|
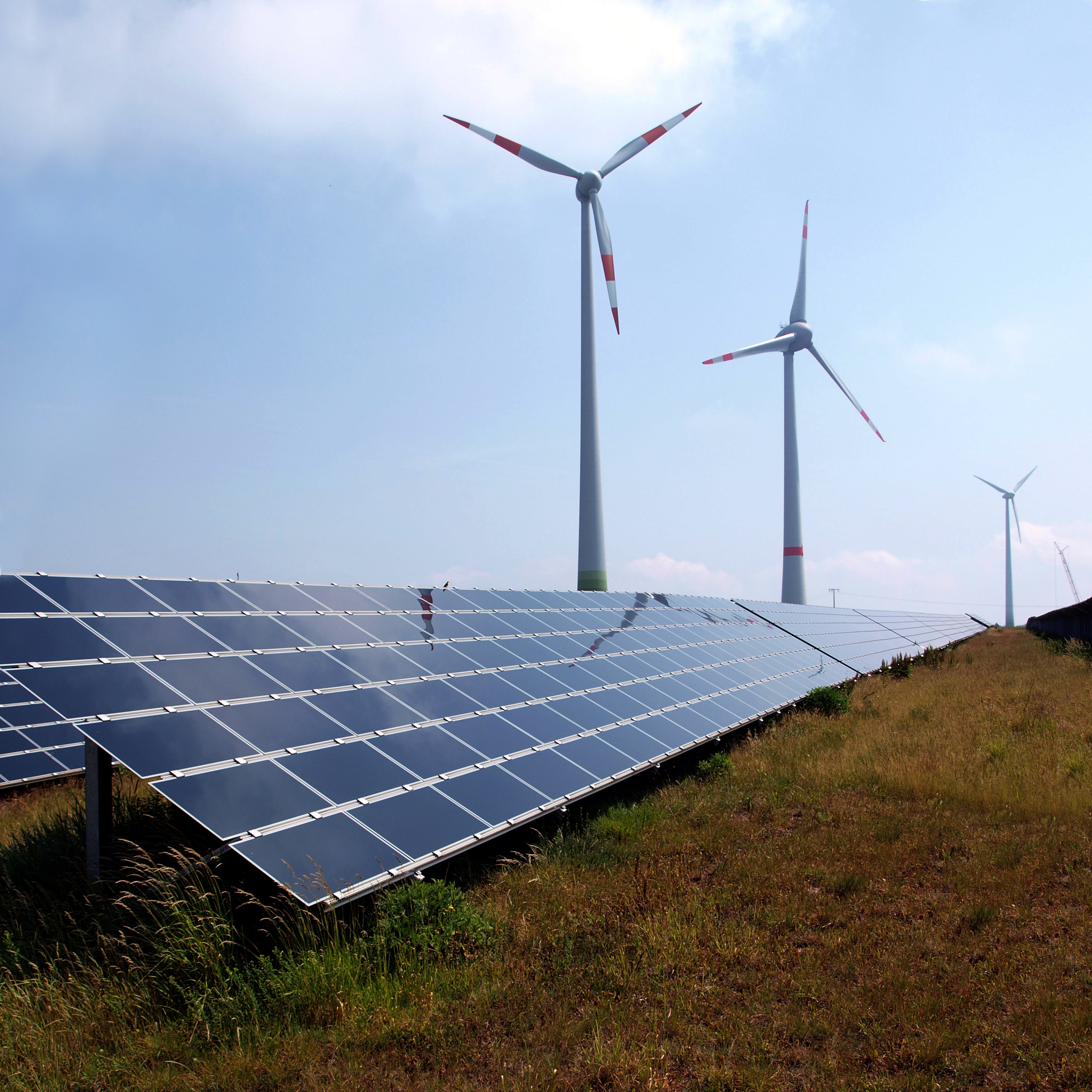
Solar Power In Portugal
Solar power is a growing source in the Portuguese energy mix. At the end of 2020, solar power installed capacity totalled 1.03 GW and represented 3.6% of total power generation in 2020. Portugal has set a goal of between 8.1 GW and 9.9 GW in installed capacity by 2030. Photovoltaic Plants The Serpa solar power plant is an 11 megawatt plant covered and employs 52,000 PV panels. The panels are raised 2 meters off the ground thus allowing grazing to continue. The plant provides enough energy for 8,000 homes and saves an estimated 30,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions per year. On 9 October 2021, the largest solar power plant in Portugal was inaugurated in Alcoutim. With an installed capacity of 219 MW, the power plant has 661,500 solar panels and can power the needs of 200,000 homes. It occupies an area of 320 hectares and will prevent the emission of 326,000 tons of carbon dioxide every year. It surpassed the 62 MW Moura Photovoltaic Power Station. Recent and future aucti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
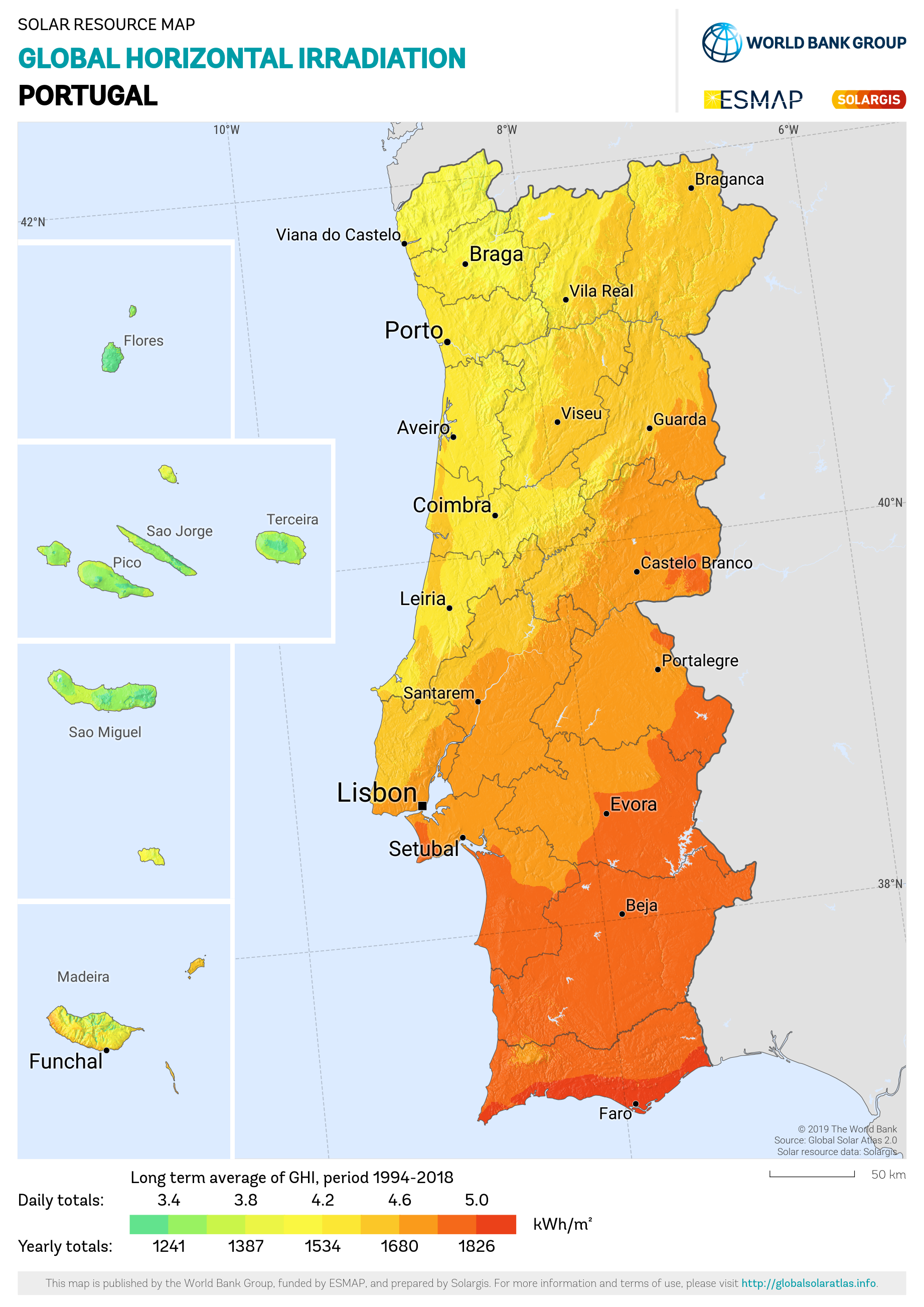
Portugal GHI Solar-resource-map GlobalSolarAtlas World-Bank-Esmap-Solargis
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, In recognized minority languages of Portugal: :* mwl, República Pertuesa is a country located on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Macaronesian archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira. It features the westernmost point in continental Europe, its mainland west and south border with the North Atlantic Ocean and in the north and east, the Portugal-Spain border, constitutes the longest uninterrupted border-line in the European Union. Its archipelagos form two autonomous regions with their own regional governments. On the mainland, Alentejo region occupies the biggest area but is one of the least densely populated regions of Europe. Lisbon is the capital and largest city by population, being also the main spot for tourists alongside Porto, the Algarve and Madeira. One of the oldest countries in Europe, its territory has been continuously settled and fought over since prehistoric t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Of Photovoltaics
Worldwide growth of photovoltaics has been close to exponential between 1992 and 2018. During this period of time, photovoltaics (PV), also known as solar PV, evolved from a niche market of small-scale applications to a mainstream electricity source. When solar PV systems were first recognized as a promising renewable energy technology, subsidy programs, such as feed-in tariffs, were implemented by a number of governments in order to provide economic incentives for investments. For several years, growth was mainly driven by Japan and pioneering European countries. As a consequence, cost of solar declined significantly due to experience curve effects like improvements in technology and economies of scale. Several national programs were instrumental in increasing PV deployment, such as the Energiewende in Germany, the Million Solar Roofs project in the United States, and China's 2011 five-year-plan for energy production. Since then, deployment of photovoltaics has gained mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Renewable Energy Topics By Country
This is a list of renewable energy topics by country and territory. These links can be used to compare developments in renewable energy in different countries and territories and to help and encourage new writers to participate in writing about developments in their own countries or countries of interest. The list refers to renewable energy in general, as well as solar power, wind power, geothermal energy, biofuel, and hydro-electricity. As of 2013, China, Germany, and Japan, and India, four of the world's largest economies generate more electricity from renewables than from nuclear power. Based on REN21's 2014 report, renewables supplied 19% of humans' global energy consumption. This energy consumption is divided as 9% coming from traditional biomass, 4.2% as heat energy (non-biomass), 3.8% hydro electricity and 2% is electricity from wind, solar, geothermal, and biomass. China is the world's largest producer of hydroelectricity, followed by Canada, Brazil, India, U.S an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Power In Portugal
Portugal is a producer of geothermal power, and their main investment is in the Azores. While electricity is only produced on São Miguel, Azores, direct-use applications are also at Chaves in northern Portugal, and at S. Pedro do Sul in central Portugal and at the Lisbon Air Force Hospital. Azores In the Azores, five geothermal power plants exist on São Miguel, one near Pico Vermelho (since 1981, 3,5 GWh in 2003) and four binary cycle power plants in Ribeira Grande (85,4 GWh in 2003) which have together an installed capacity of 16 MWe. Another one on Terceira (12 MWe). In 2003, 25% of the electricity consumed on São Miguel was produced by geothermal energy. In 2001, the geothermal energy contribution reached 35%. See also *Renewable energy in Portugal *Wind power in Portugal *Solar power in Portugal *List of renewable energy topics by country *Renewable energy in the European Union Renewable energy plays an important and growing role in the energy system of the Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Power In Portugal
Wind power is a major source of electricity in Portugal. At the end of 2020, wind power capacity in Continental Portugal was 5,456 MW. In 2020, wind power represented 23.7% of total electricity generation. The record of wind power generation was achieved on November 22, 2019 with 103.1 GWh produced Regional trends Most of the Portuguese wind capacity is located in the north-northeast ''distritos''. Viseu is the ''distrito'' with the largest installed capacity, followed by Coimbra, Vila Real and Castelo Branco. Major wind farms The 240 MW Alto Minho Wind Farm in the Viana do Castelo district became fully operational in November, 2008 when Portugal's Economy Minister Manuel Pinho inaugurated it. At the time of completion it was Europe's largest on-shore wind farm. The wind farm began generating electricity in 2007, with production increasing as more wind turbines came online, reflecting the modular nature of wind farms. The wind farm consists of 68 Enercon E-82 2MW wind turb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renewable Energy In Portugal
Renewable energy in Portugal was the source for 25.7% of total energy consumption in 2013. In 2014, 27% of Portugal's energy needs were supplied by renewable sources. In 2016, 28% of final energy consumption in Portugal came from renewable sources. Portugal aims to be climate neutral by 2050 and to cover 80% of its electricity consumption with renewables by 2030. In 2018, Portugal committed to close all of the country's coal producing facilities by 2030, making it almost completely reliant on renewable energy in the coming years. As of 2019, coal still provided 40% of Portugal's electricity needs. The last Portuguese coal power plant closed on 19 November 2021. Development In 2001, the Portuguese government launched a new energy policy instrument – the E4 Programme (Energy efficiency and Endogenous Energies), consisting of a set of multiple, diversified measures aimed at promoting a consistent, integrated approach to energy supply and demand. By promoting energy efficiency a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watt-peak
The nominal power is the nameplate capacity of photovoltaic (PV) devices, such as solar cells, modules and systems, and is determined by measuring the electric current and voltage in a circuit, while varying the resistance under precisely defined conditions. The nominal power is important for designing an installation in order to correctly dimension its cabling and converters.Die Verwirrung um das Watt-Peak The confusion around watt-peak, 14 August 2009. The peak power is not the same as the power under actual radiation conditions. In practice, this will be approximately 15-20% lower due to the considerable heating of the solar cells. Moreover, in installations where electricity is converted to [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megawatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own steam engine in 1776. Watt's invention was fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one metre per second against a constant opposing force of one newton, the rate at which work is done is one watt. : \mathrm In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the volt-ampere (the latter unit, however, is used for a different quantity from the real power of an electrical ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alqueva Dam
The Alqueva Dam is an arch dam and the centrepiece of the Alqueva Multipurpose Project. It impounds the River Guadiana, on the border of Beja and Évora Districts in south of Portugal. The dam takes its name from the town of Alqueva to its right bank. It creates a large reservoir with an inter-annual regulation capacity from which water may be distributed throughout the region. The dam was completed in 2002 and its reservoir reached the full level, for the first time, in 2010. The power station was commissioned in two stages, stage I in 2004 and stage II in 2013. The Alqueva Dam is the largest dam and artificial lake () in Western Europe. History During the 1950s, the Portuguese Prime Minister, António de Oliveira Salazar, ordered a study of the feasibility of the dam project. The potential benefits of the Alqueva dam were discussed for decades. An initial effort was undertaken after the Carnation Revolution of 1974, but it was abandoned in 1978. The Portuguese government event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Mix
The energy mix is a group of different primary energy sources from which secondary energy for direct use - such as electricity - is produced. Energy mix refers to all direct uses of energy, such as transportation and housing, and should not be confused with power generation mix, which refers only to generation of electricity. Global energy mix In 2007, the global primary energy use was oil equivalent, or . According to the International Energy Agency (IEA) 13.6% of world primary energy was used by the European Union (EU). Within the EU, 75.9% came from fossil fuels, 14.1% from nuclear power, 7% from biofuels, 2.9 from renewable energy resources. Overall primary energy consumption in the United States in 2015 relied most on petroleum (), natural gas () and coal (). Renewables contributed and nuclear power . In the same year, about 4 million GWh of electricity were generated in the United States, 67% of which was generated from fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, and <1% petro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energias De Portugal
EDP - Energias de Portugal (formerly Electricidade de Portugal) is a Portuguese electric utilities company, headquartered in Lisbon. It was founded in 1976 through the merger of 14 nationalised electricity companies. History EDP was founded as ''Electricidade de Portugal, E.P.'' by the Portuguese government though the Decreto-lei nº 502/76 published on June 30, 1976, merging 14 former energy companies that had been nationalised by 1975 in the aftermath of the regime change in 1974, of which the most significant had been the ''Companhias Reunidas de Gás e Eletricidade'' (CRGE). The Portuguese state privatised the company in several phases, from 1996 to 2011. In March 2007 the group made a US$3 billion takeover of Horizon Wind Energy, the Texan-based wind power producer. At the time, it was the largest renewable energy deal to date and made EDP the fourth largest wind power producer in the world. The firm's renewables operations (including Horizon) are now contained within i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euro
The euro (symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . The euro is divided into 100 cents. The currency is also used officially by the institutions of the European Union, by four European microstates that are not EU members, the British Overseas Territory of Akrotiri and Dhekelia, as well as unilaterally by Montenegro and Kosovo. Outside Europe, a number of special territories of EU members also use the euro as their currency. Additionally, over 200 million people worldwide use currencies pegged to the euro. As of 2013, the euro is the second-largest reserve currency as well as the second-most traded currency in the world after the United States dollar. , with more than €1.3 trillion in circulation, the euro has one of the highest combined values of banknotes and coins in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |