|
Snow Canyon State Park
Snow Canyon State Park is a state park in Utah, located in the Red Cliffs Desert Reserve. The park features a canyon carved from the red and white Navajo sandstone of the Red Mountains, as well as the extinct Santa Clara Volcano, lava tubes, lava flows, and sand dunes. Snow Canyon is located near the cities of Ivins and St. George in Washington County. Description Snow Canyon State Park contains several sandstone canyons cut in the Red Mountains. On the north end of the park, West Canyon and Snow Canyon follow a parallel southward path and converge in the middle of the park. The park then continues south-by-southeastward as a single, larger canyon, that opens near the park's southern entrance out onto the Santa Clara bench near Ivins, Utah. A paved two-lane road (formerly SR-300) enters the park from Ivins on the south, winds up the canyon, then climbs the eastern edge to the bench above Snow Canyon. There the road joins State Route 18. The park boundaries extend nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington County, Utah
Washington County is a county in the southwestern corner of Utah, United States. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 180,279, making it the fifth-most populous county in Utah. Its county seat and largest city is St. George. The county was created in 1852 and organized in 1856. It was named after the first President of the United States, George Washington. A portion of the Paiute Indian Reservation is in western Washington County. Washington County comprises the St. George, UT Metropolitan Statistical Area. History The earliest settlement was Fort Harmony in 1852. Santa Clara was established in 1854 as a mission to the natives who lived on the Santa Clara River. Hamblin and Pinto were settled along the Los Angeles - Salt Lake Road in 1856, as was Gunlock in 1857. Next came the settlements established as colonies to grow cotton before the beginning of the American Civil War. They were located along the Virgin River, in the warmer climate below the Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow Canyon 4
Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes. It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout its life cycle, starting when, under suitable conditions, the ice crystals form in the atmosphere, increase to millimeter size, precipitate and accumulate on surfaces, then metamorphose in place, and ultimately melt, slide or sublimate away. Snowstorms organize and develop by feeding on sources of atmospheric moisture and cold air. Snowflakes nucleate around particles in the atmosphere by attracting supercooled water droplets, which freeze in hexagonal-shaped crystals. Snowflakes take on a variety of shapes, basic among these are platelets, needles, columns and rime. As snow accumulates into a snowpack, it may blow into drifts. Over time, accumulated snow metamorphoses, by sintering, sublimation and freeze-thaw. Where the climate is col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th Century BC
The 5th century BC started the first day of 500 BC and ended the last day of 401 BC. This century saw the establishment of Pataliputra as a capital of the Magadha Empire. This city would later become the ruling capital of different Indian kingdoms for about a thousand years. This period saw the rise of two great philosophical schools of the east, Jainism and Buddhism. This period saw Mahavira and Buddha spreading their respective teachings in the northern plains of India. This essentially changed the socio-cultural and political dynamics of the region of South Asia. Buddhism would later go on to become one of the major world religions. This period also saw the work of Yaska, who created Nirukta, that would lay the foundation stone for Sanskrit grammar and is one of the oldest works on grammar known to mankind. This century is also traditionally recognized as the classical period of the Greeks, which would continue all the way through the 4th century until the time of Alexan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
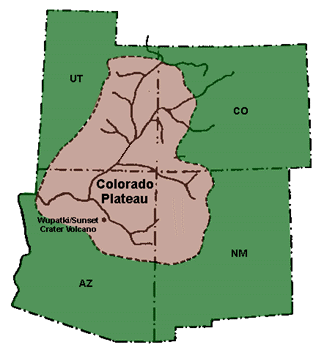
Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries. The Colorado Plateau is largely made up of high desert, with scattered areas of forests. In the south-west corner of the Colorado Plateau lies the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. Much of the Plateau's landscape is related to the Grand Canyon in both appearance and geologic history. The nickname "Red Rock Country" suggests the brightly colored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
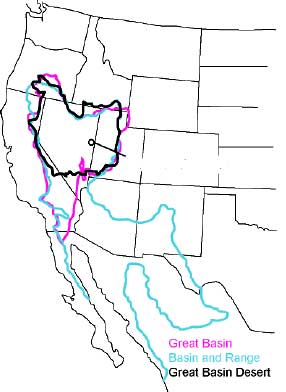
Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic basin, endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California. It is noted for both its arid climate and the basin and range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin in Death Valley to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than away at the summit of Mount Whitney. The region spans several physical geography, physiographic divisions, biomes, ecoregions, and deserts. Definition The term "Great Basin" is applied to hydrography, hydrographic, ecology, biological, floristic province, floristic, physiographic, topography, topographic, and Ethnography, ethnographic geographic areas. The name was originally coined by John C. Frémont, who, based on information gleaned from Joseph R. Walker as well as his own travels, recognized the hydrographic nature o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert ( ; mov, Hayikwiir Mat'aar; es, Desierto de Mojave) is a desert in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada mountains in the Southwestern United States. It is named for the indigenous Mojave people. It is located primarily in southeastern California and southwestern Nevada, with small portions extending into Arizona and Utah. The Mojave Desert, together with the Sonoran, Chihuahuan, and Great Basin deserts, forms a larger North American Desert. Of these, the Mojave is the smallest and driest. The Mojave Desert displays typical basin and range topography, generally having a pattern of a series of parallel mountain ranges and valleys. It is also the site of Death Valley, which is the lowest elevation in North America. The Mojave Desert is often colloquially called the "high desert", as most of it lies between . It supports a diversity of flora and fauna. The desert supports a number of human activities, including recreation, ranching, and military training. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Arch
A natural arch, natural bridge, or (less commonly) rock arch is a natural landform where an arch has formed with an opening underneath. Natural arches commonly form where inland cliffs, coastal cliffs, fins or stacks are subject to erosion from the sea, rivers or weathering ( subaerial processes). Most natural arches are formed from narrow fins and sea stacks composed of sandstone or limestone with steep, often vertical, cliff faces. The formations become narrower due to erosion over geologic time scales. The softer rock stratum erodes away creating rock shelters, or alcoves, on opposite sides of the formation beneath the relatively harder stratum, or caprock, above it. The alcoves erode further into the formation eventually meeting underneath the harder caprock layer, thus creating an arch. The erosional processes exploit weaknesses in the softer rock layers making cracks larger and removing material more quickly than the caprock; however, the caprock itself continues to er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equestrianism
Equestrianism (from Latin , , , 'horseman', 'horse'), commonly known as horse riding (Commonwealth English) or horseback riding (American English), includes the disciplines of riding, Driving (horse), driving, and Equestrian vaulting, vaulting. This broad description includes the use of horses for practical working animal, working purposes, transportation, recreational activities, artistic or cultural exercises, and animals in sport, competitive sport. Overview of equestrian activities Horses are horse training, trained and ridden for practical working purposes, such as in Mounted police, police work or for controlling herd animals on a ranch. They are also used in Horse#Sport, competitive sports including dressage, endurance riding, eventing, reining, show jumping, tent pegging, equestrian vaulting, vaulting, polo, horse racing, driving (horse), driving, and rodeo (see additional equestrian sports listed later in this article for more examples). Some popular forms of competi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Biking
Mountain biking is a sport of riding bicycles off-road, often over rough terrain, usually using specially designed mountain bikes. Mountain bikes share similarities with other bikes but incorporate features designed to enhance durability and performance in rough terrain, such as air or coil-sprung shocks used as suspension, larger and wider wheels and tires, stronger frame materials, and mechanically or hydraulically actuated disc brakes. Mountain biking can generally be broken down into five distinct categories: cross country, trail riding, all mountain (also referred to as "Enduro"), downhill, and freeride. This sport requires endurance, core strength and balance, bike handling skills, and self-reliance. Advanced riders pursue both steep technical descents and high incline climbs. In the case of freeride, downhill, and dirt jumping, aerial maneuvers are performed off both natural features and specially constructed jumps and ramps. Mountain bikers ride on off-road trails su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiking
Hiking is a long, vigorous walk, usually on trails or footpaths in the countryside. Walking for pleasure developed in Europe during the eighteenth century.AMATO, JOSEPH A. "Mind over Foot: Romantic Walking and Rambling." In ''On Foot: A History of Walking'', 101-24. NYU Press, 2004. Accessed March 1, 2021. http://www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctt9qg056.7. Religious pilgrimages have existed much longer but they involve walking long distances for a spiritual purpose associated with specific religions. "Hiking" is the preferred term in Canada and the United States; the term "walking" is used in these regions for shorter, particularly urban walks. In the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland, the word "walking" describes all forms of walking, whether it is a walk in the park or backpacking in the Alps. The word hiking is also often used in the UK, along with rambling , hillwalking, and fell walking (a term mostly used for hillwalking in northern England). The term bushwalking is end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |