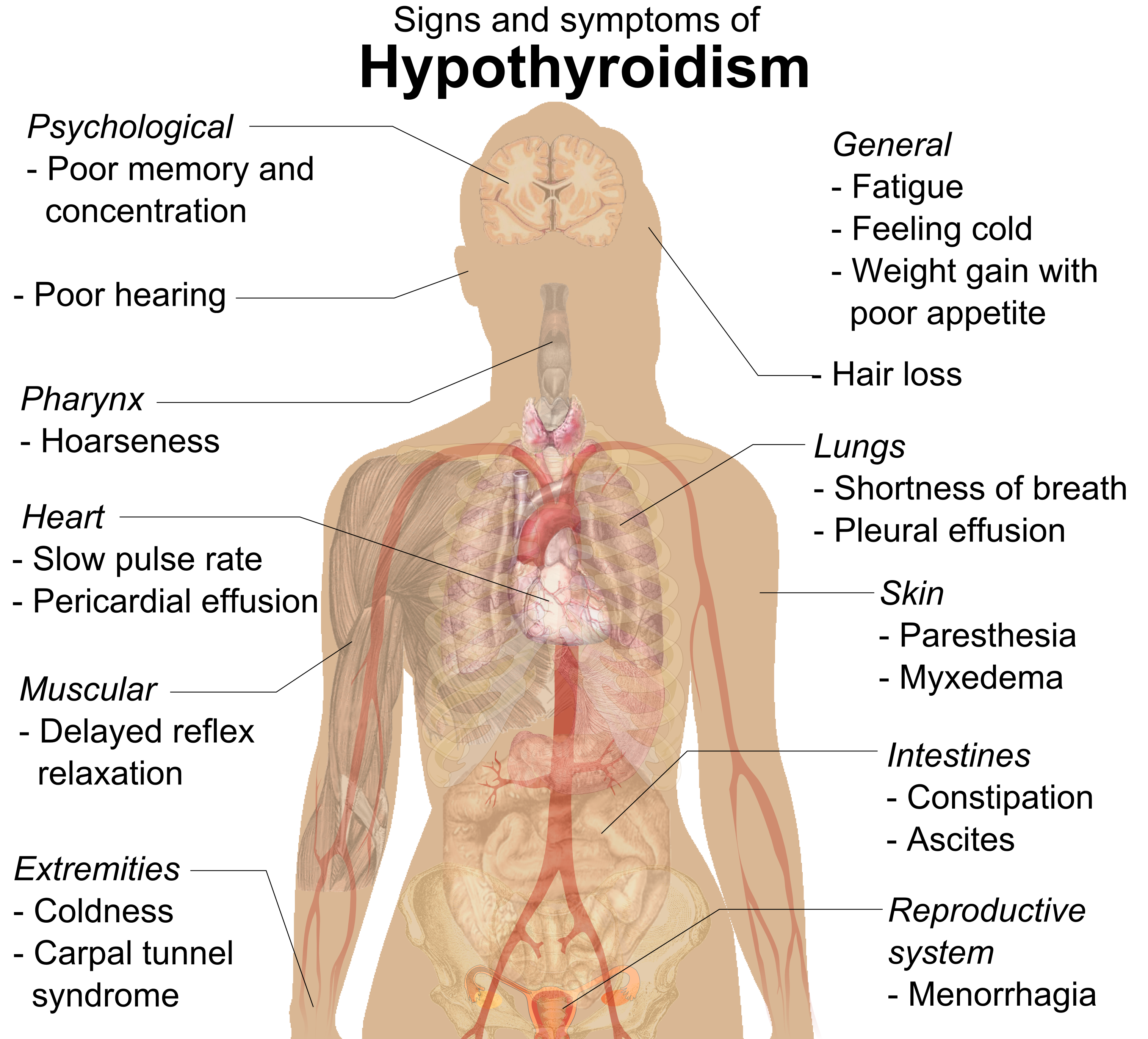
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as poor ability to tolerate cold, a feeling of tiredness, constipation, slow heart rate, depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus or the anterior pituitary gland, certain medications, a lack of a functioning thyroid at bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia or hyponatraemia is a low concentration of sodium in the blood. It is generally defined as a sodium concentration of less than 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L), with severe hyponatremia being below 120 mEq/L. Symptoms can be absent, mild or severe. Mild symptoms include a decreased ability to think, headaches, nausea, and poor balance. Severe symptoms include confusion, seizures, and coma; death can ensue. The causes of hyponatremia are typically classified by a person's body fluid status into low volume, normal volume, or high volume. Low volume hyponatremia can occur from diarrhea, vomiting, diuretics, and sweating. Normal volume hyponatremia is divided into cases with dilute urine and concentrated urine. Cases in which the urine is dilute include adrenal insufficiency, hypothyroidism, and drinking too much water or too much beer. Cases in which the urine is concentrated include syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH). High vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypermagnesemia
Hypermagnesemia is an electrolyte disorder in which there is a high level of magnesium in the blood. Symptoms include weakness, confusion, decreased breathing rate, and decreased reflexes. Complications may include low blood pressure and cardiac arrest. It is typically caused by kidney failure or is treatment-induced such as from antacids that contain magnesium. Less common causes include tumor lysis syndrome, seizures, and prolonged ischemia. Diagnosis is based on a blood level of magnesium greater than 1.1 mmol/L (2.6 mg/dL). It is severe if levels are greater than 2.9 mmol/L (7 mg/dL). Specific electrocardiogram (ECG) changes may be present. Treatment involves stopping the magnesium a person is getting. Treatment when levels are very high include calcium chloride, intravenous normal saline with furosemide, and hemodialysis. Hypermagnesemia is uncommon. Rates among hospitalized patients in renal failure may be as high as 10%. Signs and symptoms Symptoms includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range is 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L defined as hypercalcemia. Those with a mild increase that has developed slowly typically have no symptoms. In those with greater levels or rapid onset, symptoms may include abdominal pain, bone pain, confusion, depression, weakness, kidney stones or an abnormal heart rhythm including cardiac arrest. Most outpatient cases are due to primary hyperparathyroidism and inpatient cases due to cancer. Other causes of hypercalcemia include sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, Paget disease, multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN), vitamin D toxicity, familial hypocalciuric hypercalcaemia and certain medications such as lithium and hydrochlorothiazide. Diagnosis should generally include either a corrected calcium or ionized calcium level and be confirmed after a week. Specific chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Injury
A head injury is any injury that results in trauma to the skull or brain. The terms ''traumatic brain injury'' and ''head injury'' are often used interchangeably in the medical literature. Because head injuries cover such a broad scope of injuries, there are many causes—including accidents, falls, physical assault, or traffic accidents—that can cause head injuries. The number of new cases is 1.7 million in the United States each year, with about 3% of these incidents leading to death. Adults have head injuries more frequently than any age group resulting from falls, motor vehicle crashes, colliding or being struck by an object, or assaults. Children, however, may experience head injuries from accidental falls or intentional causes (such as being struck or shaken) leading to hospitalization. Acquired brain injury (ABI) is a term used to differentiate brain injuries occurring after birth from injury, from a genetic disorder, or from a congenital disorder. Unlike a broken bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a medical condition defined by the presence of chronic widespread pain, fatigue, waking unrefreshed, cognitive symptoms, lower abdominal pain or cramps, and depression. Other symptoms include insomnia and a general hypersensitivity. The cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, but is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors may include psychological stress, trauma, and certain infections. The pain appears to result from processes in the central nervous system and the condition is referred to as a "central sensitization syndrome". The treatment of fibromyalgia is symptomatic and multidisciplinary. The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology strongly recommends aerobic and strengthening exercise. Weak recommendations are given to mindfulness, psychotherapy, acupuncture, hydrotherapy, and meditative exercise such as qigong, yoga, and tai chi. The use of medication in the treatment of fibromyal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased appetite. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many health complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death. Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, damage to the nerves, damage to the eyes, and cognitive impairment. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced. Insulin is a hormone which is responsible for helping glucose from food get into cells to be used for energy. There are three main types of diabetes mellitus: * Type 1 diabetes results from failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin due to lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concussion
A concussion, also known as a mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), is a head injury that temporarily affects brain functioning. Symptoms may include loss of consciousness (LOC); memory loss; headaches; difficulty with thinking, concentration, or balance; nausea; blurred vision; sleep disturbances; and mood changes. Any of these symptoms may begin immediately, or appear days after the injury. Concussion should be suspected if a person indirectly or directly hits their head and experiences any of the symptoms of concussion. It is not unusual for symptoms to last 2 weeks in adults and 4 weeks in children. Fewer than 10% of sports-related concussions among children are associated with loss of consciousness. Common causes include motor vehicle collisions, falls, sports injuries, and bicycle accidents. Risk factors include drinking alcohol and a prior history of concussion. The mechanism of injury involves either a direct blow to the head or forces elsewhere on the body that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Pain
Chronic pain is classified as pain that lasts longer than three to six months. In medicine, the distinction between Acute (medicine), acute and Chronic condition, chronic pain is sometimes determined by the amount of time since onset. Two commonly used markers are pain that continues at three months and six months since onset, but some theorists and researchers have placed the transition from acute to chronic pain at twelve months. Others apply the term ''acute'' to pain that lasts less than 30 days, ''chronic'' to pain of more than six months duration, and ''subacute'' to pain that lasts from one to six months. A popular alternative definition of ''chronic pain'', involving no fixed duration, is "pain that extends beyond the expected period of healing". Chronic pain may originate in the body, or in the brain or spinal cord. It is often difficult to treat. Epidemiological studies have found that 8–11.2% of people in various countries have chronic widespread pain. Various Nonopiod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |