|
Small Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein
snRNPs (pronounced "snurps"), or small nuclear ribonucleoproteins, are RNA-protein complexes that combine with unmodified pre-mRNA and various other proteins to form a spliceosome, a large RNA-protein molecular complex upon which splicing of pre-mRNA occurs. The action of snRNPs is essential to the removal of introns from pre-mRNA, a critical aspect of post-transcriptional modification of RNA, occurring only in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Additionally, '' U7 snRNP'' is not involved in splicing at all, as U7 snRNP is responsible for processing the 3′ stem-loop of histone pre-mRNA. The two essential components of snRNPs are protein molecules and RNA. The RNA found within each snRNP particle is known as ''small nuclear RNA'', or snRNA, and is usually about 150 nucleotides in length. The snRNA component of the snRNP gives specificity to individual introns by " recognizing" the sequences of critical splicing signals at the 5' and 3' ends and branch site of introns. The snRNA in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Complex
A protein complex or multiprotein complex is a group of two or more associated polypeptide chains. Protein complexes are distinct from multienzyme complexes, in which multiple catalytic domains are found in a single polypeptide chain. Protein complexes are a form of quaternary structure. Proteins in a protein complex are linked by non-covalent protein–protein interactions. These complexes are a cornerstone of many (if not most) biological processes. The cell is seen to be composed of modular supramolecular complexes, each of which performs an independent, discrete biological function. Through proximity, the speed and selectivity of binding interactions between enzymatic complex and substrates can be vastly improved, leading to higher cellular efficiency. Many of the techniques used to enter cells and isolate proteins are inherently disruptive to such large complexes, complicating the task of determining the components of a complex. Examples of protein complexes include the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidney Altman
Sidney Altman (May 7, 1939 – April 5, 2022) was a Canadian-American molecular biologist, who was the Sterling Professor of Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology and Chemistry at Yale University. In 1989, he shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Thomas R. Cech for their work on the catalytic properties of RNA. Family and education Altman was born on May 7, 1939, in Montreal, Quebec, Canada.Sidney Altman nobelprize.org His parents, Ray (Arlin), a textile worker, and Victor Altman, a grocer, were , each coming from |
Cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U6atac Minor Spliceosomal RNA
U6atac minor spliceosomal RNA is a non-coding RNA which is an essential component of the minor U12-type spliceosome complex. The U12-type spliceosome is required for removal of the rarer class of eukaryotic introns (AT-AC, U12-type). U6atac snRNA is proposed to form a base-paired complex with another spliceosomal RNA U4atac via two stem loop regions. These interacting stem loops have been shown to be required for in vivo splicing. U6atac is the functional analog of U6 spliceosomal RNA U6 snRNA is the non-coding small nuclear RNA (snRNA) component of U6 snRNP (''small nuclear ribonucleoprotein''), an RNA-protein complex that combines with other snRNPs, unmodified pre-mRNA, and various other proteins to assemble a spliceosome, ... in the major U2-type spliceosomal complex. References * External links * Non-coding RNA Spliceosome RNA splicing {{molecular-cell-biology-stub fr:ARN splicéosomal U4atac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U4atac Minor Spliceosomal RNA
U4atac minor spliceosomal RNA is a ncRNA which is an essential component of the minor U12-type spliceosome complex. The U12-type spliceosome is required for removal of the rarer class of eukaryotic introns (AT-AC, U12-type). U4atac snRNA is proposed to form a base-paired complex with another spliceosomal RNA U6atac via two stem loop regions. These interacting stem loops have been shown to be required for in vivo splicing. U4atac also contains a 3' Sm protein binding site which has been shown to be essential for splicing activity. U4atac is the functional analog of U4 spliceosomal RNA in the major U2-type spliceosomal complex. The Drosophila ''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many speci ... U4atac snRNA has an additional predicted 3' stem loop terminal to the Sm binding si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U12 SnRNA
U12 minor spliceosomal RNA is formed from U12 small nuclear (snRNA), together with U4atac/ U6atac, U5, and U11 snRNAs and associated proteins, forms a spliceosome that cleaves a divergent class of low-abundance pre-mRNA introns. Although the U12 sequence is very divergent from that of U2, the two are functionally analogous. Structure The predicted secondary structure of U12 RNA is published,. However, the alternative single hairpin in the 3' end shown here seems to better match the alignment of divergent ''Drosophila melanogaster'' and '' Arabidopsis thaliana'' sequences. The sequences U12 introns that are spliced out are collected in a biological database Biological databases are libraries of biological sciences, collected from scientific experiments, published literature, high-throughput experiment technology, and computational analysis. They contain information from research areas including geno ... called the U12 intron database. References External links * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U11 SnRNA
The U11 snRNA ( small nuclear ribonucleic acid) is an important non-coding RNA in the minor spliceosome protein complex, which activates the alternative splicing mechanism. The minor spliceosome is associated with similar protein components as the major spliceosome. It uses U11 snRNA to recognize the 5' splice site (functionally equivalent to U1 snRNA) while U12 snRNA binds to the branchpoint to recognize the 3' splice site (functionally equivalent to U2 snRNA). Secondary structure U11 snRNA has a stem-loop structure with a 5' end as splice site sequence (5' ss) and contains four stem loops structures (I-IV). A structural comparison of U11 snRNA between plants, vertebrates and insects shows that it is folded into a structure with a four-way junction at the 5' site and in a stem loop structure at the 3' site. Binding site during assembly pathway The 5' splice site region possesses sequence complementarity with the 5' splice site of the eukaryotic U12 type pre-mRNA intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metazoans
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinoderms a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
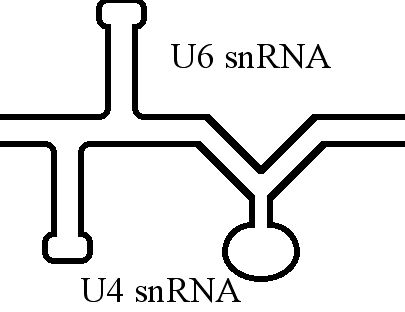
U6 SnRNA
U6 snRNA is the non-coding small nuclear RNA (snRNA) component of U6 snRNP (''small nuclear ribonucleoprotein''), an RNA-protein complex that combines with other snRNPs, unmodified pre-mRNA, and various other proteins to assemble a spliceosome, a large RNA-protein molecular complex that catalyzes the excision of introns from pre-mRNA. Splicing, or the removal of introns, is a major aspect of post-transcriptional modification and takes place only in the nucleus of eukaryotes. The RNA sequence of U6 is the most highly conserved across species of all five of the snRNAs involved in the spliceosome, suggesting that the function of the U6 snRNA has remained both crucial and unchanged through evolution. It is common in vertebrate genomes to find many copies of the U6 snRNA gene or U6-derived pseudogenes. This prevalence of "back-ups" of the U6 snRNA gene in vertebrates further implies its evolutionary importance to organism viability. The U6 snRNA gene has been isolated in many organism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U5 SnRNA
U5 snRNA is a small nuclear RNA (snRNA) that participates in RNA splicing as a component of the spliceosome. It forms the U5 snRNP (''small nuclear ribonucleoprotein'') by associating with several proteins including Prp8 - the largest and most conserved protein in the spliceosome, Brr2 - a helicase Helicases are a class of enzymes thought to be vital to all organisms. Their main function is to unpack an organism's genetic material. Helicases are motor proteins that move directionally along a nucleic acid phosphodiester backbone, separatin ... required for spliceosome activation, Snu114, and the 7 Sm proteins. U5 snRNA forms a coaxially-stacked series of helices that project into the active site of the spliceosome. Loop 1, which caps this series of helices, forms 4-5 base pairs with the 5'-exon during the two chemical reactions of splicing. This interaction appears to be especially important during step two of splicing, exon ligation. References Further reading * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U4 SnRNA
The U4 small nuclear Ribo-Nucleic Acid (U4 snRNA) is a non-coding RNA component of the major or U2-dependent spliceosome – a eukaryotic molecular machine involved in the splicing of pre-messenger RNA (pre-mRNA). It forms a duplex with U6, and with each splicing round, it is displaced from the U6 snRNA (and the spliceosome) in an ATP-dependent manner, allowing U6 to re-fold and create the active site for splicing catalysis. A recycling process involving protein Brr2 releases U4 from U6, while protein Prp24 re-anneals U4 and U6. The crystal structure of a 5′ stem-loop of U4 in complex with a binding protein has been solved. Biological role The U4 snRNA has been shown to exist in a number of different formats including: bound to proteins as a small nuclear Ribo-Nuclear Protein snRNP, involved with the U6 snRNA in the di-snRNP, as well as involved with both the U6 snRNA and the U5 snRNA in the tri-snRNP. The different formats have been proposed to coincide with different temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U2 SnRNA
U2 spliceosomal snRNAs are a species of small nuclear RNA (snRNA) molecules found in the major spliceosomal (Sm) machinery of virtually all eukaryotic organisms. ''In vivo'', U2 snRNA along with its associated polypeptides assemble to produce the U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP), an essential component of the major spliceosomal complex. The major spliceosomal-splicing pathway is occasionally referred to as U2 dependent, based on a class of Sm intron—found in mRNA primary transcripts—that are recognized exclusively by the U2 snRNP during early stages of spliceosomal assembly. In addition to U2 dependent intron recognition, U2 snRNA has been theorized to serve a catalytic role in the chemistry of pre-RNA splicing as well. Similar to ribosomal RNAs ( rRNAs), Sm snRNAs must mediate both RNA:RNA and RNA:protein contacts and hence have evolved specialized, highly conserved, primary and secondary structural elements to facilitate these types of interactions. Shortly after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |