|
Social Information Processing (theory)
Social information processing theory, also known as SIP, is an interpersonal communication theory and media studies theory developed in 1992 by Joseph Walther. Social information processing theory explains online interpersonal communication without nonverbal cues and how people develop and manage relationships in a computer-mediated environment. Walther argued that online interpersonal relationships may demonstrate the same or even greater relational dimensions and qualities (intimacy) as traditional face-to-face (FtF) relationships. However, due to the limited channel and information, it may take longer to achieve than FtF relationships. These online relationships may help facilitate interactions that would not have occurred face-to-face due to factors such as geography and intergroup anxiety. Overview Origins The term Social Information Processing Theory was originally titled by Salancik and Pfeffer in 1978. They stated that individual perceptions, attitudes, and behaviors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Information Processing
Social information processing is "an activity through which collective human actions organize knowledge." It is the creation and processing of information by a group of people. As an academic field Social Information Processing studies the information processing power of networked social systems. Typically computer tools are used such as: * Authoring tools: e.g., blogs * Collaboration tools: e.g., wikis, in particular, e.g., Wikipedia * Translating tools: Duolingo, reCAPTCHA * Tagging systems (social bookmarking): e.g., del.icio.us, Flickr, CiteULike * Social networking: e.g., Facebook, MySpace, Essembly * Collaborative filtering: e.g., Digg, the Amazon Product Recommendation System, Yahoo! Answers, Urtak Although computers are often used to facilitate networking and collaboration, they are not required. For example the '' Trictionary'' in 1982 was entirely paper and pen based, relying on neighborhood social networks and libraries. The creation of the ''Oxford English Dicti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Accommodation Theory
Communication accommodation theory (CAT) is a theory of communication developed by Howard Giles. This theory concerns "(1) the behavioral changes that people make to attune their communication to their partner, (2) the extent to which people perceive their partner as appropriately attuning to them." The basis of the theory lies in the idea that people adjust (or accommodate) their style of speech to one another. Doing this helps the message sender gain approval from the receiver, increases efficiency in communication between both parties, and helps the sender maintain a positive social identity. This theory is concerned with the links between language, context, and identity. It focuses on both the intergroup and interpersonal factors that lead to accommodation, as well as the ways that power, macro and micro-context concerns affect communication behaviors. Accommodation is usually considered to be between the message sender and the message receiver, but the communicator also often ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncertainty Reduction Theory
The uncertainty reduction theory, also known as initial interaction theory, developed in 1975 by Charles Berger and Richard Calabrese, is a communication theory from the post-positivist tradition. It is one of the few communication theories that specifically looks into the initial interaction between people prior to the actual communication process. The theory asserts the notion that, when interacting, people need information about the other party in order to reduce their uncertainty. In gaining this information people are able to predict the other's behavior and resulting actions, all of which according to the theory is crucial in the development of any relationship. Berger and Calabrese explain the connection between their central concept of uncertainty and seven key variables of relationship development with a series of axioms, and deduce a series of theorems accordingly. Within the theory two types of uncertainty are identified; cognitive uncertainty and behavioral uncertainty. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-fulfilling Prophecy
A self-fulfilling prophecy is a prediction that comes true at least in part as a result of a person's or group of persons' belief or expectation that said prediction would come true. This suggests that people's beliefs influence their actions. The principle behind this phenomenon is that people create consequences regarding people or events, based on previous knowledge of the subject. There are three factors within an environment that can come together to influence the likelihood of a self-fulfilling prophecy becoming a reality: appearance, perception, and belief. When a phenomenon cannot be seen, appearance is what we rely upon when a self-fulfilling prophecy is in place. When it comes to a self-fulfilling prophecy there also must be a distinction "between 'brute and institutional' facts". The philosopher John Searle states the difference as "facts hatexist independently of any human institutions; institutional facts can only exist within institutions." There is an inability of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attribution (psychology)
Attribution is a term used in psychology which deals with how individuals perceive the causes of everyday experience, as being either external or internal. Models to explain this process are called attribution theory. Psychological research into attribution began with the work of Fritz Heider in the early 20th century, and the theory was further advanced by Harold Kelley and Bernard Weiner. Heider first introduced the concept of perceived 'locus of causality' to define the perception of one's environment. For instance, an experience may be perceived as being caused by factors outside the person's control (external) or it may be perceived as the person's own doing (internal). These initial perceptions are called attributions. Psychologists use these attributions to better understand an individual's motivation and competence. The theory is of particular interest to employers who use it to increase worker motivation, goal orientation, and productivity. Psychologists have identified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Dating Service
Online dating, also known as Internet dating, Virtual dating, or Mobile app dating, is a relatively recent method used by people with a goal of searching for and interacting with potential romantic or sexual partners, via the internet. An online dating service is a company that promotes and provides specific mechanisms for the practice of online dating, generally in the form of dedicated websites or software applications accessible on personal computers or mobile devices connected to the internet. A wide variety of unmoderated matchmaking services, most of which are profile-based with various communication functionalities, is offered by such companies. Online dating services allow users to become "members" by creating a profile and uploading personal information including (but not limited to) age, gender, sexual orientation, location, and appearance. Most services also encourage members to add photos or videos to their profile. Once a profile has been created, members can view ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impression Management
Impression management is a conscious or subconscious process in which people attempt to influence the perceptions of other people about a person, object or event by regulating and controlling information in social interaction.Sanaria, A. D. (2016). A conceptual framework for understanding the impression management strategies used by women in indian organizations. South Asian Journal of Human Resources Management, 3(1), 25-39. https://doi.org/10.1177/2322093716631118 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/299373178_A_Conceptual_Framework_for_Understanding_the_Impression_Management_Strategies_Used_by_Women_in_Indian_Organizations It was first conceptualized by Erving Goffman in 1959 in '' The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life,'' and then was expanded upon in 1967. Impression management behaviors include accounts (providing "explanations for a negative event to escape disapproval"), excuses (denying "responsibility for negative outcomes"), and opinion conformity ("speak(ing) o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperpersonal Model
The hyperpersonal model is a model of interpersonal communication that suggests computer-mediated communication (CMC) can become hyperpersonal because it "exceeds ace-to-faceinteraction", thus affording message senders a host of communicative advantages over traditional face-to-face (FtF) interaction. The hyperpersonal model demonstrates how individuals communicate uniquely, while representing themselves to others, how others interpret them, and how the interactions create a reciprocal spiral of FtF communication. Compared to ordinary FtF situations, a hyperpersonal message sender has a greater ability to strategically develop and edit self-presentation, enabling a selective and optimized presentation of one's self to others. Communication professor Joseph Walther is credited with the development of this theory in 1996, synthesizing his and others' extensive research on computer-mediated communication. Conditions and key components Conditions The hyperpersonal model addresses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
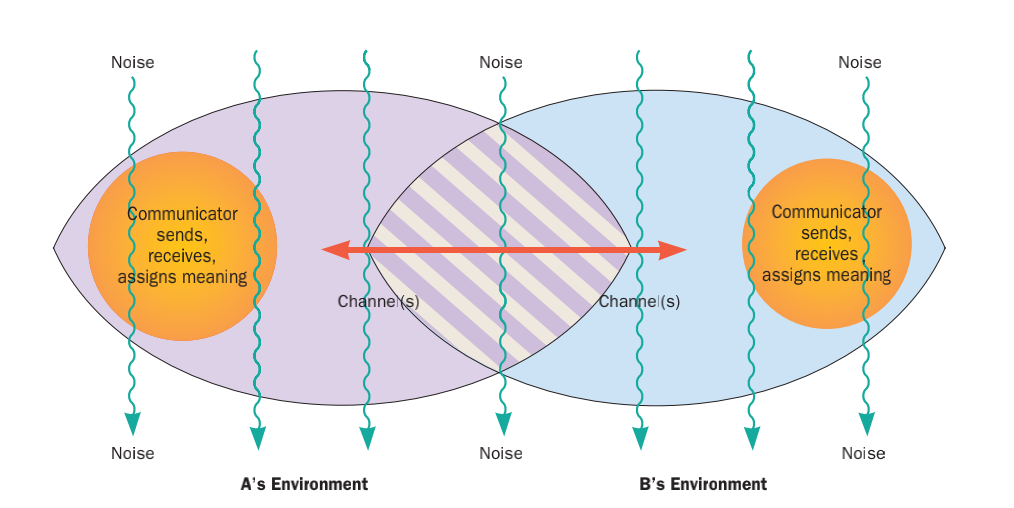
Interpersonal Communication
Interpersonal communication is an exchange of information between two or more people. It is also an area of research that seeks to understand how humans use verbal and nonverbal cues to accomplish a number of personal and relational goals. Interpersonal communication research addresses at least six categories of inquiry: 1) how humans adjust and adapt their verbal communication and nonverbal communication during face-to-face communication; 2) how messages are produced; 3) how uncertainty influences behavior and information-management strategies; 4) deceptive communication; 5) relational dialectics; and 6) social interactions that are mediated by technology. A large number of scholars have described their work as research into interpersonal communication. There is considerable variety in how this area of study is conceptually and operationally defined.Knapp & Daly, 2011) Researchers in interpersonal communication come from many different research paradigms and theoretical tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facebook
Facebook is an online social media and social networking service owned by American company Meta Platforms. Founded in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with fellow Harvard College students and roommates Eduardo Saverin, Andrew McCollum, Dustin Moskovitz, and Chris Hughes, its name comes from the face book directories often given to American university students. Membership was initially limited to Harvard students, gradually expanding to other North American universities and, since 2006, anyone over 13 years old. As of July 2022, Facebook claimed 2.93 billion monthly active users, and ranked third worldwide among the most visited websites as of July 2022. It was the most downloaded mobile app of the 2010s. Facebook can be accessed from devices with Internet connectivity, such as personal computers, tablets and smartphones. After registering, users can create a profile revealing information about themselves. They can post text, photos and multimedia which are shared w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Networking Sites
A social networking service or SNS (sometimes called a social networking site) is an online platform which people use to build social networks or social relationships with other people who share similar personal or career content, interests, activities, backgrounds or real-life connections. Social networking services vary in format and the number of features. They can incorporate a range of new information and communication tools, operating on desktops and on laptops, on mobile devices such as tablet computers and smartphones. This may feature digital photo/video/sharing and diary entries online (blogging). Online community services are sometimes considered social-network services by developers and users, though in a broader sense, a social-network service usually provides an individual-centered service whereas online community services are groups centered. Generally defined as "websites that facilitate the building of a network of contacts in order to exchange various types of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impression Management
Impression management is a conscious or subconscious process in which people attempt to influence the perceptions of other people about a person, object or event by regulating and controlling information in social interaction.Sanaria, A. D. (2016). A conceptual framework for understanding the impression management strategies used by women in indian organizations. South Asian Journal of Human Resources Management, 3(1), 25-39. https://doi.org/10.1177/2322093716631118 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/299373178_A_Conceptual_Framework_for_Understanding_the_Impression_Management_Strategies_Used_by_Women_in_Indian_Organizations It was first conceptualized by Erving Goffman in 1959 in '' The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life,'' and then was expanded upon in 1967. Impression management behaviors include accounts (providing "explanations for a negative event to escape disapproval"), excuses (denying "responsibility for negative outcomes"), and opinion conformity ("speak(ing) o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |