|
Skip Bombing
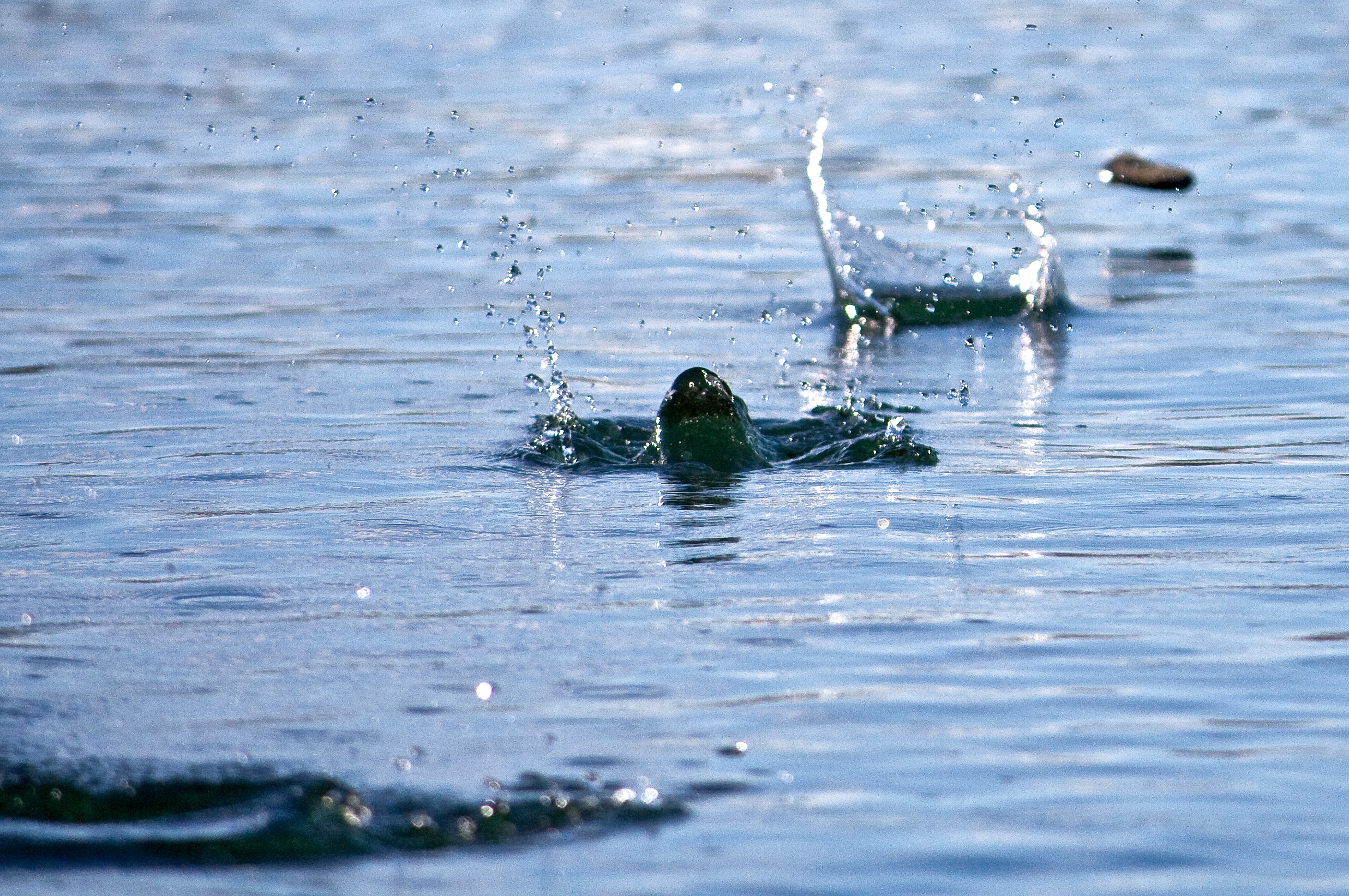
Skip bombing was a low-level bombing technique independently developed by several of the combatant nations in World War II, notably Italy, Australia, Britain, Soviet Union and the United States. It allows an aircraft to attack shipping by skipping the bomb across the water like a stone. Dropped at very low altitudes, the bomb never rises more than about above the surface of the water, ensuring that it will hit the side of the ship as long as it is aimed correctly. As the technique required the aircraft to fly at very low altitudes directly at the ship, it made shooting down the aircraft easier as well. In the immediate pre-war era, there was considerable effort to develop new bombsights that would allow the aircraft to remain at higher altitudes. The most notable was the US Navy's Norden bombsight, which was fitted to most Navy aircraft. In practice, these proved largely useless, and the skip-bombing technique was soon introduced operationally. After Pearl Harbor (December 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A20BismarckSea
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, " a", and its variant " an", are indefinite articles. History The earliest certain ancestor of "A" is aleph (also written 'aleph), the first letter of the Phoenician alphabet, which consisted entirely of consonants (for that reason, it is also called an abjad to distinguish it fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Chastise
Operation Chastise or commonly known as the Dambusters Raid was an attack on German dams carried out on the night of 16/17 May 1943 by 617 Squadron RAF Bomber Command, later called the Dam Busters, using special " bouncing bombs" developed by Barnes Wallis. The Möhne and Edersee dams were breached, causing catastrophic flooding of the Ruhr valley and of villages in the Eder valley; the Sorpe Dam sustained only minor damage. Two hydroelectric power stations were destroyed and several more damaged. Factories and mines were also damaged and destroyed. An estimated 1,600 civilians – about 600 Germans and 1,000 forced labourers, mainly Soviet – were killed by the flooding. Despite rapid repairs by the Germans, production did not return to normal until September. The RAF lost 53 aircrew killed and 3 captured, with 8 aircraft destroyed. Background Before the Second World War, the British Air Ministry had identified the industrialised Ruhr Valley, especially its dams, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
