|
Società Generale Semiconduttori
SGS (''Società Generale Semiconduttori'', English: ''General Semiconductor Company'') was an Italian manufacturer of semiconductor devices, most notably diodes, transistors and DIP ICs. History In 1957, Mario Tchou, an engineer from Olivetti, convinced Adriano Olivetti to found an Italian electronic manufacturing company for production of solid-state electronic devices. Olivetti sent his son Roberto Olivetti and Mario Tchou to negotiate with Virgilio Floriani, president of Telettra, to establish a joint venture. Within the same year, Olivetti and Telettra founded ''Società Generale Semiconduttori'' (SGS). One of the reasons for SGS's foundation was the need of parts (diodes and transistors in particular) for Elea, a mainframe that was being developed by Olivetti. The headquarters of the company was located in Agrate Brianza. In 1960, Fairchild Semiconductor acquired one third of the company and a joint venture called SGS-Fairchild was formed. That gave SGS access to Fairch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Company
A public company is a company whose ownership is organized via shares of share capital, stock which are intended to be freely traded on a stock exchange or in over-the-counter (finance), over-the-counter markets. A public (publicly traded) company can be listed on a stock exchange (listing (finance), listed company), which facilitates the trade of shares, or not (unlisted public company). In some jurisdictions, public companies over a certain size must be listed on an exchange. In most cases, public companies are ''private'' enterprises in the ''private'' sector, and "public" emphasizes their reporting and trading on the public markets. Public companies are formed within the legal systems of particular states and so have associations and formal designations, which are distinct and separate in the polity in which they reside. In the United States, for example, a public company is usually a type of corporation, though a corporation need not be a public company. In the United Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mario Tchou
Mario Tchou (; 1924–1961), also known as Tchou Wang Li, was an Italian engineer of Chinese descent. He was a pioneer of computer science in Italy, who led a group of scientists from the University of Pisa to invent in 1959 the Olivetti Elea—the world's most powerful computer at the time. Biography Born in Rome on 26 June 1924, he was the son of Evelyn Wang and the diplomat Yin Tchou, who worked within the Consulate of the Republic of China at the Holy See. After obtaining his classical high school diploma at the Torquato Tasso Gymnasium High School in Rome, he undertook his studies in electrical engineering in Rome, at the La Sapienza University, and continued them with a scholarship in the United States, where, in 1947, he obtained a Bachelor of electrical engineering at the Catholic University of America in Washington. He graduated from the New York University Polytechnic School of Engineering in 1949. Having moved to New York, he began teaching at Manhattan College while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomson-CSF
Thomson-CSF was a French company that specialized in the development and manufacture of electronics with a heavy focus upon the aerospace and defence sectors of the market. Thomson-CSF was formed in 1968 following the merger of Thomson-Houston-Hotchkiss-Brandt with the Compagnie Générale de Télégraphie Sans Fil (''General Wireless Telegraphy Company'', commonly abbreviated as ''CSF''), these two companies being the source of the name ''Thomson-CSF''. It operated as an electronics specialist on products such as broadcasting equipment, electroacoustics, shortwave radio sets, radar systems and television. During the 1970s, it began manufacturing backend telephony equipment, semiconductors and medical imaging apparatus. It also entered into large deals outside of the domestic market, acquiring considerable business in the Middle East. During the late 1980s, Thomson-CSF, anticipating defence spending cutbacks, conducted a radical business restructuring, merging its semicon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mostek
Mostek Corporation was a semiconductor integrated circuit manufacturer, founded in 1969 by L. J. Sevin, Louay E. Sharif, Richard L. Petritz and other ex-employees of Texas Instruments. At its peak in the late 1970s, Mostek held an 85% market share of the dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) memory chip market worldwide, until being eclipsed by lower-priced Japanese DRAM manufacturers who were accused of Dumping (pricing policy), dumping memory on the market. In 1979, soon after its market peak, Mostek was purchased by United Technologies Corporation for . In 1985, after several years of red ink and declining market share, UTC closed Mostek completely and sold it for to the French electronics firm Thomson-CSF, which later spun it off into STMicroelectronics. Early Products Mostek's first contract was from Burroughs Corporation, Burroughs, a $400 contract for circuit design. Initially Mostek products were manufactured in Worcester, Massachusetts in cooperation with Sprague Elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
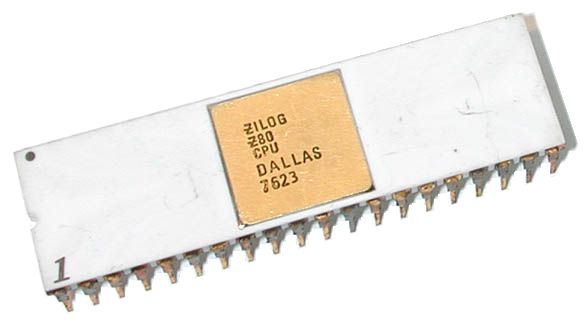
Zilog
Zilog, Inc. is an American manufacturer of microprocessors, microcontrollers, and application-specific embedded System on a chip, system-on-chip (SoC) products. The company was founded in 1974 by Federico Faggin and Ralph Ungermann, who were soon joined by Masatoshi Shima. All three had left Intel after working on the Intel 4004, 4004 and Intel 8080, 8080 microprocessors. The company's most famous product is the Zilog Z80, Z80 microprocessor, which played an important role in the evolution of early computing. Backward compatible, Software-compatible with the Intel 8080, it offered a compelling alternative due to its lower cost and increased performance, propelling it to widespread adoption in video game systems and home computers during the late 1970s and early 1980s. The name, pronounced with a long "i" (), is an acronym of ''Z integrated logic'', also thought of as "Z for the last word of Integrated Logic". History Zilog was started in California in 1974 by Federico Faggin and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonardo (company)
