|
Social Vision
Social vision is a sub-topic of social psychology that investigates the ways from which individuals extract information and perceive others using their vision alone. The field of social vision is highly interdisciplinary and located at the nexus of social psychology, communication studies, and vision science.Johnson, K. L., & Adams, R. B. (2013). Social Vision: An introduction. ''Social Cognition, 31'' (6), 633-635. Much of the research in social vision is based on the prevailing theory that the visual system is particularly attuned to social cues in the environment. More of the human brain is devoted to vision than all other senses combined, and social vision research seeks to understand how humans are able to use vision to accurately perceive characteristics of other individuals such as age, race, gender, and sexual orientation in a short time frame as well as how individual beliefs may bias the way humans perceive said individuals. Historical development Social vision was dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Psychology
Social psychology is the scientific study of how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the real or imagined presence of other people or by social norms. Social psychologists typically explain human behavior as a result of the relationship between mental states and social situations, studying the social conditions under which thoughts, feelings, and behaviors occur, and how these variables influence social interactions. History Although issues in social psychology have been discussed in philosophy for much of human history, the scientific discipline of social psychology formally began in the late 19th to early 20th century. 19th century In the 19th century, social psychology began to emerge from the larger field of psychology. At the time, many psychologists were concerned with developing concrete explanations for the different aspects of human nature. They attempted to discover concrete cause-and-effect relationships that explained social interactions. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Health
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing cognition, perception, and behavior. It likewise determines how an individual handles stress, interpersonal relationships, and decision-making. Mental health includes subjective well-being, perceived self-efficacy, autonomy, competence, intergenerational dependence, and self-actualization of one's intellectual and emotional potential, among others. From the perspectives of positive psychology or holism, mental health may include an individual's ability to enjoy life and to create a balance between life activities and efforts to achieve psychological resilience. Cultural differences, subjective assessments, and competing professional theories all affect how one defines "mental health". Some early signs related to mental health problems are sleep irritation, lack of energy, lack of appetite and thinking of harming yourself or others. Mental disorders Mental health, as defined by the Public Heal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed-circuit Television Camera
A closed-circuit television camera can produce images or recordings for surveillance or other private purposes. Cameras can be either video cameras, or digital stills cameras. Walter Bruch was the inventor of the CCTV camera. The main purpose of a CCTV camera is to capture light and convert it into a video signal. Underpinning a CCTV camera is a CCD sensor (charge-coupled device). The CCD converts light into an electrical signal and then signal processing converts this electrical signal into a video signal that can be recorded or displayed on the screen. Video cameras Video cameras are either analogue or digital, which means that they work on the basis of sending analogue or digital signals to a storage device such as a video tape recorder or desktop computer or laptop computer. Analogue These cameras can record straight to a video tape recorder which can record analogue signals as pictures. If the analogue signals are recorded to tape, then the tape must run at a very slo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
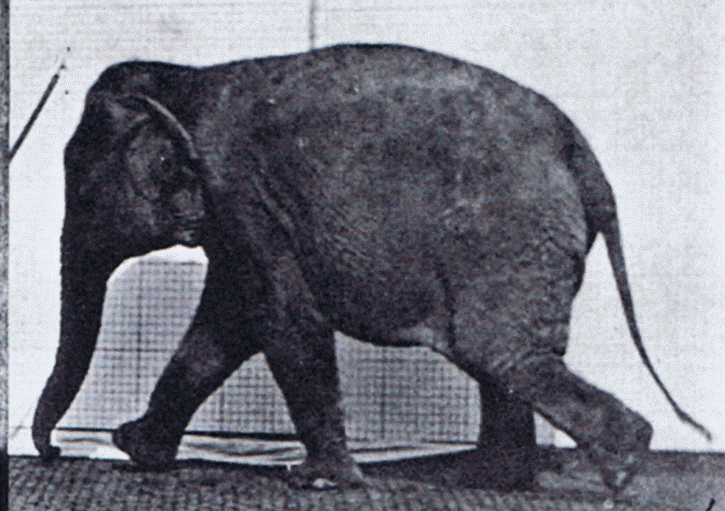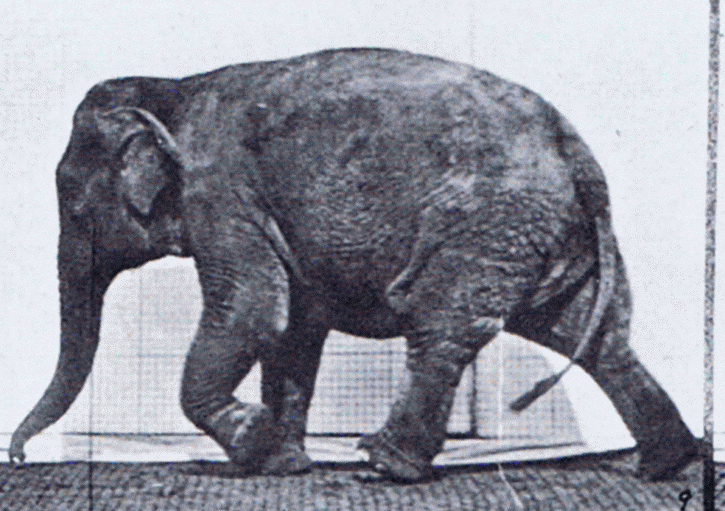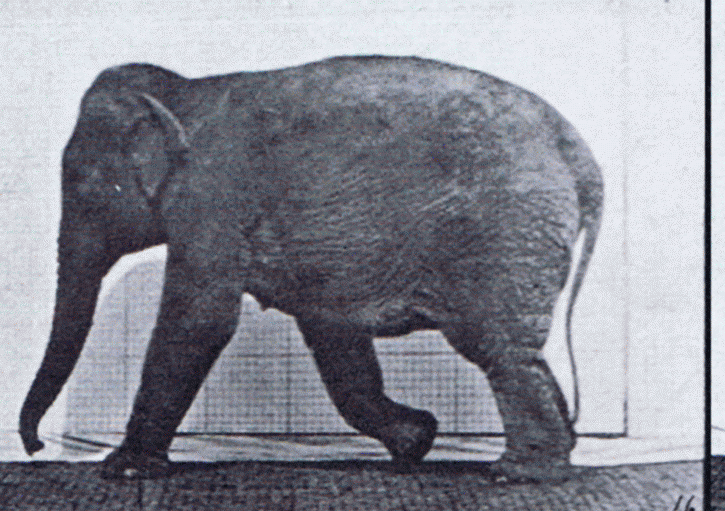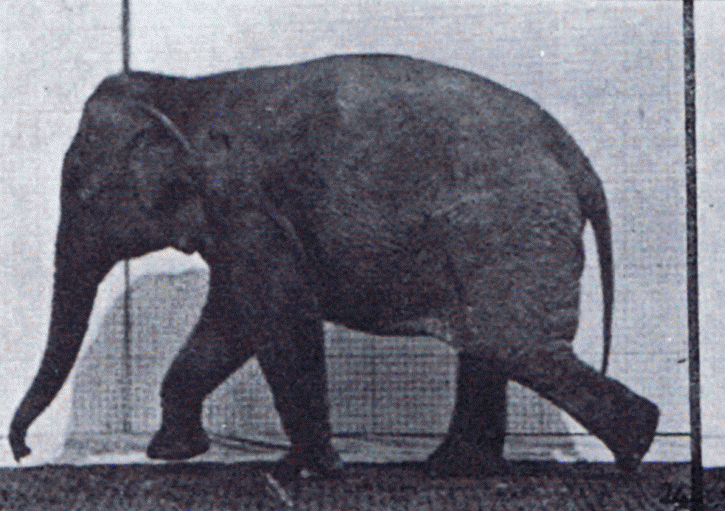
Gait
Gait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency. Different animal species may use different gaits due to differences in anatomy that prevent use of certain gaits, or simply due to evolved innate preferences as a result of habitat differences. While various gaits are given specific names, the complexity of biological systems and interacting with the environment make these distinctions "fuzzy" at best. Gaits are typically classified according to footfall patterns, but recent studies often prefer definitions based on mechanics. The term typically does not refer to limb-based propulsion through fluid mediums such as water or air, but rather to propulsion across a solid substrate by generating reactive forces against it (which can apply to walking while underwater as well as on land). Due to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personality Disorders
Personality disorders (PD) are a class of mental disorders characterized by enduring maladaptive patterns of behavior, cognition, and inner experience, exhibited across many contexts and deviating from those accepted by the individual's culture. These patterns develop early, are inflexible, and are associated with significant distress or disability. The definitions vary by source and remain a matter of controversy. Official criteria for diagnosing personality disorders are listed in the sixth chapter of the ''International Classification of Diseases'' (ICD) and in the American Psychiatric Association's ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM). Personality, defined psychologically, is the set of enduring behavioral and mental traits that distinguish individual humans. Hence, personality disorders are defined by experiences and behaviors that deviate from social norms and expectations. Those diagnosed with a personality disorder may experience difficulties i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychiatric Hospital
Psychiatric hospitals, also known as mental health hospitals, behavioral health hospitals, are hospitals or wards specializing in the treatment of severe mental disorders, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, eating disorders, dissociative identity disorder, major depressive disorder and many others. Psychiatric hospitals vary widely in their size and grading. Some hospitals may specialize only in short-term or outpatient therapy for low-risk patients. Others may specialize in the temporary or permanent containment of patients who need routine assistance, treatment, or a specialized and controlled environment due to a psychiatric disorder. Patients often choose voluntary commitment, but those whom psychiatrists believe to pose significant danger to themselves or others may be subject to involuntary commitment and involuntary treatment. Psychiatric hospitals may also be called psychiatric wards/units (or "psych" wards/units) when they are a subunit of a regular hospital. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meta-analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting measurements that are expected to have some degree of error. The aim then is to use approaches from statistics to derive a pooled estimate closest to the unknown common truth based on how this error is perceived. Meta-analytic results are considered the most trustworthy source of evidence by the evidence-based medicine literature.Herrera Ortiz AF., Cadavid Camacho E, Cubillos Rojas J, Cadavid Camacho T, Zoe Guevara S, Tatiana Rincón Cuenca N, Vásquez Perdomo A, Del Castillo Herazo V, & Giraldo Malo R. A Practical Guide to Perform a Systematic Literature Review and Meta-analysis. Principles and Practice of Clinical Research. 2022;7(4):47–57. https://doi.org/10.21801/ppcrj.2021.74.6 Not only can meta-analyses provide an estimate of the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racial Bias
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagonism directed against other people because they are of a different race or ethnicity. Modern variants of racism are often based in social perceptions of biological differences between peoples. These views can take the form of social actions, practices or beliefs, or political systems in which different races are ranked as inherently superior or inferior to each other, based on presumed shared inheritable traits, abilities, or qualities. There have been attempts to legitimize racist beliefs through scientific means, such as scientific racism, which have been overwhelmingly shown to be unfounded. In terms of political systems (e.g. apartheid) that support the expression of prejudice or aversion in discriminatory practices or laws, racist ideolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Studies
Communication studies or communication science is an academic discipline that deals with processes of human communication and behavior, patterns of communication in interpersonal relationships, social interactions and communication in different cultures. Communication is commonly defined as giving, receiving or exchanging ideas, information, signals or messages through appropriate media, enabling individuals or groups to persuade, to seek information, to give information or to express emotions effectively. Communication studies is a social science that uses various methods of empirical investigation and critical analysis to develop a body of knowledge that encompasses a range of topics, from face-to-face conversation at a level of individual agency and interaction to social and cultural communication systems at a macro level. Scholarly communication theorists focus primarily on refining the theoretical understanding of communication, examining statistics in order to help subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Satisfaction
Life satisfaction is a measure of a person's well-being, assessed in terms of mood, relationship satisfaction, achieved goals, self-concepts, and self-perceived ability to cope with life. Life satisfaction involves a favorable attitude towards one's life—rather than an assessment of current feelings. Life satisfaction has been measured in relation to economic standing, degree of education, experiences, residence, and other factors. Life satisfaction is a key part of subjective well-being. Many factors influence subjective well-being and life satisfaction. Socio-demographic factors include gender, age, marital status, income, and education. Psychosocial factors include health and illness, functional ability, activity level, and social relationships. People tend to gain life satisfaction as they get older. Factors affecting life satisfaction Personality A meta-analysis using The Big Five personality model found that, among the Big Five, low neuroticism was the strongest pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroticism
In the study of psychology, neuroticism has been considered a fundamental personality trait. For example, in the Big Five approach to personality trait theory, individuals with high scores for neuroticism are more likely than average to be moody and to experience such feelings as anxiety, worry, fear, anger, frustration, envy, jealousy, guilt, depressed mood, and loneliness. Such people are thought to respond worse to stressors and are more likely to interpret ordinary situations, such as minor frustrations, as appearing hopelessly difficult. People with high scores on the neuroticism index are thought to be at risk of developing common mental disorders (mood disorders, anxiety disorders, and substance use disorders have been studied), and the sorts of symptoms traditionally referred to as "neuroses". Definition Neuroticism is a trait in many models within personality theory, but there is significant disagreement on its definition. It is sometimes defined as a tendency for quick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |