|
Skepsis Ry
Skepsis is a scientific skepticism organization of Finland founded in 1987. Purpose Its mission is to promote objective, impartial and critical investigation of paranormal claims and pseudoscience. Skepsis organizes public lectures and publishes articles and books related to skepticism, including a quarterly magazine '' Skeptikko''. Skepsis works in collaboration with other scientific skepticism organizations and is a member of the European Council of Skeptical Organisations (ECSO). Skepsis is known for its annual Huuhaa (" humbug") Prize which is awarded to a person or an organization that has diligently promoted pseudo- or fringe science, and for its Socrates Prize which is awarded for work promoting Socratic, rational thinking. Skepsis also offers a prize of €10,000, sponsored by the astronomer Hannu Karttunen and the magician Iiro Seppänen, to anybody in Finland who can produce paranormal phenomena under satisfactory observing conditions. The same sum is also offered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helsinki
Helsinki ( or ; ; sv, Helsingfors, ) is the Capital city, capital, primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Finland, most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of Uusimaa in southern Finland, and has a population of . The Helsinki urban area, city's urban area has a population of , making it by far the List of urban areas in Finland by population, most populous urban area in Finland as well as the country's most important center for politics, education, finance, culture, and research; while Tampere in the Pirkanmaa region, located to the north from Helsinki, is the second largest urban area in Finland. Helsinki is located north of Tallinn, Estonia, east of Stockholm, Sweden, and west of Saint Petersburg, Russia. It has History of Helsinki, close historical ties with these three cities. Together with the cities of Espoo, Vantaa, and Kauniainen (and surrounding commuter towns, including the eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folk High School
Folk high schools (also ''Adult Education Center'', Danish: ''Folkehøjskole;'' Dutch: ''Volkshogeschool;'' Finnish: ''kansanopisto'' and ''työväenopisto'' or ''kansalaisopisto;'' German: ''Volkshochschule'' and (a few) ''Heimvolkshochschule;'' Norwegian: ''Folkehøgskole( NB)/Folkehøgskule( NN);'' Swedish: ''Folkhögskola;'' Hungarian: ''népfőiskola'') are institutions for adult education that generally do not grant academic degrees, though certain courses might exist leading to that goal. They are most commonly found in Nordic countries and in Germany, Switzerland and Austria. The concept originally came from the Danish writer, poet, philosopher, and pastor N. F. S. Grundtvig (1783–1872). Grundtvig was inspired by the Marquis de Condorcet's ''Report on the General Organization of Public Instruction'' which was written in 1792 during the French Revolution. The revolution had a direct influence on popular education in France. In the United States, a Danish folk school ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-profit Organisations Based In Finland
A nonprofit organization (NPO) or non-profit organisation, also known as a non-business entity, not-for-profit organization, or nonprofit institution, is a legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public or social benefit, in contrast with an entity that operates as a business aiming to generate a profit for its owners. A nonprofit is subject to the non-distribution constraint: any revenues that exceed expenses must be committed to the organization's purpose, not taken by private parties. An array of organizations are nonprofit, including some political organizations, schools, business associations, churches, social clubs, and consumer cooperatives. Nonprofit entities may seek approval from governments to be tax-exempt, and some may also qualify to receive tax-deductible contributions, but an entity may incorporate as a nonprofit entity without securing tax-exempt status. Key aspects of nonprofits are accountability, trustworthiness, honesty, and openness to eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeptic Organisations In Finland
Skepticism, also spelled scepticism, is a questioning attitude or doubt toward knowledge claims that are seen as mere belief or dogma. For example, if a person is skeptical about claims made by their government about an ongoing war then the person doubts that these claims are accurate. In such cases, skeptics normally recommend not disbelief but suspension of belief, i.e. maintaining a neutral attitude that neither affirms nor denies the claim. This attitude is often motivated by the impression that the available evidence is insufficient to support the claim. Formally, skepticism is a topic of interest in philosophy, particularly epistemology. More informally, skepticism as an expression of questioning or doubt can be applied to any topic, such as politics, religion, or pseudoscience. It is often applied within restricted domains, such as morality (moral skepticism), atheism (skepticism about the existence of God), or the supernatural. Some theorists distinguish "good" or modera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nils Mustelin
Nils Olof Mustelin (11 August 1931 in Turku – 28 April 2004 in Helsinki) was a Finnish professor of physics, noted astronomer, and popular skeptic. Mustelin was born in Turku (Åbo in Swedish), where he also went to school and attended university. He enrolled at the Åbo Akademi in 1949 and studied physics, graduating as a Ph.D. in 1963. He also studied theoretical physics for two years at MIT, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, MA, USA. He worked in many places, including the University of Helsinki; Nordforsk, an institute for technological research collaboration among the Nordic countries (Finland, Sweden, Norway, Denmark, and Iceland); Tekes, ''Teknologian edistämiskeskus'' ("Center for Advancement of Technology") and COST. After retiring he was a member of the Helsinki city council, representing the Swedish People's Party. Mustelin was known for his many scientific essays, articles, and books, primarily his astronomic book ''Liv Bland Miljarder St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esko Valtaoja
Esko Jorma Johannes Valtaoja (; born 20 June 1951) is a Finnish professional astronomer and writer. Valtaoja worked as a professor at the University of Turku where he studied quasars. Valtaoja retired in 2015 after holding a popular farewell lecture, that was also televised by Finnish national public broadcaster YLE. According to the Finnish Science Barometer conducted in 2013, Esko Valtaoja was the most well known Finnish scientist in Finland. Valtaoja was honored in 2019 when the town of Kemi decided to name a street, Valtaojankatu, after him. The naming of the street was a part of Kemi's 150th anniversary celebrations. In 2002 his book '' Kotona maailmankaikkeudessa'' (''At Home in the Cosmos'', 2001) won the Finlandia Prize for the best non-fiction work. After this he became a popular guest-speaker at TV shows, science fiction conventions, popular science seminars, etc. Part of his popularity comes from his ability to present complex scientific theories and ideas in an unders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kari Enqvist
Kari-Pekka Enqvist (born February 16, 1954 in Lahti, Finland) is a professor of cosmology in the Department of Physical Sciences at the University of Helsinki. Enqvist was awarded his PhD in theoretical physics in 1983. Enqvist is the chairman of the scientific advisory board of Skepsis ry (a Finnish sceptics' society) and has written many books that popularize physics. In 1997 Enqvist was granted the Magnus Ehrnrooth Foundation Physics Award for his efforts in particle physics and cosmology Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount (lexicographer), Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', and in 1731 taken up in .... In 1999, he was awarded the Tieto-Finlandia award, Finland's most significant award for non-fiction, for his book ''Olemisen porteilla ("At the gates of being")''. Enqvist retired from the University of Helsinki in 2019. References Ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Docent
The title of docent is conferred by some European universities to denote a specific academic appointment within a set structure of academic ranks at or below the full professor rank, similar to a British readership, a French " ''maître de conférences''" (MCF), and equal to or above the title of " associate professor". Docent is also used at some (mainly German) universities generically for a person who has the right to teach. The term is derived from the Latin word ''docēns'', which is the present active participle of ''docēre'' (to teach, to lecture). Becoming a docent is often referred to as Habilitation or doctor of science and is an academic qualification that shows that the holder is qualified to be employed at the level of associate or full professor. Docent is the highest academic title in several countries, and the qualifying criteria are research output that corresponds to 3-5 doctoral dissertations, supervision of PhD students, and experience in teaching at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seasonal Affective Disorder
Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a mood disorder subset, in which people who have normal mental health throughout most of the year exhibit depressive symptoms at the same time each year. Common symptoms include sleeping too much, having little to no energy, and overeating. The condition in the summer can include heightened anxiety.Seasonal affective disorder (SAD): Symptoms MayoClinic.com (September 22, 2011). Retrieved on March 24, 2013. In the '''' DSM-IV and |
Magneettimedia
''Magneettimedia'' is a Finnish free and online newspaper. It was initially published by retail chain J. Kärkkäinen but currently it is published by Pohjoinen perinne, a society linked with the Finnish Resistance Movement.Leppävuori, AnnaKohuttu Magneettimedia jatkaa ilmestymistään - lehden paperiversio kolahti postilaatikkoihinYle. April 20, 2015. Retrieved January 22, 2017. Controversies In 2011 Skepsis ry, a society of Finnish sceptics, awarded J. Kärkkäinen a Huuhaa Prize, a prize for promoting pseudo-science, for publishing ''Magneettimedia''. Skepsis accused ''Magneettimedia'' of promoting alternative medicine and conspiracy theories.Huuhaa-palkinnot Skepsis. Retrieved January 22, 2017. In October 2013 ''Magneettimedias editor-in-chief [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Balance
Power Balance is the original brand of hologram bracelets claimed by its manufacturers and vendors to use "holographic technology" to "resonate with and respond to the natural energy field of the body" to increase athletic performance. Numerous independent studies of the device have found it to be no more effective than placebo for enhancing athletic performance. As a result, in 2010, the Australian distributor, Power Balance Australia Pty Ltd, was forced by the Australian Competition & Consumer Commission (ACCC) to retract any previous claims. The product was originally promoted at trade shows in the beginning of 2006 utilizing applied kinesiology as its most effective sales tool. The bracelets went on sale in 2007 and had several celebrity endorsements. The bracelets became a trend among high school, collegiate, and professional sports teams between 2008 and 2012. This sustained prevalence compelled journalist Darren Rovell to remark that "a growing number of professional spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
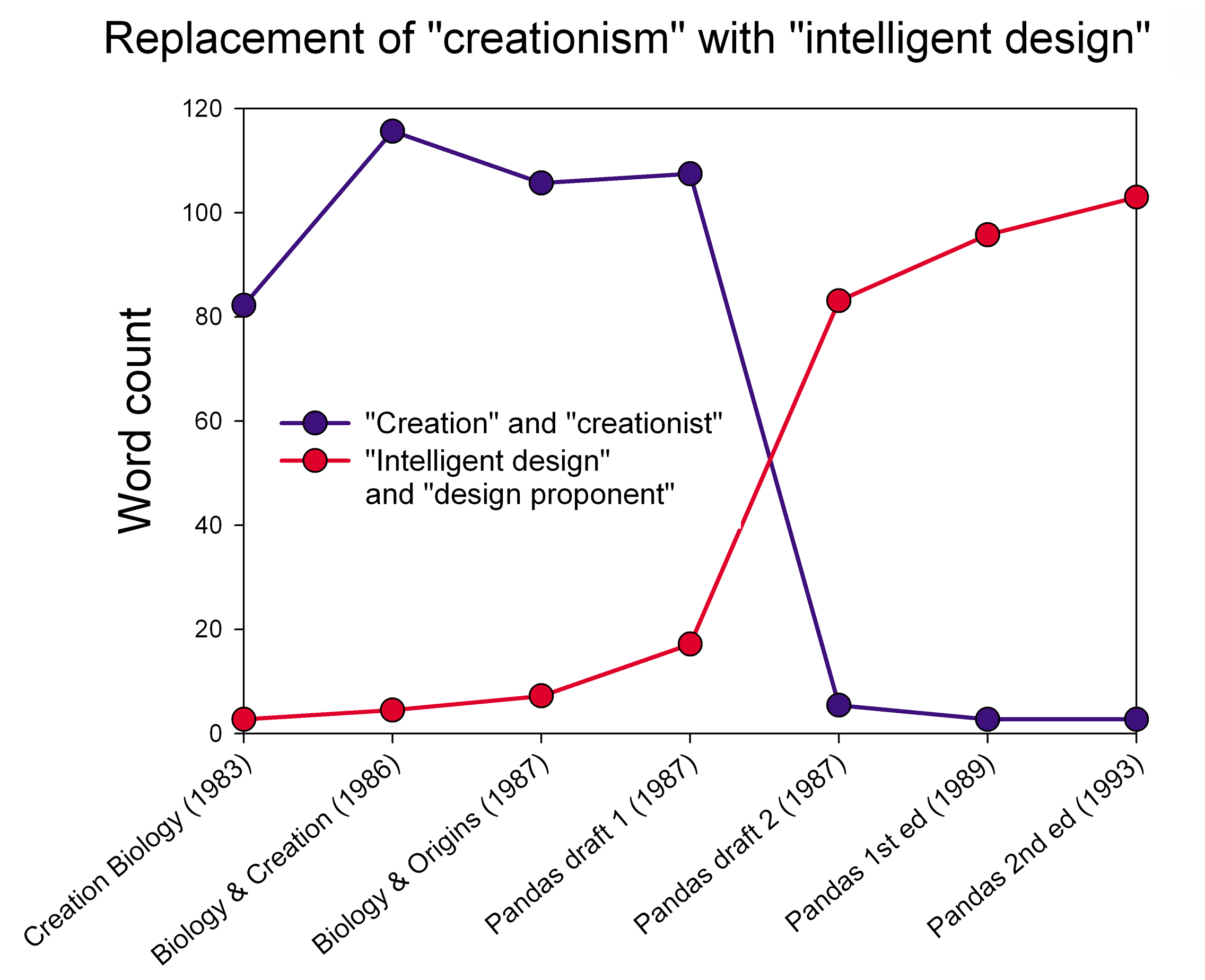
Intelligent Design
Intelligent design (ID) is a pseudoscientific argument for the existence of God, presented by its proponents as "an evidence-based scientific theory about life's origins". Numbers 2006, p. 373; " Dcaptured headlines for its bold attempt to rewrite the basic rules of science and its claim to have found indisputable evidence of a God-like being. Proponents, however, insisted it was 'not a religious-based idea, but instead an evidence-based scientific theory about life's origins – one that challenges strictly materialistic views of evolution.' Although the intellectual roots of the design argument go back centuries, its contemporary incarnation dates from the 1980s" Article available froUniversiteit Gent/ref> Proponents claim that "certain features of the universe and of living things are best explained by an intelligent cause, not an undirected process such as natural selection." * * ID is a form of creationism that lacks empirical support and offers no testable or tenable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)