|
Small-angle Scattering
Small-angle scattering (SAS) is a scattering technique based on deflection of collimated radiation away from the straight trajectory after it interacts with structures that are much larger than the wavelength of the radiation. The deflection is small (0.1-10°) hence the name ''small-angle''. SAS techniques can give information about the size, shape and orientation of structures in a sample. SAS is a powerful technique for investigating large-scale structures from 10 Å up to thousands and even several tens of thousands of angstroms. The most important feature of the SAS method is its potential for analyzing the inner structure of disordered systems, and frequently the application of this method is a unique way to obtain direct structural information on systems with random arrangement of density inhomogeneities in such large-scales. Currently, the SAS technique, with its well-developed experimental and theoretical procedures and wide range of studied objects, is a self-contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scattering
In physics, scattering is a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiation) in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of reflected radiation from the angle predicted by the law of reflection. Reflections of radiation that undergo scattering are often called ''diffuse reflections'' and unscattered reflections are called ''specular'' (mirror-like) reflections. Originally, the term was confined to light scattering (going back at least as far as Isaac Newton in the 17th century). As more "ray"-like phenomena were discovered, the idea of scattering was extended to them, so that William Herschel could refer to the scattering of "heat rays" (not then recognized as electromagnetic in nature) in 1800. John Tyndall, a pioneer in light scattering research, noted the connecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of List of virus species, virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dispersity
In chemistry, the dispersity is a measure of the heterogeneity of sizes of molecules or particles in a mixture. A collection of objects is called uniform if the objects have the same size, shape, or mass. A sample of objects that have an inconsistent size, shape and mass distribution is called non-uniform. The objects can be in any form of chemical dispersion, such as particles in a colloid, droplets in a cloud, crystals in a rock, or polymer macromolecules in a solution or a solid polymer mass. Polymers can be described by molecular mass distribution; a population of particles can be described by size, surface area, and/or mass distribution; and thin films can be described by film thickness distribution. IUPAC has deprecated the use of the term ''polydispersity index'', having replaced it with the term ''dispersity'', represented by the symbol Đ (pronounced D-strokeStepto, R. F. T.; Gilbert, R. G.; Hess, M.; Jenkins, A. D.; Jones, R. G.; Kratochvíl P. (2009).Dispersity in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
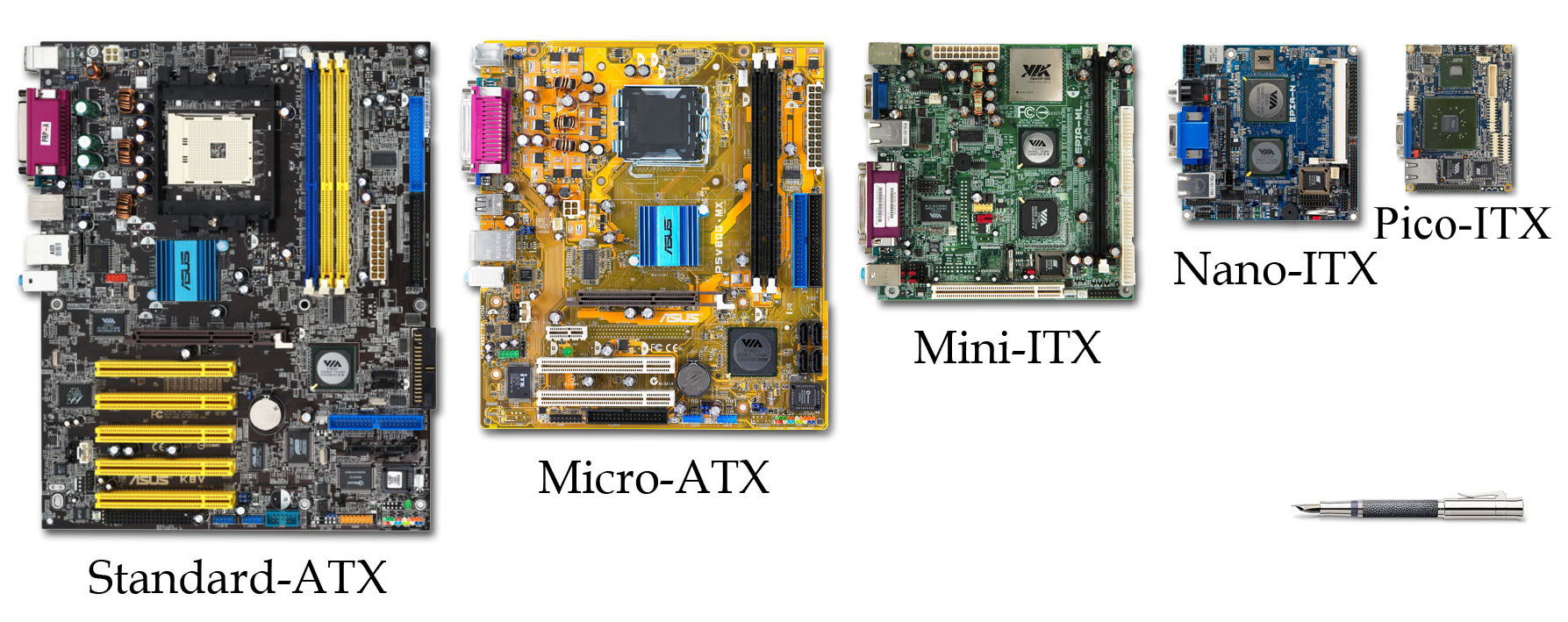
Formfactor Sphere Huygens
Form factor is a hardware design aspect that defines and prescribes the size, shape, and other physical specifications of components, particularly in electronics. A form factor may represent a broad class of similarly sized components, or it may prescribe a specific standard. It may also define an entire system, as in a computer form factor. Evolution and standardization As electronic hardware has become smaller following Moore's law and related patterns, ever-smaller form factors have become feasible. Specific technological advances, such as PCI Express, have had a significant design impact, though form factors have historically evolved slower than individual components. Standardization of form factors is vital for hardware compatibility between different manufacturers. Trade-offs Smaller form factors may offer more efficient use of limited space, greater flexibility in the placement of components within a larger assembly, reduced use of material, and greater ease of transportat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere
A sphere (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ) is a surface (mathematics), surface analogous to the circle, a curve. In solid geometry, a sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the center (geometry), ''center'' of the sphere, and the distance is the sphere's ''radius''. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the Greek mathematics, ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental surface in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubble (physics), Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is spherical Earth, often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres rolling, roll smoothly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Size Distribution
Size in general is the magnitude or dimensions of a thing. More specifically, ''geometrical size'' (or ''spatial size'') can refer to three geometrical measures: length, area, or volume. Length can be generalized to other linear dimensions (width, height, diameter, perimeter). Size can also be measured in terms of mass, especially when assuming a density range. In mathematical terms, "size is a concept abstracted from the process of measuring by comparing a longer to a shorter". Size is determined by the process of comparing or measuring objects, which results in the determination of the magnitude of a quantity, such as length or mass, relative to a unit of measurement. Such a magnitude is usually expressed as a numerical value of units on a previously established spatial scale, such as meters or inches. The sizes with which humans tend to be most familiar are body dimensions (measures of anthropometry), which include measures such as human height and human body weigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractal Dimension
In mathematics, a fractal dimension is a term invoked in the science of geometry to provide a rational statistical index of complexity detail in a pattern. A fractal pattern changes with the Scaling (geometry), scale at which it is measured. It is also a measure of the Space-filling curve, space-filling capacity of a pattern and tells how a fractal scales differently, in a fractal (non-integer) dimension. The main idea of "fractured" Hausdorff dimension, dimensions has a long history in mathematics, but the term itself was brought to the fore by Benoit Mandelbrot based on How Long Is the Coast of Britain? Statistical Self-Similarity and Fractional Dimension, his 1967 paper on self-similarity in which he discussed ''fractional dimensions''. In that paper, Mandelbrot cited previous work by Lewis Fry Richardson describing the counter-intuitive notion that a coastline's measured length changes with the length of the measuring stick used (see #coastline, Fig. 1). In terms of that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Roughness
Surface roughness or simply roughness is the quality of a surface of not being smooth and it is hence linked to human ( haptic) perception of the surface texture. From a mathematical perspective it is related to the spatial variability structure of surfaces, and inherently it is a multiscale property. It has different interpretations and definitions depending on the disciplines considered. In surface metrology, surface roughness is a component of surface finish (surface texture). It is quantified by the deviations in the direction of the normal vector of a real surface from its ideal form. If these deviations are large, the surface is rough; if they are small, the surface is smooth. Roughness is typically assumed to be the high-frequency, short-wavelength component of a measured surface. However, in practice it is often necessary to know both the amplitude and frequency to ensure that a surface is fit for a purpose. Role and effect Roughness plays an important role in determin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porod's Law
In X-ray or neutron small-angle scattering (SAS), Porod's law, discovered by Günther Porod, describes the asymptote of the scattering intensity ''I(q)'' for large scattering wavenumbers ''q''. Context Porod's law is concerned with wave numbers ''q'' that are small compared to the scale of usual Bragg diffraction; typically q\lesssim1\text^. In this range, the sample must not be described at an atomistic level; one rather uses a continuum description in terms of an electron density or a neutron scattering length density. In a system composed of distinct mesoscopic particles, all small-angle scattering can be understood as arising from surfaces or interfaces. Normally, SAS is measured in order to detect correlations between different interfaces, and in particular, between remote surface segments of one and the same particle. This allows conclusions about the size and shape of the particles, and their correlations. Porod's ''q'' is relatively large on the usual scale of SAS. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bragg Diffraction
In many areas of science, Bragg's law — also known as Wulff–Bragg's condition or Laue–Bragg interference — is a special case of Laue diffraction that gives the angles for coherent scattering of waves from a large crystal lattice. It describes how the superposition of wave fronts scattered by lattice planes leads to a strict relation between the wavelength and scattering angle. This law was initially formulated for X-rays, but it also applies to all types of matter waves including neutron and electron waves if there are a large number of atoms, as well as to visible light with artificial periodic microscale lattices. History Bragg diffraction (also referred to as the Bragg formulation of X-ray diffraction) was first proposed by Lawrence Bragg and his father, William Henry Bragg, in 1913 after their discovery that crystalline solids produced surprising patterns of reflected X-rays (in contrast to those produced with, for instance, a liquid). They found that these cryst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Scattering Length
A neutron may pass by a nucleus with a probability determined by the nuclear interaction distance, or be absorbed, or undergo scattering that may be either coherent or incoherent. The interference effects in coherent scattering can be computed via the coherent scattering length of neutrons, being proportional to the amplitude of the spherical scattered waves according to Huygens–Fresnel theory. This scattering length varies by isotope (and by element as the weighted arithmetic mean over the constituent isotopes) in a way that appears random, whereas the X-ray scattering length is just the product of atomic number and Thomson scattering length, thus monotonically increasing with atomic number. The scattering length may be either positive or negative. The scattering cross-section is equal to the square of the scattering length multiplied by 4π, i.e. the area of a circle with radius twice the scattering length. In some cases, as with titanium and nickel, it is possible to mix iso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Guinier
André Guinier (1 August, 1911 – 3 July, 2000) was a French physicist and crystallographer who did pioneering work in the field of X-ray diffraction and solid-state physics. He was credited for the discovery and developments of small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) into an indispensable tool for materials science and crystallography. Education and career Guinier was born in Nancy, France, his father Philibert Guinier was a botanist and director of the Nancy branch of the French National School of Forestry. Guinier studied at Lycée Henri-Poincaré before entering the École Normale Supérieure (ENS), where he studied physics from 1930 to 1934. After graduation, he worked as an agrégé-preparateur in the physics laboratory of ENS. In 1939, Guinier discovered SAXS and received his doctorate with a thesis on X-ray crystallography under Charles Mauguin. He then worked at the Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers, where he became deputy director of the test laboratory in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |