|
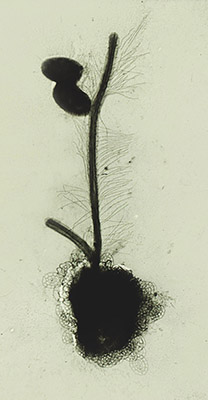
Solenicola
''Solenicola setigera'' is a species of marine stramenopile, and the only species classified within the genus ''Solenicola''. The species ranges between 4–7 µm in diameter and has a complex feeding strategy. Its ecological role within the marine planktonic food chain is generally as a grazer, feeding on photoautotrophic diatoms. It is a parasite of the species '' Leptocylindrus mediterraneus''. ''S. setigera'' will grow on the frustule, the protective shell made of silica, of ''L. mediterraneus'' alongside the cyanobacteria ''Synechococcus ''Synechococcus'' (from the Greek ''synechos'', in succession, and the Greek ''kokkos'', granule) is a unicellular cyanobacterium that is very widespread in the marine environment. Its size varies from 0.8 to 1.5 µm. The photosynthetic c ...'', which it may also eat. ''S. setigera'' combines herbivorous grazing, parasitism, and predation into its survival strategy. In 2013, the genus was placed in the family Solenicolidae. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptocylindrus Mediterraneus
''Leptocylindrus'' is a genus of diatoms belonging to the family Leptocylindraceae. They are long, cylindrical diatoms that are made up of multiple cells in a line (described as a chain). These cells have chloroplast to allow it to produce energy through photosynthesis by taking in sunlight and carbon dioxide to create sugars. the cells are attached at the cell walls called valves, the cell wall is slightly concave on one side and convex on the other so that the other cell wall attached will fit together. Reproduction ''Leptocylindrus'' reproduction is both asexual and (in some species) sexual. For the specific species '' Leptocylindrus danicus'', it goes through sexual reproduction when its cells are between 3 and 8 micrometers in width (cells above this width go through asexual reproduction). It begins with ''Leptoclindrus'' cells splitting into two uneven gametangia. The female gametangia are longer and more brightly colored cell than the male gametangia. Then the process of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placidozoa
Placidozoa is a recently defined non-photosynthetic lineage of Heterokonts. Phylogeny Taxonomy Infraphylum Placidozoa Cavalier-Smith 2013 * Superclass Wobblata Cavalier-Smith 2006 stat. n. 2013 (paraphyletic) ** Class Placididea Moriya, Nakayama & Inouye 2002 *** Order Placidida Moriya, Nakayama & Inouye 2002 lacidae Cavalier-Smith 2006**** Family Placidiaceae Moriya, Nakayama & Inouye 2002 ***** Genus '' Pendulomonas'' Tong 1997 ***** Genus ''Placidia'' Moriya, Nakayama & Inouye 2002 ***** Genus '' Wobblia'' Moriya, Nakayama & Inouye 2000 ***** Genus '' Allegra'' Rybarski et al. 2015 ** Class Nanomonadea Cavalier-Smith 2013 *** Order Uniciliatida Cavalier-Smith 2013 **** Family Solenicolidae Cavalier- Smith 2013 ***** Genus ''Solenicola'' Pavillard 1916 **** Family Incisomonadidae Cavalier-Smith & Scoble 2013 ***** Genus '' Incisomonas'' Scoble & Cavalier-Smith 2013 ** Class Opalomonadea Cavalier-Smith 2013 *** Genus '' Barthelona'' Bernard, Simpson & Patterson 2000 *** G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanomonadea
Nanomonadea is a class of biciliate phagotrophic, non-photosynthetic free-living opalozoans, coontaining the sole order Uniciliatida. This monophyletic group previously known as clade MAST-3 is characterized by a single hairless posterior cilium and absence of an anterior cilium. Phylogeny The cladogram below shows the relationships between Nanomonadea and the rest of Opalozoans. Taxonomy The taxonomy of Nanomonadea is as follows: *Subphylum Opalozoa **Infraphylum Placidozoa ***Superclass Wobblata (paraphyletic) ****Class Nanomonadea *****Order Uniciliatida ******Family Solenicolidae – ''Solenicola ''Solenicola setigera'' is a species of marine stramenopile, and the only species classified within the genus ''Solenicola''. The species ranges between 4–7 µm in diameter and has a complex feeding strategy. Its ecological role within th ...'' ******Family Incisomonadidae – '' Incisomonas'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q28373662 Placidozoa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterokonta
Heterokonts are a group of protists (formally referred to as Heterokonta, Heterokontae or Heterokontophyta). The group is a major line of eukaryotes. Most are algae, ranging from the giant multicellular kelp to the unicellular diatoms, which are a primary component of plankton. Other notable members of the Stramenopiles include the (generally) parasitic oomycetes, including ''Phytophthora'', which caused the Great Famine of Ireland, and ''Pythium'', which causes seed rot and damping off. The name "heterokont" refers to the type of motile life cycle stage, in which the flagellated cells possess two differently arranged flagella (see zoospore). History In 1899, Alexander Luther created the term "Heterokontae" for some algae with unequal flagella, today called Xanthophyceae. Later, some authors (e.g., Copeland, 1956) included other groups in Heterokonta, expanding the name's sense. The term continues to be applied in different ways, leading to Heterokontophyta being applied al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bigyra
Bigyra is a grouping of heterokont organisms. It includes Bicosoecida, Blastocystis and Labyrinthulida. It has also been described as containing Opalozoa, Bicoecia, and Sagenista. Phylogeny The cladogram below shows the internal relationships within Bigyra: Classification The modern taxonomy of Bigyra is as follows: *Phylum Bigyra **Subphylum Opalozoa ***Infraphylum Placidozoa ****Superclass Wobblata ( paraphyletic) *****Class Placididea *****Class Nanomonadea *****Class Opalomonadea ****Superclass Opalinata *****Class Opalinea *****Class Blastocystea ''Blastocystis'' is a genus of single-celled heterokont parasites belonging to a group of organisms that are known as the Stramenopiles (also called Heterokonts) that includes algae, diatoms, and water molds. Blastocystis consists of several ... ***Infraphylum Bikosia ****Class Bikosea **Subphylum Sagenista ***Class Labyrinthulea ***Class Eogyrea References External links * * SAR supergroup unranked cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opalozoa
Opalozoa is a subphylum of heterotrophic protists of the phylum Bigyra, and is the sister group to Sagenista. Opalozoans are non-photosynthetic heterokonts that are ancestrally phagotrophic but many times have evolved to be osmotrophic saprotrophs in the gut of vertebrate animals. Taxonomy History: phylum Opalozoa In 1993 the name “Opalozoa” referred to a group of protists that was very different from what it is now. It was a phylum composed of many unrelated zooflagellates, grouped together because of the common presence of tubular mitochondrial cristae and the lack of cortical alveoli or rigid tubular ciliary hairs ( retronemes). It also included the opalinids, proteomyxids and plasmodiophorids. Modern classification The modern taxonomy of Opalozoa, down to order level, is as follows: * Subphylum Opalozoa ** Infraphylum Bikosia *** Class Bikosea ****Subclass Bicosidia *****Superorder Cyathobodoniae ******Order Bicoecida ******Order Anoecida ******Order Pseud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wobblata
Wobblata is a paraphyletic grouping of all placidozoans except Opalinata. It unites the classes Placididea, Nanomonadea and Opalomonadea. Description Members of this group are ancestrally aerobic phagotrophic biciliates. They have tubular mitochondrial cristae and a hairy anterior cilium The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projecti .... They have a split right microtubular root, i.e. one of the two (left and right) microtubular roots that support the feeding groove is split in two. They lack a cytopharynx, and some of them have lost their anterior cilium. Phylogeny The cladogram below shows the relationships between Wobblata and the rest of Opalozoans. References {{reflist Placidozoa Paraphyletic groups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAR Supergroup
The SAR supergroup, also just SAR or Harosa, is a clade that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and Rhizaria. The name is an acronym derived from the first letters of each of these clades; it has been alternatively spelled "RAS". The term "Harosa" (at the subkingdom level) has also been used. The SAR supergroup is a node-based taxon. Note that as a formal taxon, "Sar" has only its first letter capitalized, while the earlier abbreviation, SAR, retains all uppercase letters. Both names refer to the same group of organisms, unless further taxonomic revisions deem otherwise. Members of the SAR supergroup were once included under the separate supergroups Chromalveolata (Chromista and Alveolata) and Rhizaria, until phylogenetic studies confirmed that stramenopiles and alveolates diverged with Rhizaria. This apparently excluded haptophytes and cryptomonads, leading Okamoto ''et al.'' (2009) to propose the clade Hacrobia to accommodate them. Phylogeny Based on a compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halvaria
Halvaria is a grouping that includes Alveolata and Heterokonta (Stramenopiles). Analyses in 2007 and 2008 revealed that the Stramenopiles and the Alveolata are related, and form a reduced chromalveolate clade. They group together with the Rhizaria (originally one of the six major eukaryote groups) to form a clade dubbed the SAR supergroup. A phylogenomic analysis from 2016 cast doubt on Halvaria, suggesting that Alveolata is the sister group to Rhizaria (making the ''R + A clade'') through new rhizarian sequence data, and that support for Halvaria might be an artifact of low taxon sampling as well as long branch attraction. However, later analyses from 2021 support Halvaria as a solid clade. See also *Chromalveolata *Rhizaria The Rhizaria are an ill-defined but species-rich supergroup of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus Paulinella in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthethic, but many foramini ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stramenopile
Stramenopile is a clade of organisms distinguished by the presence of stiff tripartite external hairs. In most species, the hairs are attached to flagella, in some they are attached to other areas of the cellular surface, and in some they have been secondarily lost (in which case relatedness to stramenopile ancestors is evident from other shared cytological features or from genetic similarity). Stramenopiles represent one of the three major clades in the SAR supergroup, along with Alveolata and Rhizaria. Members of the clade are referred to as 'stramenopiles'. Stramenopiles are eukaryotes; since they are neither fungi, animals, nor plants, they are classified as protists. Most stramenopiles are single-celled, but some are multicellular algae including some brown algae. The group includes a variety of algal protists, heterotrophic flagellates, opalines and closely related proteromonad flagellates (all endobionts in other organisms); the actinophryid heliozoa, and oomycetes. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoautotrophism
Photoautotrophs are organisms that use light energy and inorganic carbon to produce organic materials. Eukaryotic photoautotrophs absorb energy through the chlorophyll molecules in their chloroplasts while prokaryotic photoautotrophs use chlorophylls and bacteriochlorophylls present in their cytoplasm. All known photoautotrophs perform photosynthesis. Examples include plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. Origin and the Great Oxidation Event Chemical and geological evidence indicate that photosynthetic cyanobacteria existed about 2.6 billion years ago and anoxygenic photosynthesis had been taking place since a billion years before that. Oxygenic photosynthesis was the primary source of oxygenation and led to the Great Oxidation Event (the Oxygen Catastrophe) roughly 2.4 to 2.1 billion years ago. Although the end of the Great Oxidation Event was marked by a significant decrease in gross primary productivity that eclipsed extinction events, the development of aerobic respiration enabled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising several genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion metric tons of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The shells of dead diatoms can reach as much as a half-mile (800 m) deep on the ocean floor, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |