|
Solar Eclipse Of October 31, 1902
A partial solar eclipse occurred on October 31, 1902. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. Related eclipses Solar eclipses 1901–1902 Note: The Solar eclipse of April 8, 1902, partial solar eclipse of April 8, 1902, the Solar eclipse of March 29, 1903, annular solar eclipse of March 29, 1903 and the Solar eclipse of September 21, 1903, total solar eclipse of September 21, 1903 occur during the next lunar year set. Notes References External links 1902 in science 20th-century solar eclipses, 1902 10 31 October 1902 events {{Solar-eclipse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of the Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the new moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Earth's orbit. In a total eclipse, the disk of the Sun is fully obscured by the Moon. In partial and annular eclipses, only part of the Sun is obscured. Unlike a lunar eclipse, which may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth, a solar eclipse can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world. As such, although total solar eclipses occur somewhere on Earth every 18 months on average, they recur at any given place only once every 360 to 410 years. If the Moon were in a perfectly circular orbit and in the same orbital plane as Earth, there would be total solar eclipses once a month, at every new moon. Instead, because the Moon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synodic period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of April 8, 1902
A partial solar eclipse occurred on April 8, 1902. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ..., thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. This was the 76th and final event from Solar Saros 108. Related eclipses Solar eclipses 1902–1907 Metonic series Notes References External links 1902 4 8 1902 in science 1902 4 8 April 1902 events {{Solar-eclipse-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of March 29, 1903
An annular solar eclipse occurred on March 29, 1903. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from China (now northwestern China, Mongolia and northeastern China), Russia on March 29th (Sunday), and Northern Canada Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three Provinces_and_territories_of_Canada#Territories, territor ... on March 28th (Saturday). Related eclipses Solar eclipses 1902–1907 Saros 118 It is a part of Saros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
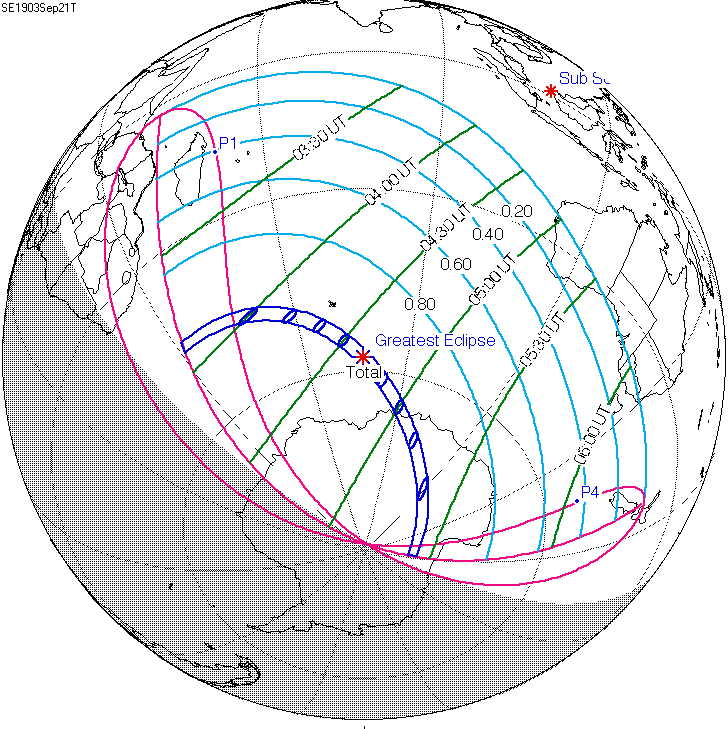
Solar Eclipse Of September 21, 1903
A total solar eclipse occurred on September 21, 1903. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter The angular diameter, angular size, apparent diameter, or apparent size is an angular distance describing how large a sphere or circle appears from a given point of view. In the vision sciences, it is called the visual angle, and in optics, it is ... is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Related eclipses Solar eclipses 1902–1907 Inex series In the 19th century: * Solar Saros 120: Total Solar Eclipse of 1816 Nov 19 * Solar Saros 121: Hybrid Solar Eclipse of 1845 Oct 30 * Solar Saros 122: Annular Solar Eclipse of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1902 In Science
The year 1902 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below. Aeronautics * May 15 – Lyman Gilmore claims to have flown his steam-powered fixed-wing aircraft, although his proof is supposedly destroyed in a 1935 fire. Chemistry * Hermann Emil Fischer and Joseph von Mering discover that barbitone (barbital or Veronal) is an effective hypnotic agent. It becomes the first commercially marketed barbiturate, being used as a treatment for insomnia from 1903. * Auguste Verneuil develops the Verneuil process for making synthetic rubies. * German chemist Wilhelm Ostwald developed the Ostwald process and patented it in 1902. Earth sciences * April–August – Eruption of Mount Pelée in Martinique. * Mercalli intensity scale introduced as a seismic scale for earthquakes by Giuseppe Mercalli. Exploration * December 30 – ''Discovery'' Expedition: British explorers Scott, Shackleton and Wilson reach the furthest southern point reached thus far by man, south o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |