|
Soga Sukenobu
Soga Sukenobu (曾我 祐信) was a Japanese samurai lord and ''gokenin'' of the late Heian and early Kamakura period. He was the lord of Soga Manor in Sagami Province. He was the adoptive father of Soga Tokimune and Sukenari, known for the Revenge of the Soga Brothers incident. He was also known as Soga Tarō. Life Soga Sukenobu was born to the Soga clan, who claimed descent from Emperor Kanmu's lineage of the Taira clan. His mother was the daughter of Itō Sukeie. He was a resident of Soga township in Sagami Province (present-day Odawara, Kanagawa Prefecture). In 1180, he sided with the Taira clan in the Battle of Ishibashiyama, but later surrendered to Minamoto no Yoritomo. He was rewarded a territory and became a close retainer (''gokenin'') to Yoritomo. Later, Sukenobu remarried the widow of Kawazu Sukeyasu and mother of Kawazu Hako'ō and Ichimanmaru, later known as Soga Tokimune and Sukenari, respectively. The Soga brothers thus became his adoptive sons. In 119 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese People
The are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Japanese archipelago."人類学上は,旧石器時代あるいは縄文時代以来,現在の北海道〜沖縄諸島(南西諸島)に住んだ集団を祖先にもつ人々。" () Japanese people constitute 97.9% of the population of the country of Japan. Worldwide, approximately 129 million people are of Japanese descent; of these, approximately 122.5 million are residents of Japan. People of Japanese ancestry who live outside Japan are referred to as , the Japanese diaspora. Depending on the context, the term may be limited or not to mainland Japanese people, specifically the Yamato (as opposed to Ryukyuan and Ainu people). Japanese people are one of the largest ethnic groups in the world. In recent decades, there has also been an increase in the number of multiracial people with both Japanese and non-Japanese roots, including half Japanese people. History Theories of origins Archaeological evidence indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minamoto No Yoritomo
was the founder and the first shogun of the Kamakura shogunate of Japan, ruling from 1192 until 1199.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Minamoto no Yoriie" in . He was the husband of Hōjō Masako who acted as regent (''shikken'') after his death. Yoritomo was the son of Minamoto no Yoshitomo and belonged to Seiwa Genji's prestigious Kawachi Genji family. After setting himself the rightful heir of the Minamoto clan, he led his clan against the Taira clan from his capital in Kamakura, beginning the Genpei War in 1180. After five years of war, he finally defeated the Taira clan in the Battle of Dan-no-ura in 1185. Yoritomo thus established the supremacy of the warrior samurai caste and the first shogunate (''bakufu'') at Kamakura, beginning the feudal age in Japan, which lasted until the mid-19th century. Early life Yoritomo was the third son of Minamoto no Yoshitomo, heir of the Minamoto (Seiwa Genji) clan, and his official wife, Yura-Gozen, daughter of Fujiwara no Sue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hōkyōintō
A is a Japanese pagoda, so called because it originally contained the .Iwanami Kōjien Japanese dictionary A Chinese variant of the Indian stūpa, it was originally conceived as a cenotaph of the King of Wuyue – Qian Liu. Structure and function Usually made in stone and occasionally metal or wood, ''hōkyōintō'' started to be made in their present form during the Kamakura period. Like a ''gorintō'', they are divided in five main sections called (from the bottom up) , or "inverted flower seat", , or base, , or body, , or umbrella, and , or pagoda finial. The ''tōshin'' is the most important part of the ''hōkyōintō'' and is carved with a Sanskrit letter. The ''sōrin'' has the same shape as the tip of a five-storied pagoda. The ''kasa'' can also be called , or roof. It's decorated with four characteristic wings called or . Different structures exist, and the ''hōkyōintō'' property of the Yatsushiro Municipal Museum in Kyushu for example is divided in just four parts, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soga Clan Yakata Ato
Soga may refer to: People * Soga clan, a Japanese clan of the Yamato period * Soga clan (Sagami Province), a Japanese clan * Soga people, of the Busoga kingdom in present-day Uganda * Machiko Soga, Japanese voice actress * Soga Tokimune, Japanese samurai * Soga Sukenari, Japanese samurai Places * Soga (river), a tributary of the Sogozha in Poshekhonye District, Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia * Soga, Tanzania, a railway station in Tanzania * Soga, an island in the Bissagos Islands off the coast of Guinea-Bissau * Soga Station, a railway station in Japan Other * Soga language, a Bantu language spoken in Uganda and the native language of the Soga people * Soga Monogatari, a Japanese tale of the Soga brothers * Sale of Goods Act (SOGA), legislation in the United Kingdom relating to the sale of goods * Soga, a percussion instrument See also * Busoga Busoga ( Lusoga: Obwakyabazinga bwa Busoga) is a kingdom and one of four constitutional monarchies in present-day Uganda. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
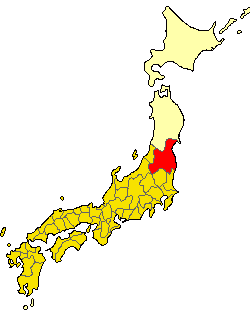
Mutsu Province
was an old province of Japan in the area of Fukushima, Miyagi, Iwate and Aomori Prefectures and the municipalities of Kazuno and Kosaka in Akita Prefecture. Mutsu Province is also known as or . The term is often used to refer to the combined area of Mutsu and the neighboring province Dewa, which together make up the entire Tōhoku region. History Invasion by the Kinai government Mutsu, on northern Honshū, was one of the last provinces to be formed as land was taken from the indigenous Emishi, and became the largest as it expanded northward. The ancient regional capital of the Kinai government was Tagajō in present-day Miyagi Prefecture. * 709 ('' Wadō 2, 3rd month''), an uprising against governmental authority took place in Mutsu and in nearby Echigo Province. Troops were dispatched to subdue the revolt. * 712 (''Wadō 5''), Mutsu was separated from Dewa Province. Empress Genmei's ''Daijō-kan'' made cadastral changes in the provincial map of the Nara period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daikan
''Daikan'' (代官) was an official in Japan that acted on behalf of a ruling monarch or a lord at the post they had been appointed to. Since the Middle Ages, ''daikan'' were in charge of their territory and territorial tax collection. In the Edo period, ''daikan'' were local governors in charge of the government and security of domain and shogunate territories. History In the Middle Ages, ''azukaridokoro'' and ''ukesho'' referred to ''daikan'' of a feudal lord, and ''shugo-dai'' and ''jitō-dai'' referred to ''daikan'' of ''shugo'' and ''jitō'' governors, respectively. In the Azuchi-Momoyama period, territorial rulers in charge of local tax collection were called ''daikan''. In the Edo period, high-ranking ''hatamoto'' retainers of the shogun were appointed ''daikan'' to govern the shogunal demesne across Japan and were given a 50,000-100,000 ''koku'' territory. The ''daikan'' worked from their administrative headquarters (''jin'ya'') at their territory or their mansion in E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jitō
were medieval territory stewards in Japan, especially in the Kamakura and Muromachi shogunates. Appointed by the ''shōgun'', ''jitō'' managed manors including national holdings governed by the provincial governor ( kokushi). There were also deputy ''jitōs'', ''jitōdai''. History The term ''jitō'' (literally meaning "land head") began to be used in the late Heian period as an adjectival word like "local". For example, a jitō person (地頭人) meant an influential local. Later, the term was sometimes used for persons who managed each local manor. Modern historians cannot clarify the character of the early ''jitō'' appointed by Minamoto no Yoritomo, as the conditions of these precursors are not well known. ''Jitō'' were officially established when Minamoto no Yoritomo was appointed to the office of Head of ''jitō'' by the Imperial court with the right to their appointment. Yoritomo appointed many ''jitō'' nationwide, however mainly in the Kantō region. During the Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokusō
was the title (post) held by the head of the mainline Hōjō clan, who also monopolized the position of ''shikken'' (regents to the shogunate) of the Kamakura shogunate in Japan during the period of Regent Rule (1199–1333). It’s important not to confuse a regent of the shogunate with a regent of the Emperor (the latter are called ''Sesshō'' and ''Kampaku''). ''Shikkens'' were the first regents to the shogunate. The ''tokusō'' from 1256 to 1333 was the military dictator of Japan as de facto head of the ''bakufu'' (shogunate); despite the actual shōgun being merely a puppet. This implies that all other positions in Japan—the Emperor, the Imperial Court, ''Sesshō'' and ''Kampaku'', and the ''shikken'' (regent of the shōgun)—had also been reduced to figureheads.「執権 (一)」(『国史大辞典 6』( 吉川弘文館、 1985年) ) Origin The name ''tokusō'' is said to have come from , the Buddhist name of Hōjō Yoshitoki, but Hōjō Tokimasa is usually reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashikaga Shogunate
The , also known as the , was the feudal military government of Japan during the Muromachi period from 1336 to 1573.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Muromachi-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 669. The Ashikaga shogunate was established when Ashikaga Takauji was appointed ''Shōgun'' after overthrowing the Kenmu Restoration shortly after having overthrown the Kamakura shogunate in support of Emperor Go-Daigo. The Ashikaga clan governed Japan from the Imperial capital of Heian-kyō (Kyoto) as ''de facto'' military dictators along with the ''daimyō'' lords of the ''samurai'' class. The Ashikaga shogunate began the Nanboku-chō period between the Pro-Ashikaga Northern Court in Kyoto and the Pro-Go-Daigo Southern Court in Yoshino until the South conceded to the North in 1392. The Ashikaga shogunate collapsed upon outbreak of the Ōnin War in 1467, entering a state of constant civil war known as the Sengoku period, and was finally dissolved when ''Shōgun'' Ashikaga Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamakura Shogunate
The was the feudal military government of Japan during the Kamakura period from 1185 to 1333. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Kamakura-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 459. The Kamakura shogunate was established by Minamoto no Yoritomo after victory in the Genpei War and appointing himself as ''shōgun''. Yoritomo governed Japan as military dictator from the eastern city of Kamakura with the emperor of Japan and his Imperial Court in the official capital city of Heian-kyō (Kyoto) as figureheads. The Kamakura ''shōguns'' were members of the Minamoto clan until 1226, the Fujiwara clan until 1252, and the last six were minor princes of the imperial family.Nussbaum"Minamoto"at pp. 632–633. The Hōjō clan were the ''de facto'' rulers of Japan as ''shikken'' (regent) of the ''shōgun'' from 1203.Nussbaum"Fujiwara"at pp. 200–201. The Kamakura shogunate saw the Jōkyū War in 1221 and the Mongol invasions of Japan under Kublai Khan in 1274 and 1281. The Kamaku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiba Clan
The Chiba clan (千葉氏 ''Chiba-shi'') was a Japanese ''gōzoku'' and samurai family descending from the Taira clan. The clan was founded by Chiba Tsunetane, the son of Taira no Tadatsune. The Chiba governed in Shimōsa Province, and the clan was based in present-day Chiba City. Additionally, for a period, the clan controlled the Sōma Manor that extended into present-day Ibaraki. After the establishment of the Kamakura shogunate, the head of the Chiba clan became the hereditary shugo governor of Shimōsa Province. Origin The Chiba clan descends from the 8th century Emperor Kanmu through the sequence of Imperial Prince Kazurahara (786-853) — Prince Takami — Taira no Takamochi — Muraoka Yoshifumi — Muraoka Tadayori — Chiba Tadatsune — Chiba Tsunemasa — Chiba Tsunenaga — Chiba Tsunekane — Chiba Tsuneshige — Chiba Tsunetane — Azuma Taneyori . The Emperor Go-Daigo authorized the head of Chiba family, Chiba Sadatane, as chief ''daimyō'' and samurai o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taira No Yoshifumi
Taira no Yoshifumi (平 良文) was a samurai lord of the Heian period. Called the "father of Musashi Plain development," the eight Taira clans of East Japan are said to have descended from him. He was also known as Muraoka Gorō. Life Yoshifumi was born in Kyoto, the fifth son of Taira no Takamochi (Prince Takamochi). He was the great-great-grandson of Emperor Kanmu. Yoshifumi is said to have been a brave warlord with a gentle appearance. He was also known as Muraoka Gorō, which derives from Muraoka, though it is disputed whether this refers to Muraoka in Kamakura, Sagami Province (present-day Fujisawa, Kanagawa Prefecture) or Ōsato, Musashi Province (present-day Kumagaya, Saitama Prefecture). When his father Takamochi was sent to the east in 898, the sons of his official wife, Taira no Kunika, Taira no Yoshikane, and Taira no Yoshimochi, followed him, but as the son of his concubine, Yoshifumi, did not. In 923, at the age of 36, Yoshifumi received an imperial order f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |