|
Soepomo
Soepomo (EYD: Supomo; 22 January 1903 – 12 September 1958) was an Indonesian politician and lawyer who served as the country's first Minister of Justice from August until November 1945 and again from December 1949 until 6 September 1950. Known as the father of Indonesia's constitution, he was posthumously declared an Indonesian National Hero by President Sukarno in 1965. Early life and education Soepomo was born on 22 January 1903, in Sukoharjo, Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia). He came from a noble family; his maternal and paternal grandfathers were both high-ranking government officials. He began his education in 1917, when he was enrolled at a '' Europeesche Lagere School'' (ELS) in Boyolali. He graduated in 1920, and continued his studies to a '' Meer Uitgebreid Lager Onderwijs'' (MULO) in Surakarta. In 1923, he moved to Batavia (now Jakarta) and attended the '' Rechts Hogeschool'' (RHS). After graduating from RHS, he took a job at a court in Surakarta, befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ministers Of Law And Human Rights Of Indonesia
Indonesia's Minister of Law and Human Rights (') is the head of the Ministry of Law and Human Rights. The first minister was Soepomo, who took office on 19 August 1945. The current minister is Yasonna Laoly, who took office on 27 October 2014. The longest serving was Ismael Saleh, who served ten years from 19 March 1983 to 17 March 1993. The shortest serving was Marsillam Simanjuntak, who served 48 days from 2 June to 20 July 2001. History The position was established, along with the ministry, with the release of Law Number 2 of 1945 under the title Minister of Justice ('). The first minister, Soepomo, was announced on 19 August 1945, 2 days after Indonesia's independence. Soepomo had control over several branches, including the high religious court, civil courts, supreme court, and, after its formation on 1 October 1945, the prosecutor general's office. In 1946, duty over the high religious courts was given to the Minister of Religion. Through Legal Guideline number 19 of 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
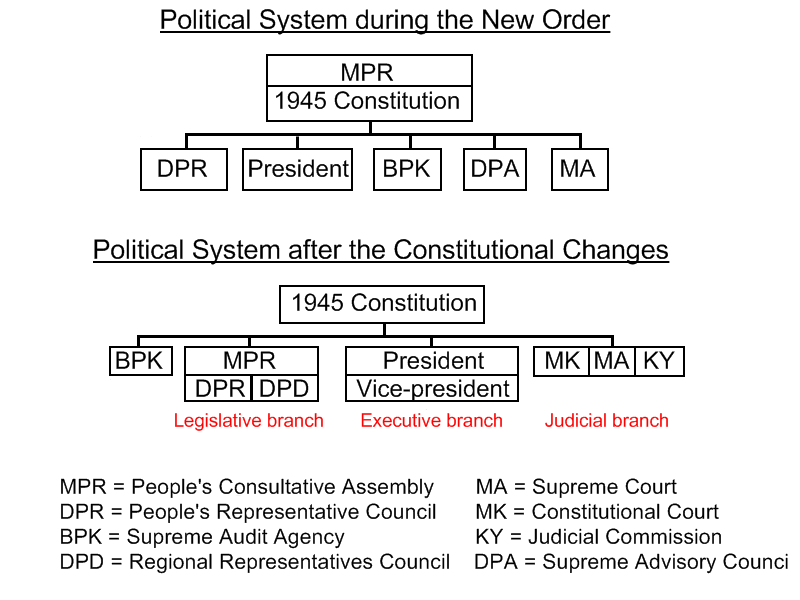
Constitution Of Indonesia
The 1945 State Constitution of the Republic of Indonesia ( id, Undang-Undang Dasar Negara Republik Indonesia Tahun 1945, commonly abbreviated as ''UUD 1945'' or ''UUD '45'') is the supreme law and basis for all laws of Indonesia. The constitution was written in June, July, and August 1945, in the final months of the Japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies at the end of World War II. It was abrogated by the Federal Constitution of 1949 and the Provisional Constitution of 1950, but restored by President Sukarno's 1959 Decree. The 1945 Constitution sets forth the Pancasila, the five nationalist principles, as the embodiment of basic principles of an independent Indonesian state. It provides for a limited separation of executive, legislative, and judicial powers. The governmental system has been described as "presidential with parliamentary characteristics."King (2007) Following major upheavals in 1998 and the resignation of President Suharto, several political reforms w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subandrio
Subandrio (15 September 1914 – 3 July 2004) was an Indonesian politician and Foreign Minister and First Deputy Prime Minister of Indonesia under President Sukarno. Removed from office following the failed 1965 coup, he spent 29 years in prison. The spelling "Subandrio" has been official in Indonesia since 1947 but the older spelling Soebandrio is still sometimes used. Early career Subandrio was born in Malang, East Java, and educated at the Sekolah Tinggi Kedokteran Jakarta (GHS) in Jakarta. As a medical student he was active in the movement for independence. During World War II, while practicing medicine, he worked with anti-Japanese resistance forces. His wife, Hurustiati Subandrio, was also a politically active medical doctor. After the war he was appointed secretary-general of the information ministry. After 1945 Subandrio became a supporter of the nationalist leader Sukarno, and was sent as Sukarno's special envoy in Europe, establishing an information office in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soenario
Soenario Sastrowardoyo (EYD: Sunario Sastrowardoyo; 28 August 1902 – 18 May 1997), more commonly known simply as Soenario, was an Indonesian politician, and diplomat, who served as the 7th Foreign Minister of Indonesia, from 1953 until 1955, during the First Ali Sastroamidjojo cabinet, under Prime Minister Ali Sastroamidjojo. He was one of Indonesia's leading figures during the Indonesian independence movement and served as an administrator for the ''Perhimpoenan Indonesia'' association in the Netherlands. He was born in Madiun, East Java, Indonesia, on 28 August 1902. He started his education at the '' Frobelschool'', before continuing to ''Europeesche Lagere School'' (ELS) and later to the '' Meer Uitgebreid Lager Onderwijs'' (MULO). He then continued to the '' Rechtshoogeschool'' in Batavia and later the Leiden University in Leiden. While studying in the Netherlands, he was active in the management of the ''Perhimpoenan Indonesia'' association. Upon his return fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of National Heroes Of Indonesia
National Hero of Indonesia ( id, Pahlawan Nasional Indonesia) is the highest-level Orders, decorations, and medals of Indonesia, title awarded in Indonesia. It is posthumously given by the Government of Indonesia for actions which are deemed to be heroic, defined as "actual deeds which can be remembered and exemplified for all time by other citizens" or "extraordinary service furthering the interests of the state and people". The Ministry of Social Affairs (Indonesia), Ministry of Social Affairs gives seven criteria which an individual must fulfill, as follows: #Have been an Indonesian citizen who is deceased and, during his lifetime, led an armed struggle or produced a concept or product useful to the state; #Have continued the struggle throughout his life and performed above and beyond the call of duty; #Have had a wide-reaching impact through his actions; #Have shown a high degree of nationalism; #Have been of good moral standing and respectable character; #Never surrendered to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Sastroamidjojo
Ali Sastroamidjojo (EYD: Ali Sastroamijoyo; 21 May 1903 – 13 March 1975) was an Indonesian politician and diplomat who served as prime minister of Indonesia from 1953 until 1955 and again from 1956 until 1957. He also served as the Indonesian Permanent Representative to the United Nations from 1957 until 1960, the first Indonesian Ambassador to the United States, the first Indonesian Ambassador to Canada and the first Indonesian Ambassador to Mexico. In addition, he was also appointed chairman of the Asian-African Conference in Bandung, and also was the chairman of the Indonesian National Party (PNI), from 1960 until 1966. Raden Ali Sastroamidjojo was born in Grabag, Central Java, in what was then the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia), to an aristocratic family of the Magelang Regency belonging to the Indonesian elite. In his youth, he was active in a number of youth organizations, including the Jong Java and the Perhimpoenan Indonesia associations. Because of his ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jong Java
, was a Dutch East Indies youth organization founded on March 7, 1915 by at the STOVIA building under the name Tri Koro Dharmo ('Three Noble Goals'). It was founded in response to the perceived elitism of the Budi Utomo movement by many young people at the time. Three Noble Goals Tri Koro Dharmo 3 Goals are Sakti, Budi, Bakti (Power and intelligence, wise and affection). History 1915–1921 Tri Koro Dharmo was founded with Dr. Satiman Wirjosandjojo as chairman, Wongsonegoro as vice chairman, Sutomo as secretary, and Muslich, Mosodo and Abdul Rahman as members. The goals of Tri Koro Dharmo were to unite the '' pribumi'' students, promote the arts and national language, and improve the general knowledge of its members. To achieve these goals, their activities included organizing meetings and courses, establishing scholarship funds, organizing art performances, and publishing the magazine ''Tri Koro Dharmo''. On June 12, 1918, Tri Koro Dharmo was renamed to Jong Java duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yogyakarta
Yogyakarta (; jv, ꦔꦪꦺꦴꦒꦾꦏꦂꦠ ; pey, Jogjakarta) is the capital city of Special Region of Yogyakarta in Indonesia, in the south-central part of the island of Java. As the only Indonesian royal city still ruled by a monarchy, Yogyakarta is regarded as an important centre for classical Javanese fine arts and culture such as ballet, ''batik'' textiles, drama, literature, music, poetry, silversmithing, visual arts, and '' wayang'' puppetry. Renowned as a centre of Indonesian education, Yogyakarta is home to a large student population and dozens of schools and universities, including Gadjah Mada University, the country's largest institute of higher education and one of its most prestigious. Yogyakarta is the capital of the Yogyakarta Sultanate and served as the Indonesian capital from 1946 to 1948 during the Indonesian National Revolution, with Gedung Agung as the president's office. One of the districts in southeastern Yogyakarta, Kotagede, was the capital o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornelis Van Vollenhoven
Cornelis van Vollenhoven (8 May 1874, Dordrecht – 29 April 1933, Leiden) was a Dutch law professor and legal scholar, best known for his work on the legal systems of the East Indies. Cornelis van Vollenhoven began his university studies at Leiden at the age of 17, where he would earn many degrees, including: a master's in law (1895), a bachelor's degree in Semitic languages (1896), a master's in political science (1897), and finally his PhD in law and political science (1898). He received a ''cum laude'' for his thesis, “Scope and content of international law” (''Omtrek en inhoud van het internationale recht''), which foreshadows his later focus on the laws of Southeast Asia. After finishing his studies, Van Vollenhoven became the private secretary of J.Th. Cremer, a colonial ''captain of industry'' and minister of Colonial Affairs. In 1901 Van Vollenhoven became professor of the Adat Law of the Dutch East Indies at Leiden University. As legal scholar he had enormous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Indonesia
The University of Indonesia ( id, Universitas Indonesia, abbreviated as UI) is a public university in Depok, West Java and Salemba, Jakarta, Indonesia. It is one of the oldest tertiary-level educational institutions in Indonesia (known as the Dutch East Indies when UI was established), and is generally considered one of the most prestigious universities in Indonesia, along with the Gadjah Mada University and Bandung Institute of Technology. In the 2019 QS World Universities Ranking, UI is ranked 1st in Indonesia, 57th in Asia and 292nd in the world. History The roots of UI date back to 1851. At that time, the colonial government of the Dutch East Indies established a school to train medical assistants. Training lasted for two years, and the graduates were certified to provide basic medical treatments. The degree conferred was Javanese Doctor, as the graduates were certified only to open their practice in the Dutch East Indies, especially Java. The program became more com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batavia, Dutch East Indies
Batavia was the capital of the Dutch East Indies. The area corresponds to present-day Jakarta, Indonesia. Batavia can refer to the city proper or its suburbs and hinterland, the Ommelanden, which included the much-larger area of the Residency of Batavia in the present-day Indonesian provinces of Jakarta, Banten and West Java. The founding of Batavia by the Dutch in 1619, on the site of the ruins of Jayakarta, led to the establishment of a Dutch colony; Batavia became the center of the Dutch East India Company's trading network in Asia. Monopolies on local produce were augmented by non-indigenous cash crops. To safeguard their commercial interests, the company and the colonial administration absorbed surrounding territory. Batavia is on the north coast of Java, in a sheltered bay, on a land of marshland and hills crisscrossed with canals. The city had two centers: Oud Batavia (the oldest part of the city) and the relatively-newer city, on higher ground to the south. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)