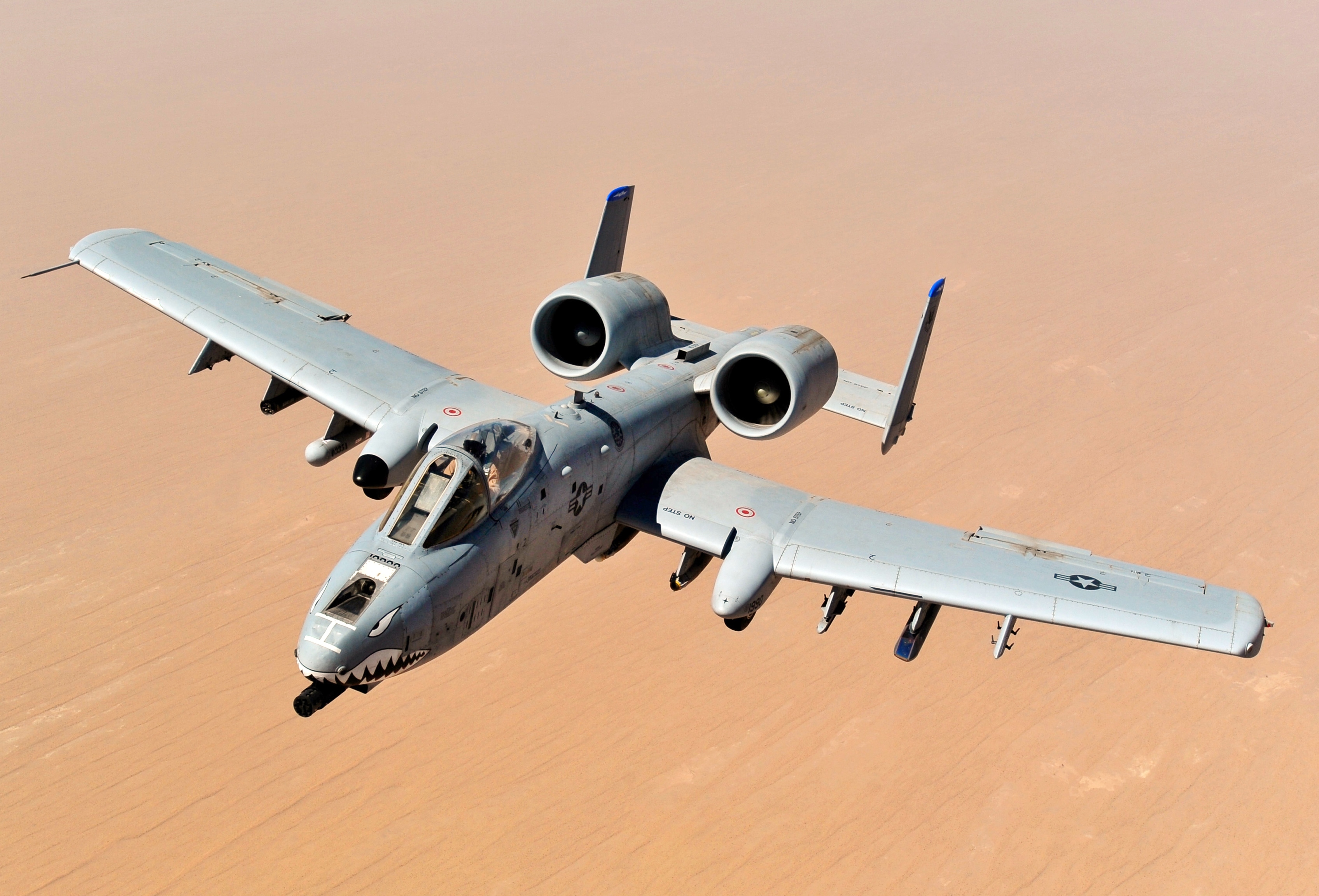
Ground-attack Aircraft
An attack aircraft, strike aircraft, or attack bomber is a tactical military aircraft that has a primary role of carrying out airstrikes with greater precision than bombers, and is prepared to encounter strong low-level air defenses while pressing the attack.Mortensen 1987, pp. 24–25. This class of aircraft is designed mostly for close air support and naval air-to-surface missions, overlapping the tactical bomber mission. Designs dedicated to non-naval roles are often known as ground-attack aircraft.Gunston 2009, p. 73. Fighter aircraft often carry out the attack role, although they would not be considered attack aircraft ''per se'', although fighter-bomber conversions of those same aircraft would be considered part of the class. Strike fighters, which have effectively replaced the fighter-bomber and light bomber concepts, also differ little from the broad concept of an attack aircraft. The dedicated attack aircraft as a separate class existed primarily during and after W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
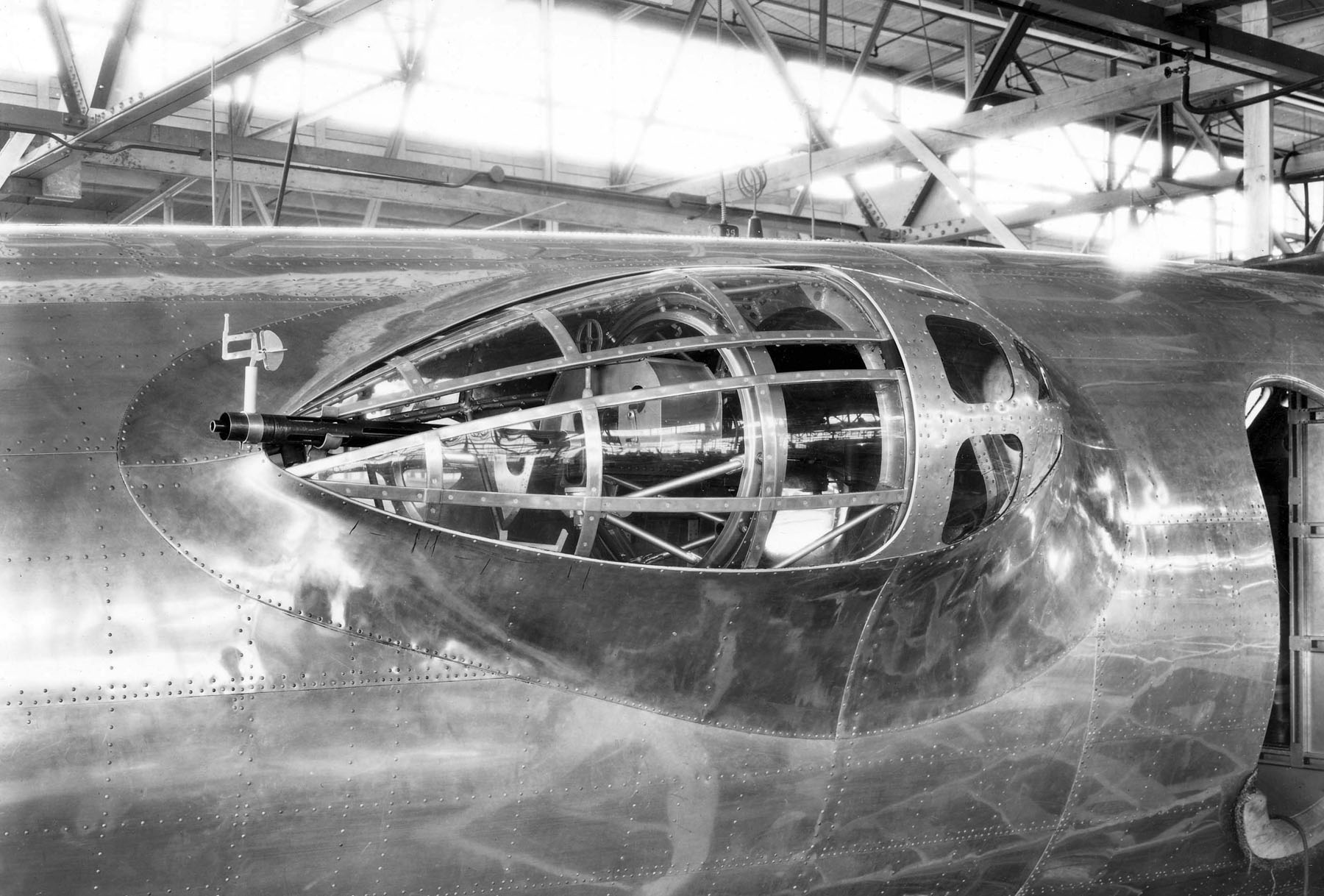
Douglas A-20 Havoc
The Douglas A-20 Havoc (company designation DB-7) is an American medium bomber, attack aircraft, night intruder, night fighter, and reconnaissance aircraft of World War II. Designed to meet an Army Air Corps requirement for a bomber, it was ordered by France for their air force before the USAAC decided it would also meet their requirements. French DB-7s were the first to see combat; after the fall of France, the bomber served with the Royal Air Force under the service name Boston. From 1941, night fighter and intruder versions were given the service name Havoc. In 1942 USAAF A-20s saw combat in North Africa. It served with several Allied air forces, principally the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF), the Soviet Air Forces (''VVS''), Soviet Naval Aviation (''AVMF''), and the Royal Air Force (RAF) of the United Kingdom. A total of 7,478 aircraft were built, of which more than a third served with Soviet units. It was also used by the air forces of Australia, South Africa, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medium Bomber
A medium bomber is a military bomber aircraft designed to operate with medium-sized bombloads over medium range distances; the name serves to distinguish this type from larger heavy bombers and smaller light bombers. Mediums generally carried about two tons of bombs, compared to light bombers that carried one ton, and heavies that carried four or more. The term was used prior to and during World War II, based on available parameters of engine and aeronautical technology for bomber aircraft designs at that time. After the war, medium bombers were replaced in world air forces by more advanced and capable aircraft. History In the early 1930s many air forces were looking to modernize their existing bomber aircraft fleets, which frequently consisted of older biplanes. The new designs were typically twin-engined monoplanes, often of all-metal construction, and optimized for high enough performance and speed to help evade rapidly evolving fighter aircraft designs of the time. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American B-25 Mitchell
The North American B-25 Mitchell is an American medium bomber that was introduced in 1941 and named in honor of Major General William "Billy" Mitchell, a pioneer of U.S. military aviation. Used by many Allied air forces, the B-25 served in every theater of World War II, and after the war ended, many remained in service, operating across four decades. Produced in numerous variants, nearly 10,000 B-25s were built. These included several limited models such as the F-10 reconnaissance aircraft, the AT-24 crew trainers, and the United States Marine Corps' PBJ-1 patrol bomber. Design and development The Air Corps issued a specification for a medium bomber in March 1939 that was capable of carrying a payload of over at North American Aviation used its NA-40B design to develop the NA-62, which competed for the medium bomber contract. No YB-25 was available for prototype service tests. In September 1939, the Air Corps ordered the NA-62 into production as the B-25, along with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Bomber
Heavy bombers are bomber aircraft capable of delivering the largest payload of air-to-ground weaponry (usually bombs) and longest range (takeoff to landing) of their era. Archetypal heavy bombers have therefore usually been among the largest and most powerful military aircraft at any point in time. In the second half of the 20th century, heavy bombers were largely superseded by strategic bombers, which were often smaller in size, but had much longer ranges and were capable of delivering nuclear bombs. Because of advances in aircraft design and engineering — especially in powerplants and aerodynamics — the size of payloads carried by heavy bombers has increased at rates greater than increases in the size of their airframes. The largest bombers of World War I, the four engine aircraft built by the Sikorsky company in the Soviet Union, could carry a payload of up to of bombs. By the middle of World War II even a single-engine fighter-bomber could carry a bomb load, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress
The Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress is a four-engined heavy bomber developed in the 1930s for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC). Relatively fast and high-flying for a bomber of its era, the B-17 was used primarily in the European Theater of Operations and dropped more bombs than any other aircraft during World War II. It is the third-most produced bomber of all time, behind the four-engined Consolidated B-24 Liberator and the multirole, twin-engined Junkers Ju 88. It was also employed as a transport, antisubmarine aircraft, drone controller, and search-and-rescue aircraft. In a USAAC competition, Boeing's prototype Model 299/XB-17 outperformed two other entries but crashed, losing the initial 200-bomber contract to the Douglas B-18 Bolo. Still, the Air Corps ordered 13 more B-17s for further evaluation, then introduced it into service in 1938. The B-17 evolved through numerous design advances but from its inception, the USAAC (later, the USAAF) promoted the aircraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Bismarck Sea
The Battle of the Bismarck Sea (2–4 March 1943) took place in the South West Pacific Area (SWPA) during World War II when aircraft of the U.S. Fifth Air Force and the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) attacked a Japanese convoy carrying troops to Lae, New Guinea. Most of the Japanese task force was destroyed, and Japanese troop losses were heavy. The Japanese convoy was a result of a Japanese Imperial General Headquarters decision in December 1942 to reinforce their position in the South West Pacific. A plan was devised to move some 6,900 troops from Rabaul directly to Lae. The plan was understood to be risky, because Allied air power in the area was strong, but it was decided to proceed because otherwise the troops would have to be landed a considerable distance away and march through inhospitable swamp, mountain and jungle terrain without roads before reaching their destination. On 28 February 1943, the convoy – comprising eight destroyers and eight troop transport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouncing Bomb
A bouncing bomb is a bomb designed to bounce to a target across water in a calculated manner to avoid obstacles such as torpedo nets, and to allow both the bomb's speed on arrival at the target and the timing of its detonation to be pre-determined, in a similar fashion to a regular naval depth charge. The inventor of the first such bomb was the British engineer Barnes Wallis, whose "Upkeep" bouncing bomb was used in the RAF's Operation Chastise of May 1943 to bounce into German dams and explode under water, with effect similar to the underground detonation of the Grand Slam and Tallboy earthquake bombs, both of which he also invented. British bouncing bombs After the outbreak of the Second World War in 1939, Wallis saw strategic bombing as the means to destroy the enemy's ability to wage war and he wrote a paper entitled "A Note on a Method of Attacking the Axis Powers". Referring to the enemy's power supplies, he wrote (as Axiom 3): "If their destruction or paralysis ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Skipping
Stone skipping and stone skimming are considered related but distinct activities: both refer to the art of throwing a flat stone across the water in such a way (usually sidearm) that it bounces off the surface. The objective of "skipping" is to see how many times a stone can bounce before it sinks into the water; the objective of "skimming" is to see how far a bouncing stone can travel across the water before it sinks into the water. In Japan, the practice is referred to as ''Mizu Kiri'', which loosely translates to "water cutting". In ''Mizu Kiri'' contests, both skimming and skipping principles, as well as a throw's overall aesthetic quality, are taken into account to determine the winners. History The act of skipping stones was mentioned by Marcus Minucius Felix in his dialogue ''Octavius'', in which he described children playing a game on the beach. Greek scholar Julius Pollux also noted the game in ''Onomastikon''. Among the first documented evidence stone skipping as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
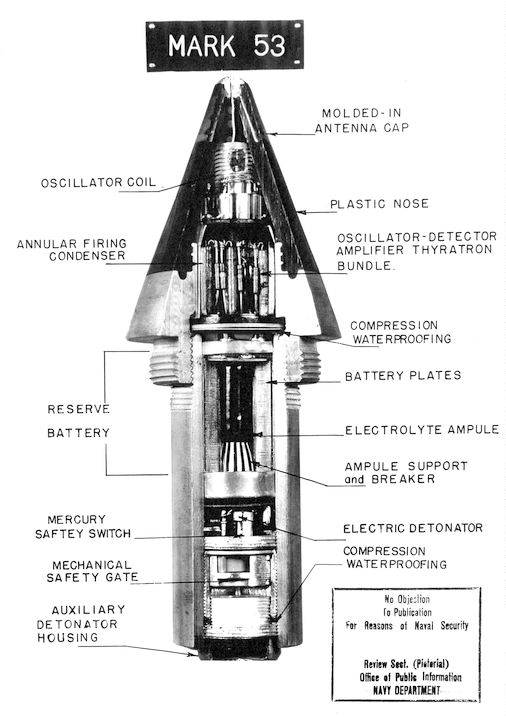
Fuze
In military munitions, a fuze (sometimes fuse) is the part of the device that initiates function. In some applications, such as torpedoes, a fuze may be identified by function as the exploder. The relative complexity of even the earliest fuze designs can be seen in cutaway diagrams. A fuze is a device that detonates a munition's explosive material under specified conditions. In addition, a fuze will have safety and arming mechanisms that protect users from premature or accidental detonation. For example, an artillery fuze's battery is activated by the high acceleration of cannon launch, and the fuze must be spinning rapidly before it will function. "Complete bore safety" can be achieved with mechanical shutters that isolate the detonator from the main charge until the shell is fired. A fuze may contain only the electronic or mechanical elements necessary to signal or actuate the detonator, but some fuzes contain a small amount of primary explosive to initiate the detonation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_16_-_17_May_1943_C(AM)1603.jpg)

.jpg)