|
Soliva Sessilis
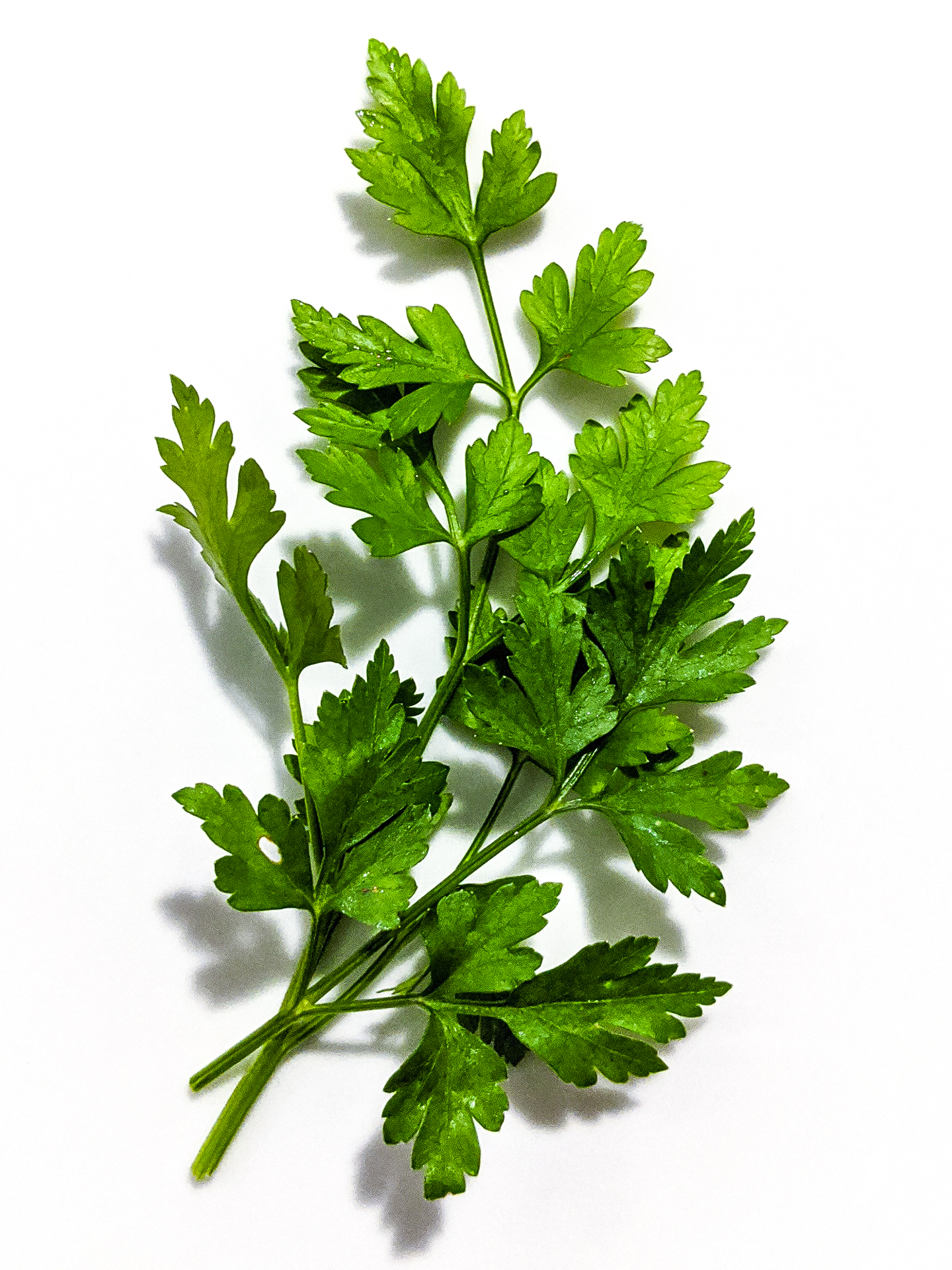
''Soliva sessilis'', one of up to nine species of the genus '' Soliva'', is a low-growing herbaceous annual plant. Its common names include field burrweed, Onehunga-weed, lawn burrweed, lawnweed, and common soliva. It is one of several plants known as bindi weed, bindii, or bindi-eye. A weedy plant known for its tiny sharp-needled seeds. It appears with small feathery leaves reminiscent of parsley, with an exposed upward-pointing rosette of seeds in a pod nestled at the branch junctions. Eventually small flowers appear if the plant is allowed to develop. Those familiar with the plant may also know it as "bindi patches", which can't be walked on barefoot. Dogs and cats are no less affected and tend to avoid areas where they have encountered it. Originally native to South America, the plant is now well established in many places around the world, including Australia, New Zealand, southwest France, Hawaii, California, and several other states in the United States. It is mainly found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hipólito Ruiz López
Hipólito Ruiz López (August 8, 1754 in Belorado, Burgos, Spain – 1816 in Madrid), or Hipólito Ruiz, was a Spanish botanist known for researching the floras of Peru and Chile during an expedition under Carlos III from 1777 to 1788. During the reign of Carlos III, three major botanical expeditions were sent to the New World; Ruiz and José Antonio Pavón Jiménez were the botanists for the first of these expeditions, to Peru and Chile. Background After studying Latin with an uncle who was a priest, at the age of 14 Ruiz López went to Madrid to study logic, physics, chemistry and pharmacology. He also studied botany at the Migas Calientes Botanical Gardens (now the Real Jardín Botánico de Madrid), under the supervision of Casimiro Gómez Ortega (1741–1818) and Antonio Palau Verdera (1734–1793). Ruiz had not yet completed his pharmacology studies when he was named the head botanist of the expedition. The French physician Joseph Dombey was named as his assistant, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Antonio Pavón Jiménez
José Antonio Pavón Jiménez or José Antonio Pavón (April 22, 1754 in Casatejada, Cáceres, Spain – 1840 in Madrid) was a Spanish botanist known for researching the flora of Peru and Chile. During the reign of Charles III of Spain, three major botanical expeditions were sent to the New World; Pavón and Hipólito Ruiz López were the botanists for the first of these expeditions, to Peru and Chile from 1777 to 1788. The standard author abbreviation Ruiz & Pav. is used to indicate Pavón and his colleague Ruiz as joint authors when citing a botanical name. The genus '' Pavonia'' was named in his honor by his contemporary, Spanish botanist Antonio José Cavanilles — plants with the specific epithet of ''pavonii'' also commemorate his name. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soliva
''Soliva'' is a genus of South American plants in the sunflower family. Burrweed is a common name for some species in this genus. Species * '' Soliva anthemidifolia'' (Juss.) Sweet - Colombia * '' Soliva anthemifolia'' (Juss.) Sweet - Ecuador, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay * '' Soliva macrocephala'' Cabrera - Uruguay, northern Argentina * ''Soliva sessilis ''Soliva sessilis'', one of up to nine species of the genus '' Soliva'', is a low-growing herbaceous annual plant. Its common names include field burrweed, Onehunga-weed, lawn burrweed, lawnweed, and common soliva. It is one of several plants kno ...'' Ruiz & Pav. - Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, northern Argentina, Chile * '' Soliva stolonifera'' (Brot.) R.Br. ex Sweet - Peru, Bolivia, Uruguay * '' Soliva triniifolia'' Griseb. - Argentina References Anthemideae Asteraceae genera Flora of Southern America {{Anthemideae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbaceous
Herbaceous plants are vascular plants that have no persistent woody stems above ground. This broad category of plants includes many perennials, and nearly all annuals and biennials. Definitions of "herb" and "herbaceous" The fourth edition of the ''Shorter Oxford English Dictionary'' defines "herb" as: #"A plant whose stem does not become woody and persistent (as in a tree or shrub) but remains soft and succulent, and dies (completely or down to the root) after flowering"; #"A (freq. aromatic) plant used for flavouring or scent, in medicine, etc.". (See: Herb) The same dictionary defines "herbaceous" as: #"Of the nature of a herb; esp. not forming a woody stem but dying down to the root each year"; #"BOTANY Resembling a leaf in colour or texture. Opp. scarious". Botanical sources differ from each other on the definition of "herb". For instance, the Hunt Institute for Botanical Documentation includes the condition "when persisting over more than one growing season, the parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Plant
An annual plant is a plant that completes its life cycle, from germination to the production of seeds, within one growing season, and then dies. The length of growing seasons and period in which they take place vary according to geographical location, and may not correspond to the four traditional seasonal divisions of the year. With respect to the traditional seasons, annual plants are generally categorized into summer annuals and winter annuals. Summer annuals germinate during spring or early summer and mature by autumn of the same year. Winter annuals germinate during the autumn and mature during the spring or summer of the following calendar year. One seed-to-seed life cycle for an annual plant can occur in as little as a month in some species, though most last several months. Oilseed rapa can go from seed-to-seed in about five weeks under a bank of fluorescent lamps. This style of growing is often used in classrooms for education. Many desert annuals are therophytes, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weed
A weed is a plant considered undesirable in a particular situation, "a plant in the wrong place", or a plant growing where it is not wanted.Harlan, J. R., & deWet, J. M. (1965). Some thoughts about weeds. ''Economic botany'', ''19''(1), 16-24. This introduces the concept of humans and their goals in a particular setting.Holzner, W., & Numata, M. (Eds.). (2013). ''Biology and ecology of weeds'' (Vol. 2). Springer Science & Business Media. The concept of weeds is particularly significant in agriculture, where the aim is growing crops or pastures of a single species, or a mixture of a few desired species. In such environments, other plant species are considered undesirable and therefore a weed. Besides, some weeds have undesirable characteristics making them a plant pest in most human settings.Harlan, J. R., & deWet, J. M. (1965). Some thoughts about weeds. ''Economic botany'', ''19''(1), 16-24.Holzner, W., & Numata, M. (Eds.). (2013). ''Biology and ecology of weeds'' (Vol. 2). Spri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parsley
Parsley, or garden parsley (''Petroselinum crispum'') is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae that is native to the central and eastern Mediterranean region (Sardinia, Lebanon, Israel, Cyprus, Turkey, southern Italy, Greece, Portugal, Spain, Malta, Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia), but has been naturalized elsewhere in Europe, and is widely cultivated as a herb, and a vegetable. Parsley is widely used in European, Middle Eastern, and American cuisine. Curly leaf parsley is often used as a garnish. In central Europe, eastern Europe, and southern Europe, as well as in western Asia, many dishes are served with fresh green chopped parsley sprinkled on top. Flat leaf parsley is similar, but it is easier to cultivate, some say it has a stronger flavor. Root parsley is very common in central, eastern, and southern European cuisines, where it is used as a snack or a vegetable in many soups, stews, and casseroles. It is believed to have been originally grown in Sardinia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weedkillers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page for EPA reports on pesticide use ihere Selective herbicides control specific weed species, while leaving the desired crop relatively unharmed, while non-selective herbicides (sometimes called total weedkillers in commercial products) can be used to clear waste ground, industrial and construction sites, railways and railway embankments as they kill all plant material with which they come into contact. Apart from selective/non-selective, other important distinctions include ''persistence'' (also known as ''residual action'': how long the product stays in place and remains active), ''means of uptake'' (whether it is absorbed by above-ground foliage only, through the roots, or by other means), and ''mechanism of action'' (how it works). Historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MCPA
MCPA (2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid) is a powerful, selective, widely used phenoxy herbicide. The pure compound is a brown-colored powder. MCPA has been extensively used in agriculture to control broad-leaf weeds as a growth regulator primarily in pasture and cereal crops field since 1945. The mode of action of MCPA is as an auxin, which are growth hormones that naturally exist in plants. Overdose application of MCPA acts as an herbicide and results in abnormal growth. History In 1936 investigations began at ICIs Jealott's Hill research center into the effects of auxins on plant growth looking specifically for a way to kill weeds without harming crops such as wheat and oats. William Templeman found that when indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), the naturally occurring auxin, was used at high concentrations, it could stop plant growth. In 1940, he published his finding that IAA killed broadleaf plants within a cereal field. Templeman and the ICI group were searching for compounds w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicamba
Dicamba (3,6-dichloro-2-methoxybenzoic acid) is a broad-spectrum herbicide first registered in 1967. Brand names for formulations of this herbicide include Dianat, Banvel, Diablo, Oracle and Vanquish. This chemical compound is a chlorinated derivative of ''o''-anisic acid. Around 2016, dicamba's use came under significant scrutiny due to its tendency to spread from treated fields into neighboring fields, causing damage. Use as an herbicide Dicamba kills annual and perennial broadleaf weeds. Its primary commercial applications are weed control for grain crops and turf areas. It is also used to control brush and bracken in pastures, as well as controlling legumes and cacti. In combination with a phenoxy herbicide or with other herbicides, dicamba can be used for weed control in range land and other noncrop areas (fence rows, roadways, and wastage). Dicamba is toxic to conifer species but is in general less toxic to grasses.Arnold P. Appleby, Franz Müller. "Weed Control, 2" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
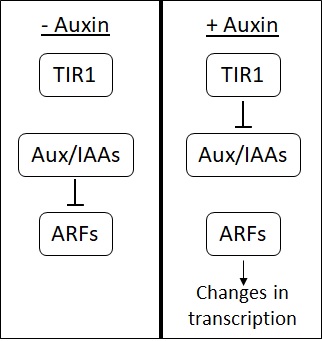
Auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essential for plant body development. The Dutch biologist Frits Warmolt Went first described auxins and their role in plant growth in the 1920s. Kenneth V. Thimann became the first to isolate one of these phytohormones and to determine its chemical structure as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Went and Thimann co-authored a book on plant hormones, ''Phytohormones'', in 1937. Overview Auxins were the first of the major plant hormones to be discovered. They derive their name from the Greek word αυξειν (''auxein'' – "to grow/increase"). Auxin is present in all parts of a plant, although in very different concentrations. The concentration in each position is crucial developmental information, so it is subject to tight regulation through both meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grass
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, providing staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, barley, and millet as well as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials (bamboo, thatch, and straw); others can provide a source of biofuel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)