Leonardo S.p.A., formerly Leonardo-Finmeccanica and originally Finmeccanica, is an Italian Multinational corporation, multinational company specialising in Aerospace manufacturer, aerospace, arms industry, defence and Information security, security. Headquartered in Rome, the company has 180 sites worldwide. It is the 12th largest List of defense contractors, defence contractor in the world based on 2020 revenues.Top 100 Arms-Producing and Military Service Companies SIPRI. Received 2019-12-18. The company is partially owned by the Italian government, which holds 30.2% of the company's shares and is its largest shareholder. On 1 January 2016, Leonardo-Finmeccanica became a single industrial company by int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TIM (Italy)
TIM S.p.A. (formerly Telecom Italia S.p.A.) is an Italian telecommunications company with headquarters in Rome, Milan, and Naples (with the Telecom Italia Tower), which provides fixed, public and mobile telephony, and DSL data services. It is the largest Italian telecommunications services provider in revenues and subscribers. It was founded in 1994 by the merger of several state-owned telecommunications companies, the most prominent of which was SIP, the former state monopoly telephone operator in Italy. The company's stock is traded in the Borsa Italiana. The Italian State has exercised the "Golden Power" on TIM since 2017, which allows the government to take a number of actions when the strategic interests of the country are concerned. It has also a subsidiary in Brazil, known as TIM Brasil, with 72.6 million customers. The brand covers over 114 million customers worldwide. As April 2024, Net sales are distributed geographically as follows: Italy (72.9%) and Brazil (27.1%) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planar Process
The planar process is a semiconductor device fabrication, manufacturing process used in the semiconductor industry to build individual components of a transistor, and in turn, connect those transistors together. It is the primary process by which silicon integrated circuit chips are built, and it is the most commonly used method of producing Junction (electricity), junctions during the manufacture of semiconductor devices. The process utilizes the surface passivation and thermal oxidation methods. The planar process was developed at Fairchild Semiconductor in 1959 and process proved to be one of the most important single advances in semiconductor technology. Overview The key concept is to view a circuit in its two-dimensional projection (a plane), thus allowing the use of photographic processing concepts such as film negatives to mask the projection of light exposed chemicals. This allows the use of a series of exposures on a substrate (silicon) to create silicon oxide (insulators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. was an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1957 as a division of Fairchild Camera and Instrument by the " traitorous eight" who defected from Shockley Semiconductor Laboratory. It became a pioneer in the manufacturing of transistors and of integrated circuits. Schlumberger bought the firm in 1979 and sold it to National Semiconductor in 1987; Fairchild was spun off as an independent company again in 1997. In September 2016, Fairchild was acquired by ON Semiconductor. The company had locations in the United States at San Jose, California; San Rafael, California; South Portland, Maine; West Jordan, Utah; and Mountaintop, Pennsylvania. Outside the US, it operated locations in Australia; Singapore; Bucheon, South Korea; Penang, Malaysia; Suzhou, China; and Cebu, Philippines, among others. History 1950s In 1955, William Shockley founded Shockley Semiconductor Laboratory, funded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainframe Computer
A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron, is a computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise resource planning, and large-scale transaction processing. A mainframe computer is large but not as large as a supercomputer and has more processing power than some other classes of computers, such as minicomputers, server (computing), servers, workstations, and personal computers. Most large-scale computer-system architectures were established in the 1960s, but they continue to evolve. Mainframe computers are often used as servers. The term ''mainframe'' was derived from the large cabinet, called a ''main frame'', that housed the central processing unit and main computer memory, memory of early computers. Later, the term ''mainframe'' was used to distinguish high-end commercial computers from less powerful machines. Design Modern mainfr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivetti Elea
The Elea was a series of mainframe computers Olivetti developed starting in the late 1950s. The system, made entirely with transistors for high performance, was conceived, designed and developed by a small group of researchers led by Mario Tchou (1924–1961), with industrial design by Ettore Sottsass. The ELEA 9001 was the first solid-state computer designed and manufactured in Italy. The acronym ELEA stood for ''Elaboratore Elettronico Aritmetico'' (Arithmetical Electronic Computer, then changed to ''Elaboratore Elettronico Automatico'' for marketing reasons) and was chosen with reference to the ancient Greek colony of Elea, home of the Eleatic school of philosophy. About forty units were placed with customers. In August 1964, only a few years after releasing the 9003,Giuditta Parolini ''Olivetti Elea 9003: Between Scientific Research and Computer Business'', in: , page 37 and ff Olivetti's mainframe business was sold to GE. Generations ELEA 9001: (Macchina Zero - Machin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Venture
A joint venture (JV) is a business entity created by two or more parties, generally characterized by shared ownership, shared returns and risks, and shared governance. Companies typically pursue joint ventures for one of four reasons: to access a new market, particularly emerging market; to gain scale efficiencies by combining assets and operations; to share risk for major investments or projects; or to access skills and capabilities.' Most joint ventures are incorporated, although some, as in the oil and gas industry, are "unincorporated" joint ventures that mimic a corporate entity. With individuals, when two or more persons come together to form a temporary partnership for the purpose of carrying out a particular project, such partnership can also be called a joint venture where the parties are "''co-venturers''". A joint venture can take the form of a business. It can also take the form of a project or asset JV, created for the purpose of pursuing one specific project, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |