|
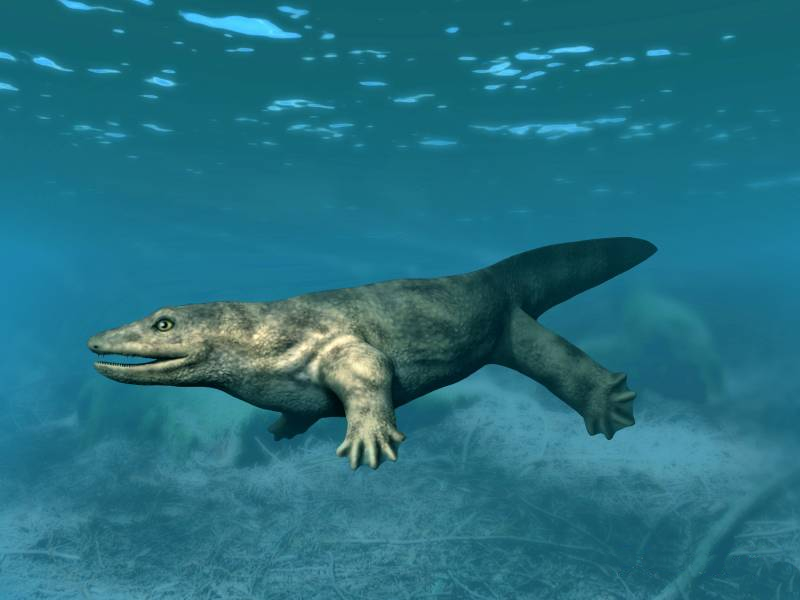
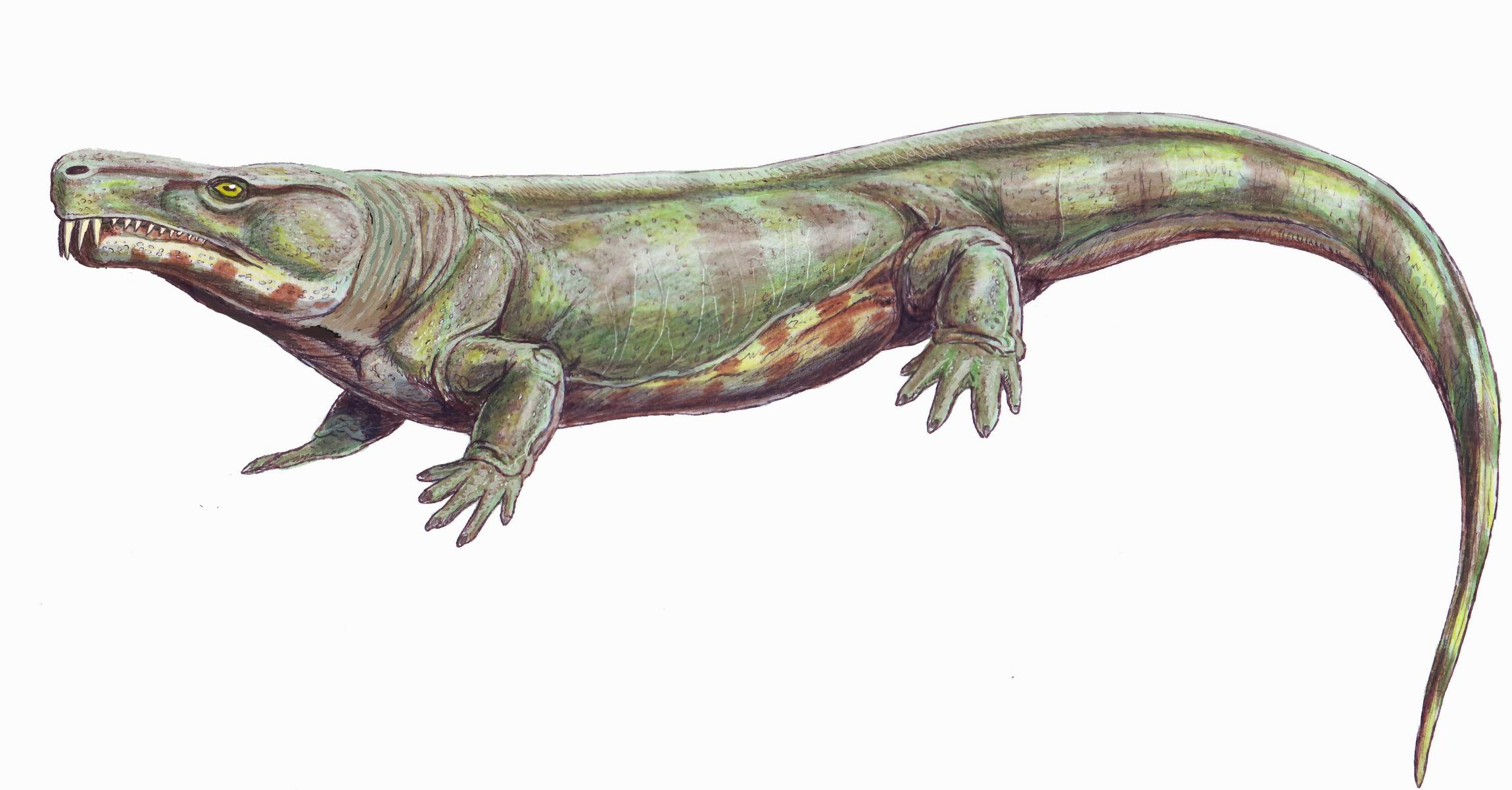
Solenodonsaurus
''Solenodonsaurus'' ("single-tooth lizard") is an extinct genus of reptiliomorphs that lived in what is now Czech Republic, during the Westphalian stage. Description ''Solenondosaurus'' had snout-vent length with a skull length . ''Solenodonsaurus'' shows a curious mix of characters making it difficult to place phylogenetically. The teeth lack labyrinthodont folding of the enamel, and it skull has a much smaller otic notch than seen in other reptiliomorph amphibians. Yet general build ties it in with the Diadectomorpha. Laurin, M. and Rize R.R. (1999): A new study of ''Solenodonsaurus janenschi'', and a reconsideration of amniote origins and stegocephalian evolution. ''Canadian Journal of Earth Science'', no 36 (8): pp 1239–1255 (1999)/ref> Paleobiology ''Solenodonsaurus'' was likely best adapted to life on land, as opposed to living in an aquatic environment like many other early tetrapods. The limbs and pelvis are incomplete in all known specimens of ''Solenodonsaurus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiliomorph
Reptiliomorpha (meaning reptile-shaped; in PhyloCode known as ''Pan-Amniota'') is a clade containing the amniotes and those tetrapods that share a more recent common ancestor with amniotes than with living amphibians (lissamphibians). It was defined by Michel Laurin (2001) and Vallin and Laurin (2004) as the largest clade that includes ''Homo sapiens'', but not '' Ascaphus truei'' (tailed frog). Laurin and Reisz (2020) defined Pan-Amniota as the largest total clade containing ''Homo sapiens'', but not '' Pipa pipa'', '' Caecilia tentaculata'', and '' Siren lacertina''. The informal variant of the name, "reptiliomorphs", is also occasionally used to refer to stem-amniotes, i.e. a grade of reptile-like tetrapods that are more closely related to amniotes than they are to lissamphibians, but are not amniotes themselves; the name is used in this meaning e.g. by Ruta, Coates and Quicke (2003). An alternative name, "Anthracosauria", is also commonly used for the group, but is confusi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labyrinthodont
"Labyrinthodontia" (Greek, 'maze-toothed') is an informal grouping of extinct predatory amphibians which were major components of ecosystems in the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras (about 390 to 150 million years ago). Traditionally considered a subclass of the class Amphibia, modern classification systems recognize that labyrinthodonts are not a formal natural group (clade) exclusive of other tetrapods. Instead, they consistute an evolutionary grade (a paraphyletic group), ancestral to living tetrapods such as lissamphibians (modern amphibians) and amniotes (reptiles, mammals, and kin). "Labyrinthodont"-grade vertebrates evolved from lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian, though a formal boundary between fish and amphibian is difficult to define at this point in time. "Labyrinthodont" generally refers to extinct four-limbed tetrapods with a large body size and a crocodile-like lifestyle. The name describes the pattern of infolding of the dentin and enamel of the teeth, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulerpeton
''Tulerpeton'' is an extinct genus of Devonian four-limbed vertebrate, known from a fossil that was found in the Tula Region of Russia at a site named Andreyevka. This genus and the closely related ''Acanthostega'' and ''Ichthyostega'' represent the earliest tetrapods. Description ''Tulerpeton'' is considered one of the first "tetrapods" (in the broad sense of the word) to have evolved. It is known from a fragmented skull, the left side of the pectoral girdle, and the entire right forelimb and right hindlimb along with a few belly scales. This species is differentiated from the less derived "aquatic tetrapods" (such as ''Acanthostega'' and ''Ichthyostega'') by a strengthened limb structure. These limbs consist of 6 toes and fingers. Additionally, its limbs appear to have evolved for powerful paddling rather than walking. The fossil fragments also indicate that its head was disconnected from the pectoral girdle. From the absence of the rough postbranchial lamina of the pectoral gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepospondyli
Lepospondyli is a diverse taxon of early tetrapods. With the exception of one late-surviving lepospondyl from the Late Permian of Morocco ('' Diplocaulus minumus''), lepospondyls lived from the Early Carboniferous (Mississippian) to the Early Permian and were geographically restricted to what is now Europe and North America. Five major groups of lepospondyls are known: Adelospondyli; Aïstopoda; Lysorophia; Microsauria; and Nectridea. Lepospondyls have a diverse range of body forms and include species with newt-like, eel- or snake-like, and lizard-like forms. Various species were aquatic, semiaquatic, or terrestrial. None were large (the biggest genus, the diplocaulid '' Diplocaulus'', reached a meter in length, but most were much smaller), and they are assumed to have lived in specialized ecological niches not taken by the more numerous temnospondyl amphibians that coexisted with them in the Paleozoic. Lepospondyli was named in 1888 by Karl Alfred von Zittel, who coined the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westphalian (stage)
The Westphalian is a stage in the regional stratigraphy of northwest Europe with an age between roughly 313 and 304 Ma (million years ago). It is a subdivision of the Carboniferous system or period and the regional Silesian series. The Westphalian is named for the region of Westphalia (German: ''Westfalen'') in western Germany where strata of this age occur. The Coal Measures of England and Wales are also largely of Westphalian age though they also extend into the succeeding Stephanian. The Westphalian age is preceded by the Namurian stage/age (which corresponds to the Millstone Grit Series of Great Britain) and succeeded by the Stephanian stage/age (which corresponds to the uppermost part of the Coal Measures of Great Britain). In the official geologic timescale of the ICS, the Westphalian is placed within the Pennsylvanian epoch (318-299 Ma).F M Gradstein, J G Ogg, A G Smith et al 2004, ‘A Geologic Time Scale 2004’. The (regionally defined) Westphalian stage corres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant taxon, extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids and all extant mammals). Tetrapods evolved from a clade of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the Tetrapodomorpha which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish (sarcopterygians) around 390 million years ago in the Middle Devonian, Middle Devonian period; their forms were transitional between lobe-finned fishes and true four-limbed tetrapods. Limbed vertebrates (tetrapods in the broad sense of the word) are first known from Middle Devonian trackways, and body fossils became common near the end of the Late Devonian but these were all aquatic. The first crown group, crown-tetrapods (last common ancestors of extant tetrapods capable of terrestrial locomotion) appeared by the very early Mississippian ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baphetes
''Baphetes'' is an extinct genus of tetrapod from the Pennine Coal Measures Group and Parrot Coal, England, the Joggins Formation of Nova Scotia, and the Kladno Formation of the Czech Republic. It was first named by Richard Owen in 1854. The type species is ''B. planiceps''. References External links ''Baphetes''in the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Paleo ... Baphetoids Carboniferous tetrapods Carboniferous tetrapods of Europe Paleozoic life of Nova Scotia Fossil taxa described in 1854 Taxa named by Richard Owen {{carboniferous-animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whatcheeria
''Whatcheeria'' is an extinct genus of early tetrapod from the Mississippian (Early Carboniferous) of Iowa. Fossils have been found in 340 million year old fissure fill deposits in the town of Delta. The type species, ''Whatcheeria deltae'' was named in 1995. It is classified within the family Whatcheeriidae, along with the closely related ''Pederpes'' and possibly ''Ossinodus.'' ''Whatcheeria'' is named after What Cheer, Iowa, the hometown of Pat McAdams, the geologist who discovered the first skeletons of the animal. The species is named after Delta, Iowa, the location where the fossils were uncovered. Description ''Whatcheeria'' possesses a mixture of both primitive and derived traits. It shares with earlier stem tetrapods a series of lateral lines across the skull, rows of teeth on the palate, and small Meckelian foramina across the surface of the lower jaw. It has a cleithrum, a bone in the pectoral girdle that extends from the scapula. The cleithrum once attached to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crassigyrinus
''Crassigyrinus'' (from la, crassus, 'thick' and el, γυρίνος el, gyrínos, 'tadpole') is an extinct genus of carnivorous stem tetrapod from the Early Carboniferous Limestone Coal Group of Scotland and possibly Greer, West Virginia. The type specimen was originally described as ''Macromerium scoticum'' and lacked a complete skull. With subsequent discoveries, ''Crassigyrinus'' is now known from three skulls, one of which is in articulation with a fairly complete skeleton, and two incomplete lower jaws. ''Crassigyrinus'' grew up to 2 meters in length, coupled with tiny limbs and unusually large jaws. ''Crassigyrinus'' is taxonomically enigmatic, having confused paleontologists for decades with its apparent fish-like and tetrapod features. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greererpeton
''Greererpeton burkemorani'' ("crawler from Greer, West Virginia") is an extinct genus of colosteid stem-tetrapods from the Early Carboniferous period (late Viséan) of North America. ''Greererpeton'' was first described by famed vertebrate paleontologist Alfred S. Romer in 1969. The skull was redescribed by Timothy R. Smithson in 1982, while postcranial remains were redescribed by Stephen J. Godfrey in 1989. ''Greererpeton'' were probably aquatic, with an elongated body adapted for swimming. Adults have overall length of or , similar in size to modern Asian giant salamanders (''Andrias''). The body was elongated, with about 40 vertebrae, while the flattened skull reached about long in adult specimens. The most complete adult specimen only preserved 12 tail vertebrae, only about a third the length of the body as in ''Andrias''. However, smaller specimens have been found preserving over 30 vertebrae, so it is not inconceivable that a complete tail was approximately as long as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colosteus
''Colosteus'' is an extinct genus of colosteid tetrapod from the Late Carboniferous (late Westphalian stage) of Ohio. Its remains have been found at the Linton site in Saline Township, Ohio, where it is one of the most common tetrapods, and at the Five Points site in Mahoning County, Ohio. It was an elongate, aquatic form with a flattened and pointed head, greatly reduced limbs, two premaxillary tusks, and heavy scalation. It would have reached about 1 m (3.2 ft) in length. It was originally described by John Strong Newberry in 1856 as a new species of the palaeonisciform fish genus '' Pygopterus''. In 1869, Edward Drinker Cope erected a new genus of " batrachian", ''Colosteus'', containing the species ''C. crassicutatus'', ''C. foveatus'', and ''C. marshii'', based on Linton material lent to him by Newberry. Cope later realized that the holotype A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyostega
''Ichthyostega'' (from el, ἰχθῦς , 'fish' and el, στέγη , 'roof') is an extinct genus of limbed tetrapodomorphs from the Late Devonian of Greenland. It was among the earliest four-limbed vertebrates in the fossil record, and was one of the first with weight-bearing adaptations for terrestrial locomotion. ''Ichthyostega'' possessed lungs and limbs that helped it navigate through shallow water in swamps. Although ''Ichthyostega'' is often labelled a 'tetrapod' due to the possession of limbs and fingers, it evolved long before true crown group tetrapods, and could more accurately be referred to as a stegocephalian or stem tetrapod. Likewise, while undoubtedly of amphibian build and habit, it is not considered a true member of the group in the narrow sense, as the first modern amphibians (members of the group Lissamphibia) appeared in the Triassic Period. Until finds of other early stegocephalians and closely related fishes in the late 20th century, ''Ichthyostega'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |