|
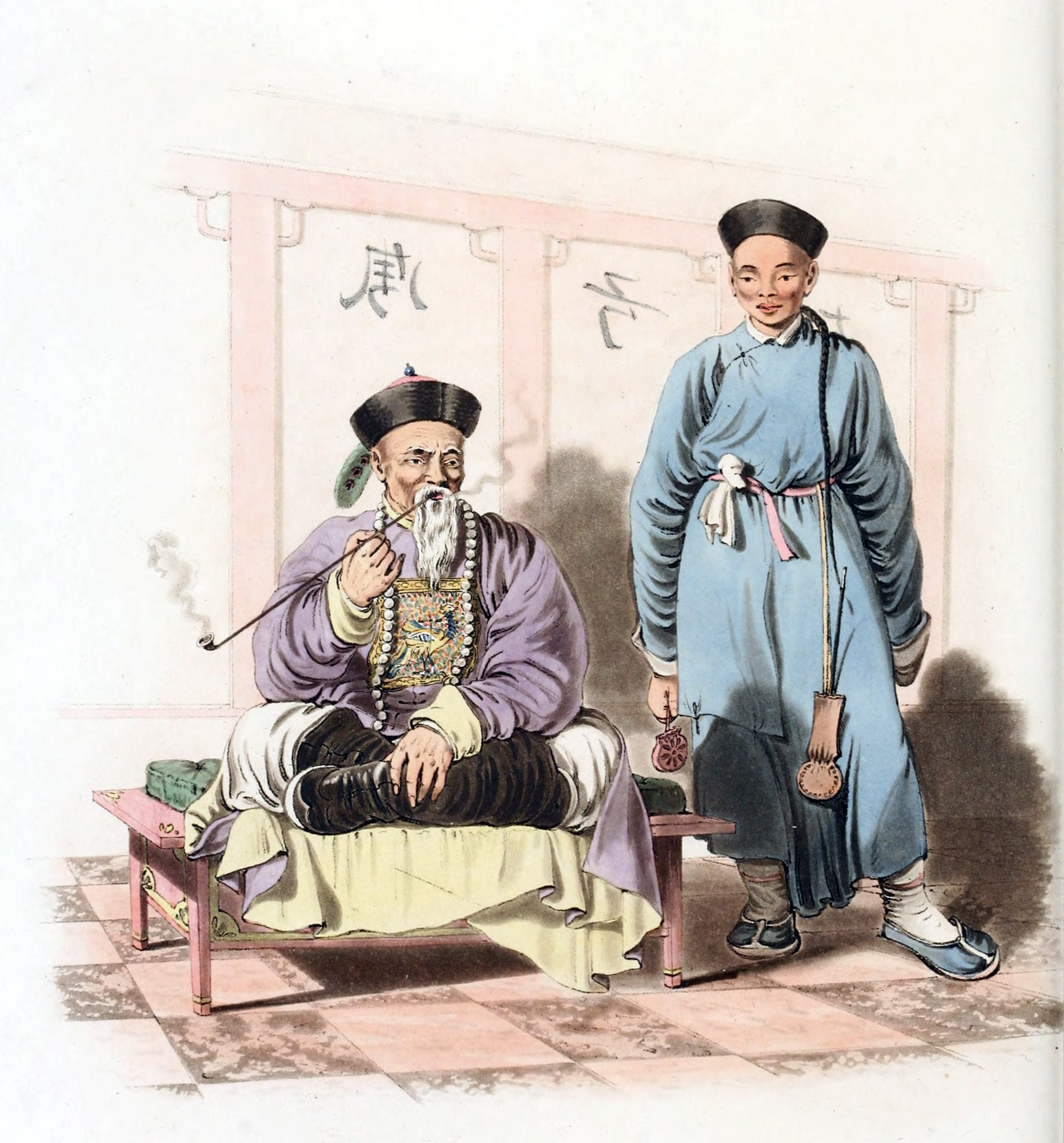
Slavery In China
Slavery in China has taken various forms throughout history. Slavery was abolished as a legally recognized institution, including in a 1909 lawHallet, Nicole.China and Antislavery". ''Encyclopedia of Antislavery and Abolition'', Vol. 1, p. 154156. Greenwood Publishing Group, 2007. . fully enacted in 1910, although the practice continued until at least 1949.Rodriguez, Junius.China, Late Imperial". ''The Historical Encyclopedia of World Slavery'', Vol. 1, p. 146. ABC-CLIO, 1997. . Illegal acts of forced labor and sexual slavery in China continue to occur in the twenty-first century, but those found guilty of such crimes are punished harshly. The Chinese term for slave (''nuli'') can also be roughly translated into 'debtor', 'dependent', or 'subject'. Slaves in China were a very small part of the population and could include war prisoners, kidnapping victims or people who had been sold. General history In Chinese society, slaves were grouped under a category of people known as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Slavery In China
Sexual slavery in China is sexual exploitation and slavery that occurs in the People's Republic of China. Background Chinese citizen and foreign victims, primarily women and girls, are unlawfully kept in a situation in which they are raped and physically and psychologically harmed in other ways. A number contract sexually transmitted diseases, and abused, beaten, and starved. Some women and girls are tortured and or murdered. Others commit suicide. Victims are forced into prostitution, marriages, and or pregnancies. Many are kept tied or locked up in homes, brothels, or indirect sex establishments, such as beer gardens, massage parlors, salons, karaoke bars, retail spaces, and non-commercial sites. Other locations include construction sites, remote mining and logging camps, and areas with high concentrations of Chinese migrant workers. Victims have been subjected to penetrative vaginal and anal rape, groping, and forced masturbation in illegal, cybersex trafficking 'online rape de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yongzheng Emperor
, regnal name = , posthumous name = Emperor Jingtian Changyun Jianzhong Biaozhen Wenwu Yingming Kuanren Xinyi Ruisheng Daxiao Zhicheng Xian()Manchu: Temgetulehe hūwangdi () , temple name = Shizong()Manchu: Šidzung () , house = Aisin Gioro , dynasty = Qing , father = Kangxi Emperor , mother = Empress Xiaogongren , religion = Tibetan Buddhism The Yongzheng Emperor (13 December 1678 – 8 October 1735), also known by his temple name Emperor Shizong of Qing, born Yinzhen, was the fourth Emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the third Qing emperor to rule over China proper. He reigned from 1722 to 1735. A hard-working ruler, the Yongzheng Emperor's main goal was to create an effective government at minimal expense. Like his father, the Kangxi Emperor, the Yongzheng Emperor used military force to preserve the dynasty's position. Although Yongzheng's reign was much shorter than that of both his father (the Kangxi Emperor) and his son (the Qianlong Emperor), the Yongzheng era ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chan Buddhist
Chan (; of ), from Sanskrit ''dhyāna in Buddhism, dhyāna'' (meaning "meditation" or "meditative state"), is a Chinese school of Mahayana, Mahāyāna Buddhism. It developed in China from the 6th century Common Era, CE onwards, becoming especially popular during the Tang dynasty, Tang and Song dynasty, Song dynasties. Chan is the originating tradition of Zen Buddhism (the Japanese pronunciation of the same Chinese characters, character, which is the most commonly used English name for the school). Chan Buddhism spread from China south to Vietnam as Vietnamese Thiền, Thiền and north to Korea as Korean Seon, Seon, and, in the 13th century, east to Japan as Japanese Zen. History The historical records required for a complete, accurate account of early Chan history no longer exist. Periodisation The history of Chan in China can be divided into several periods. Zen, as we know it today, is the result of a long history, with many changes and contingent factors. Each perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Names Of Vietnam
Throughout the history of Vietnam, many names were used in reference to Vietnam. History Throughout the history of Vietnam, official and unofficial names have been used in reference to the territory of Vietnam. Vietnam was called Văn Lang during the Hồng Bàng dynasty, Âu Lạc under Thục dynasty, Nam Việt during the Triệu dynasty, Vạn Xuân during the Early Lý dynasty, Đại Cồ Việt during the Đinh dynasty and Early Lê dynasty. Starting in 1054, Vietnam was called Đại Việt (Great Việt). During the Hồ dynasty, Vietnam was called Đại Ngu. Việt Nam ( in Vietnamese) is a variation of Nam Việt (Southern Việt), a name that can be traced back to the Triệu dynasty (2nd century BC, also known as Nanyue Kingdom). The word "Việt" originated as a shortened form of Bách Việt, a word used to refer to a people who lived in what is now southern China in ancient times. The word "Việt Nam", with the syllables in the modern order, first appears ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Kingdoms Period
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and was followed by the Western Jin dynasty. The short-lived state of Yan on the Liaodong Peninsula, which lasted from 237 to 238, is sometimes considered as a "4th kingdom". Academically, the period of the Three Kingdoms refers to the period between the establishment of Cao Wei in 220 and the conquest of the Eastern Wu by the Western Jin in 280. The earlier, "unofficial" part of the period, from 184 to 220, was marked by chaotic infighting between warlords in various parts of China during the downfall of the Eastern Han dynasty. The middle part of the period, from 220 to 263, was marked by a more militarily stable arrangement between three rival states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The later part of the era was marked by the conquest of Shu by Wei in 263, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Slave Trade
Chinese can refer to: * Something related to China * Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity **''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation ** List of ethnic groups in China, people of various ethnicities in contemporary China ** Han Chinese, the largest ethnic group in the world and the majority ethnic group in Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, and Singapore ** Ethnic minorities in China, people of non-Han Chinese ethnicities in modern China ** Ethnic groups in Chinese history, people of various ethnicities in historical China ** Nationals of the People's Republic of China ** Nationals of the Republic of China ** Overseas Chinese, Chinese people residing outside the territories of Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan * Sinitic languages, the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family ** Chinese language, a group of related languages spoken predominantly in China, sharing a written script (Chinese c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legalism (Chinese Philosophy)
Legalism or ''Fajia'' is one of the six classical schools of thought in Chinese philosophy. Literally meaning "house of (administrative) methods / standards (法, Fa)", the Fa "school" represents several branches of "men of methods", in the west often termed " realist" statesmen,who played foundational roles in the construction of the bureaucratic Chinese empire.Peng He 2011. p. 646. The Difference of Chinese Legalism and Western Legalism The earliest persona of the Fajia may be considered Guan Zhong (720–645 BC), but following the precedent of the ''Han Feizi'' (c. 240 BC), Warring States period figures Shen Buhai (400–337 BC) and Shang Yang (390–338 BC) have commonly been taken as its "founders." Commonly thought of as the greatest of all "Legalist" texts, the ''Han Feizi'' is believed to contain the first commentaries on the ''Dao De Jing'' in history.Ewan Ferlie, Laurence E. Lynn, Christopher Pollitt 2005 p. 30, ''The Oxford Handbook of Public Management''Pines, Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manumission
Manumission, or enfranchisement, is the act of freeing enslaved people by their enslavers. Different approaches to manumission were developed, each specific to the time and place of a particular society. Historian Verene Shepherd states that the most widely used term is gratuitous manumission, "the conferment of freedom on the enslaved by enslavers before the end of the slave system". The motivations for manumission were complex and varied. Firstly, it may present itself as a sentimental and benevolent gesture. One typical scenario was the freeing in the master's will of a devoted servant after long years of service. A trusted bailiff might be manumitted as a gesture of gratitude. For those working as agricultural laborers or in workshops, there was little likelihood of being so noticed. In general, it was more common for older slaves to be given freedom. Legislation under the early Roman Empire put limits on the number of slaves that could be freed in wills (''lex Fufia Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
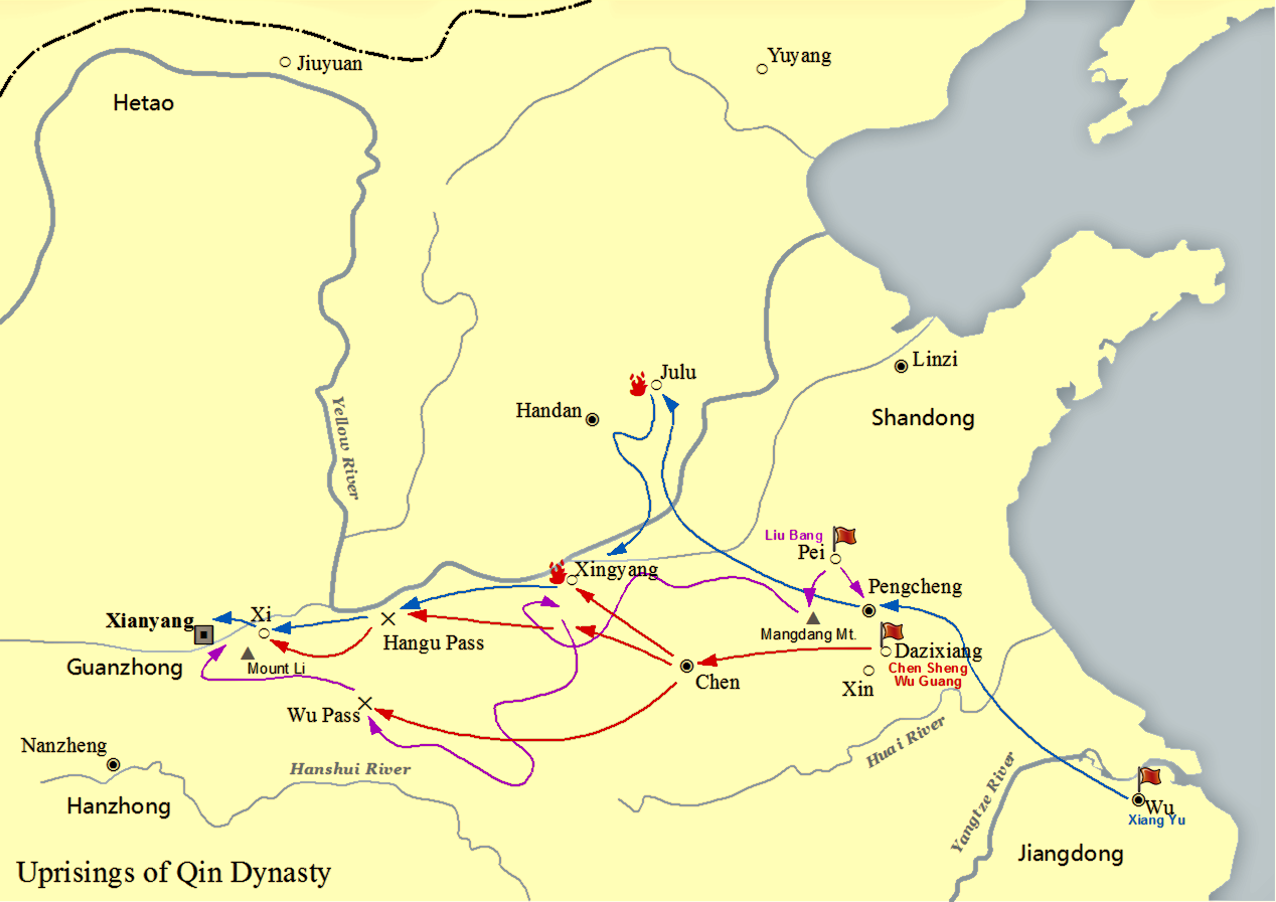
Emperor Gaozu Of Han
Emperor Gaozu of Han (256 – 1 June 195 BC), born Liu Bang () with courtesy name Ji (季), was the founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning in 202–195 BC. His temple name was "Taizu" while his posthumous name was Emperor Gao, or Gaodi; "Gaozu of Han", derived from the ''Records of the Grand Historian'', is the common way of referring to this sovereign even though he was not accorded the temple name "Gaozu", which literally means "High Founder". Liu Bang was one of the few dynasty founders in Chinese history who was born into a peasant family. Prior to coming to power, Liu Bang initially served for the Qin dynasty as a minor law enforcement officer in his home town Pei County, within the conquered state of Chu. With the First Emperor's death and the Qin Empire's subsequent political chaos, Liu Bang renounced his civil service position and became an anti-Qin rebel leader. He won the race against fellow rebel leader Xiang Yu to invade the Qin heartlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the ChuHan contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) and the Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history, and it has influenced the identity of the Chinese civilization ever since. Modern China's majority ethnic group refers to themselves as the "Han people", the Sinitic language is known as "Han language", and the written Chinese is referred to as "Han characters". The emperor was at the pinnacle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
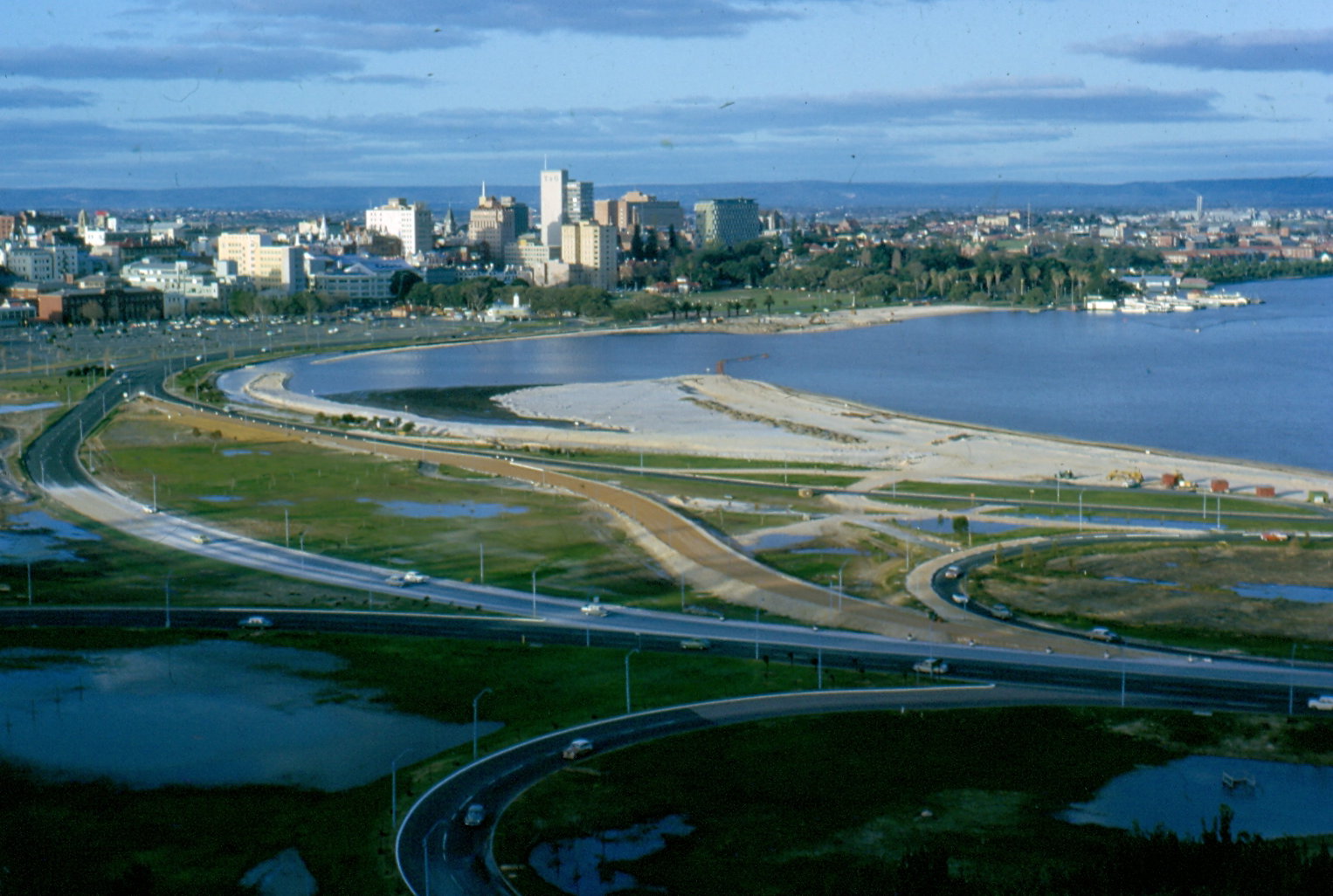
Land Reclamation
Land reclamation, usually known as reclamation, and also known as land fill (not to be confused with a waste landfill), is the process of creating new land from oceans, seas, riverbeds or lake beds. The land reclaimed is known as reclamation ground or land fill. In some jurisdictions, including parts of the United States, the term "reclamation" can refer to returning disturbed lands to an improved state. In Alberta, Canada, for example, reclamation is defined by the provincial government as "The process of reconverting disturbed land to its former or other productive uses." In Oceania, it is frequently referred to as land rehabilitation. History One of the earliest large-scale projects was the Beemster Polder in the Netherlands, realized in 1612 adding of land. In Hong Kong the Praya Reclamation Scheme added of land in 1890 during the second phase of construction. It was one of the most ambitious projects ever taken during the Colonial Hong Kong era.Bard, Solomon. 002 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |