|
Softshell Turtles
The Trionychidae are a taxonomic family of a number of turtle genera, commonly known as softshell turtles. The family was erected by Leopold Fitzinger in 1826. Softshells include some of the world's largest freshwater turtles, though many can adapt to living in highly brackish areas. Members of this family occur in Africa, Asia, and North America, with extinct species known from Australia. Most species have traditionally been included in the genus '' Trionyx'', but the vast majority have since been moved to other genera. Among these are the North American ''Apalone'' softshells that were placed in ''Trionyx'' until 1987. Characteristics They are called "softshell" because their carapaces lack horny scutes (scales), though the spiny softshell, ''Apalone spinifera'', does have some scale-like projections, hence its name. The carapace is leathery and pliable, particularly at the sides. The central part of the carapace has a layer of solid bone beneath it, as in other turtles, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelodiscus Sinensis
The Chinese softshell turtle (''Pelodiscus sinensis'') is a species of softshell turtle that is native to China (Inner Mongolia to Guangxi, including Hong Kong) and Taiwan, with records of escapees—some of which have established introduced populations—in a wide range of other Asian countries, as well as Spain, Brazil and Hawaii. Populations native to Northeast China, Russia, Korea and Japan were formerly included in this species, but are now regarded as separate as the northern Chinese softshell turtle (''P. maackii''). Furthermore, localized populations in Guangxi and Hunan (where the Chinese softshell turtle also is present), as well as Vietnam, are recognized as the lesser Chinese softshell turtle (''P. parviformis'') and Hunan softshell turtle (''P. axenaria''). The Chinese softshell turtle is a vulnerable species, threatened by disease, habitat loss, and collection for food such as turtle soup. Additionally, millions are now farmed, especially in China, to support t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snorkeling
Snorkeling ( British and Commonwealth English spelling: snorkelling) is the practice of swimming on or through a body of water while equipped with a diving mask, a shaped breathing tube called a snorkel, and usually swimfins. In cooler waters, a wetsuit may also be worn. Use of this equipment allows the snorkeler to observe underwater attractions for extended periods with relatively little effort and to breathe while face-down at the surface. Snorkeling is a popular recreational activity, particularly at tropical resort locations. It provides the opportunity to observe underwater life in a natural setting without the complicated equipment and training required for scuba diving. It appeals to all ages because of how little effort is involved and is the basis of the two surface disciplines of the underwater sport of finswimming. Snorkeling is also used by scuba divers when on the surface, in underwater sports such as underwater hockey and underwater rugby, and as part of water-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicken
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domesticated junglefowl species, with attributes of wild species such as the grey and the Ceylon junglefowl that are originally from Southeastern Asia. Rooster or cock is a term for an adult male bird, and a younger male may be called a cockerel. A male that has been castrated is a capon. An adult female bird is called a hen and a sexually immature female is called a pullet. Humans now keep chickens primarily as a source of food (consuming both their meat and eggs) and as pets. Traditionally they were also bred for cockfighting, which is still practiced in some places. Chickens are one of the most common and widespread domestic animals, with a total population of 23.7 billion , up from more than 19 billion in 2011. There are more chickens in the world than any other bird. There are numerous cultural references to chickens – in myth, folklore and religion, and in language and literature. Genetic studies have pointed to mult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stew
A stew is a combination of solid food ingredients that have been cooked in liquid and served in the resultant gravy. A stew needs to have raw ingredients added to the gravy. Ingredients in a stew can include any combination of vegetables and may include meat, especially tougher meats suitable for slow-cooking, such as beef, pork, lamb, poultry, sausages, and seafood. While water can be used as the stew-cooking liquid, stock is also common. A small amount of red wine is sometimes added for flavour. Seasoning and flavourings may also be added. Stews are typically cooked at a relatively low temperature (simmered, not boiled), allowing flavours to mingle. Stewing is suitable for the least tender cuts of meat that become tender and juicy with the slow moist heat method. This makes it popular in low-cost cooking. Cuts having a certain amount of marbling and gelatinous connective tissue give moist, juicy stews, while lean meat may easily become dry. Stews are thickened by reduction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delicacy
A delicacy is usually a rare and expensive food item that is considered highly desirable, sophisticated, or peculiarly distinctive within a given culture. Irrespective of local preferences, such a label is typically pervasive throughout a region. Often this is because of unusual flavors or characteristics or because it is rare or expensive compared to standard staple foods. Delicacies vary per different countries, customs and ages. Flamingo tongue was a highly prized dish in ancient Rome, but is not commonly eaten in modern times. Lobsters were considered poverty food in North America until the mid-19th century when they started being treated, as they were in Europe, as a delicacy. Some delicacies are confined to a certain culture, such as fugu in Japan, bird's nest soup (made out of swiftlet nests) in China, and ant larvae ( escamoles) in Mexico or refer to specific local products, such as porcino, venison or anchovy. Examples of delicacies * Abalone (Bao Yu/Jeonbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
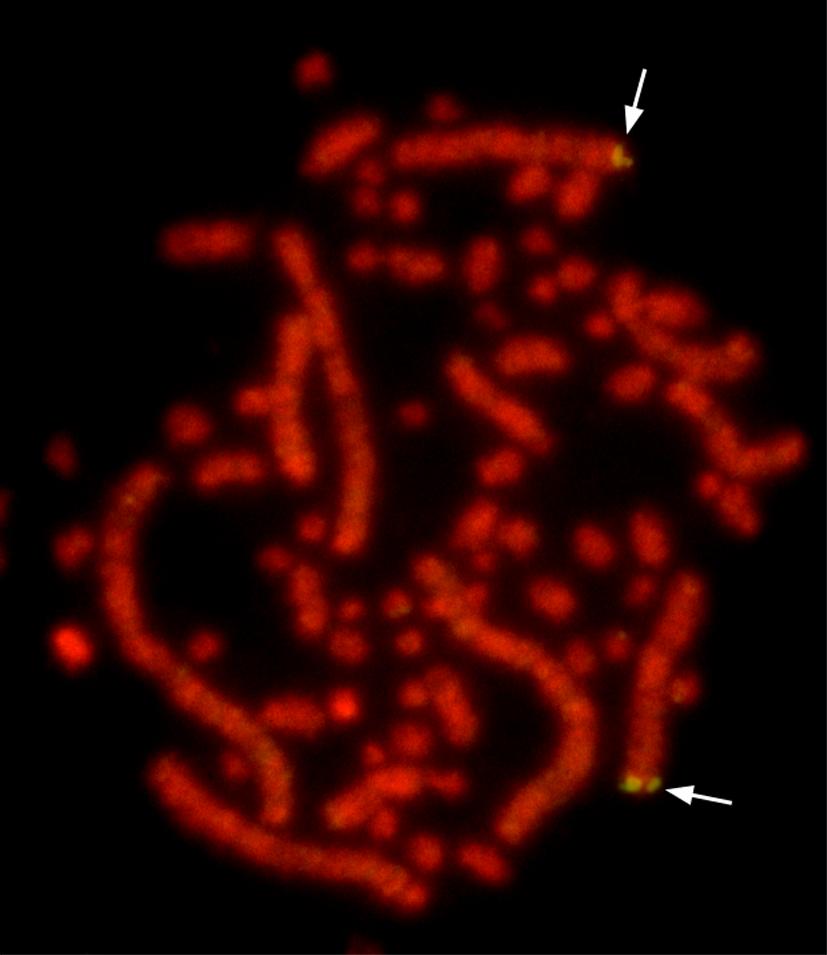
Microchromosome
A microchromosome (μChr) is a type of very small chromosome which is a typical component of the karyotype of birds, some reptiles, fish, and amphibians; they have yet to be found in mammals. They are less than 20 Mb in size; chromosomes which are greater than 40 Megabase, Mb in size are known as macrochromosomes (MChrs), while those between 20 and 40 Mb are classified as intermediate chromosomes. Microchromosomes are characteristically very small and often cytogenetically indistinguishable in a karyotype. While originally thought to be insignificant fragments of chromosomes, in species where they have been studied they have been found to be rich in genes and high in GC content. In chickens, microchromosomes have been estimated to contain between 50 and 75% of all genes. The presence of microchromosomes makes ordering and identifying chromosomes into a coherent karyotype particularly difficult. During metaphase, they appear merely as 0.5-1.5 μm long specks. Their small size and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZW Sex-determination System
The ZW sex-determination system is a chromosomal system that determines the sex of offspring in birds, some fish and crustaceans such as the giant river prawn, some insects (including butterflies and moths), the schistosome family of flatworms, and some reptiles, e.g. majority of snakes, lacertid lizards and monitors including Komodo dragons. It is also used in some plants where it has probably evolved independently on several occasions. The letters Z and W are used to distinguish this system from the XY sex-determination system. In this system, females have a pair of dissimilar ZW chromosomes, and males have two similar ZZ chromosomes. In contrast to the XY sex-determination system and the X0 sex-determination system, where the sperm determines the sex, in the ZW system, the ovum determines the sex of the offspring. Males are the homogametic sex (ZZ), while females are the heterogametic sex (ZW). The Z chromosome is larger and has more genes, like the X chromosome in the XY sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature-dependent Sex Determination
Temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD) is a type of environmental sex determination in which the temperatures experienced during embryonic/larval development determine the sex of the offspring. It is only observed in reptiles and teleost fish. TSD differs from the chromosomal sex-determination systems common among vertebrates. It is the most studied type of environmental sex determination (ESD). Some other conditions, e.g. density, pH, and environmental background color, are also observed to alter sex ratio, which could be classified either as temperature-dependent sex determination or temperature-dependent sex differentiation, depending on the involved mechanisms. As sex-determining mechanisms, TSD and genetic sex determination (GSD) should be considered in an equivalent manner, which can lead to reconsidering the status of fish species that are claimed to have TSD when submitted to extreme temperatures instead of the temperature experienced during development in the wild, si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond Ditmars
Raymond Lee Ditmars (June 22, 1876 – May 12, 1942) was an American herpetology, herpetologist, writer, public speaker and pioneering natural history filmmaker. Biography Ditmars was fascinated by all animals, but primarily reptiles, obtaining his first snakes at twelve years of age. His parents eventually allowed him to keep all manner of venomous reptiles in the attic of their house at 1666 Bathgate Avenue in the Bronx. Ditmars left school at 16 with no formal qualifications but nevertheless gained a deep understanding of zoology through his own personal study of snakes and other animals in the wild and captivity. Throughout his life, vacations were spent searching for new specimens. Such was his interest and knowledge that he would eventually be regarded as the country's foremost herpetologist. In 1893, Ditmars was hired as an assistant in the Department of Entomology at the American Museum of Natural History, primarily because of his talent as an artist. Four years la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid. Urea serves an important role in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic ( is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules () with a carbon dioxide () molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important raw material for the chemical industry. In 1828 Friedrich Wöhler discovered that urea can be produced from inorganic starting materials, which was an important conceptual milestone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Softshell Turtle
The Chinese softshell turtle (''Pelodiscus sinensis'') is a species of softshell turtle that is native to China (Inner Mongolia to Guangxi, including Hong Kong) and Taiwan, with records of escapees—some of which have established introduced populations—in a wide range of other Asian countries, as well as Spain, Brazil and Hawaii. Populations native to Northeast China, Russia, Korea and Japan were formerly included in this species, but are now regarded as separate as the northern Chinese softshell turtle (''P. maackii''). Furthermore, localized populations in Guangxi and Hunan (where the Chinese softshell turtle also is present), as well as Vietnam, are recognized as the lesser Chinese softshell turtle (''P. parviformis'') and Hunan softshell turtle (''P. axenaria''). The Chinese softshell turtle is a vulnerable species, threatened by disease, habitat loss, and collection for food such as turtle soup. Additionally, millions are now farmed, especially in China, to support t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |